Abstract
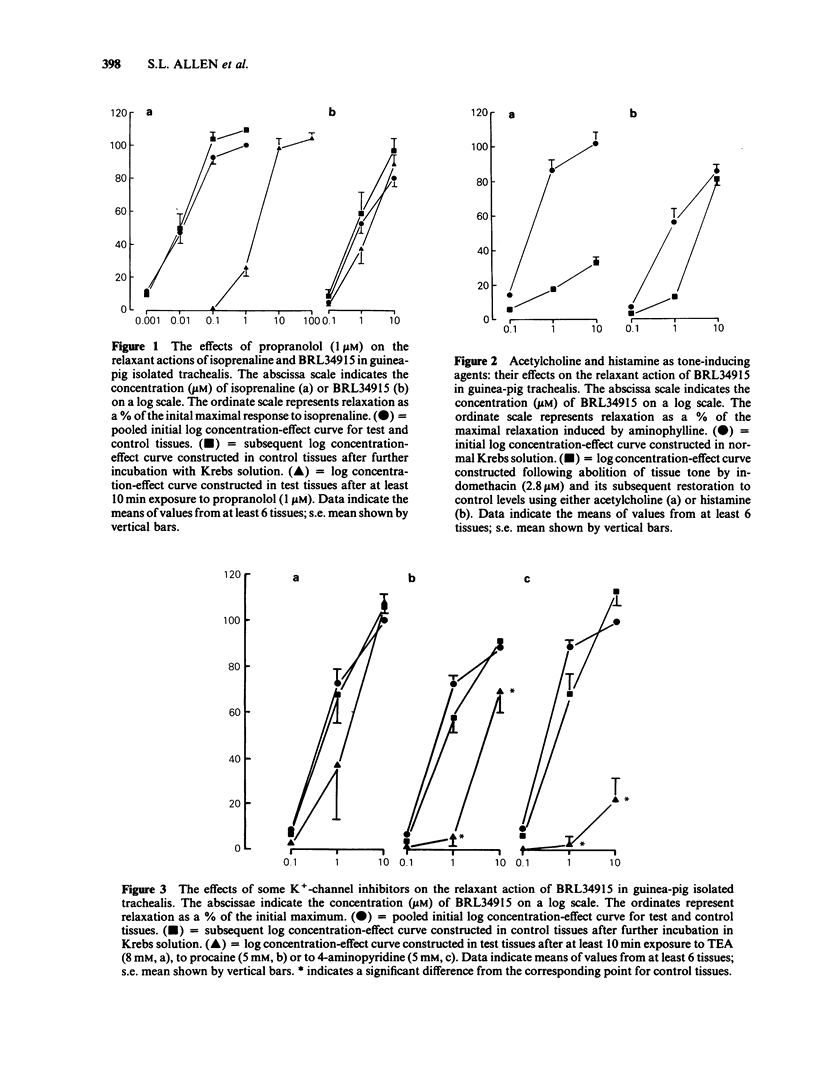
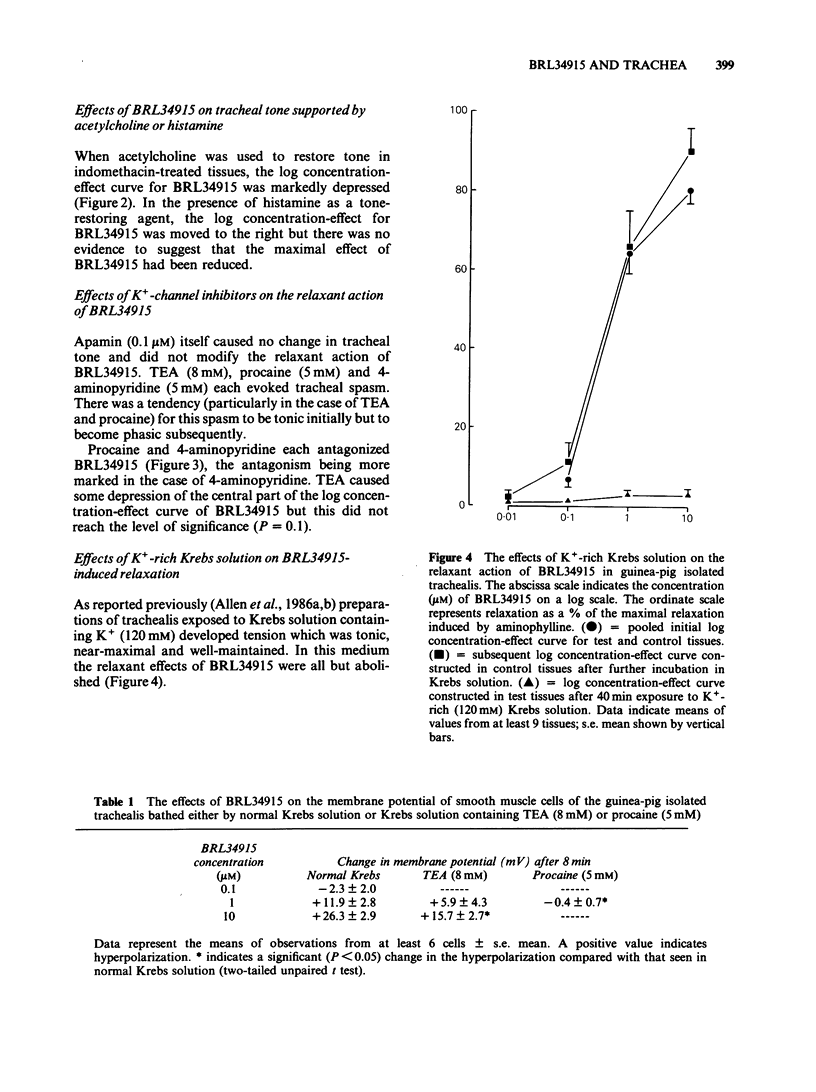
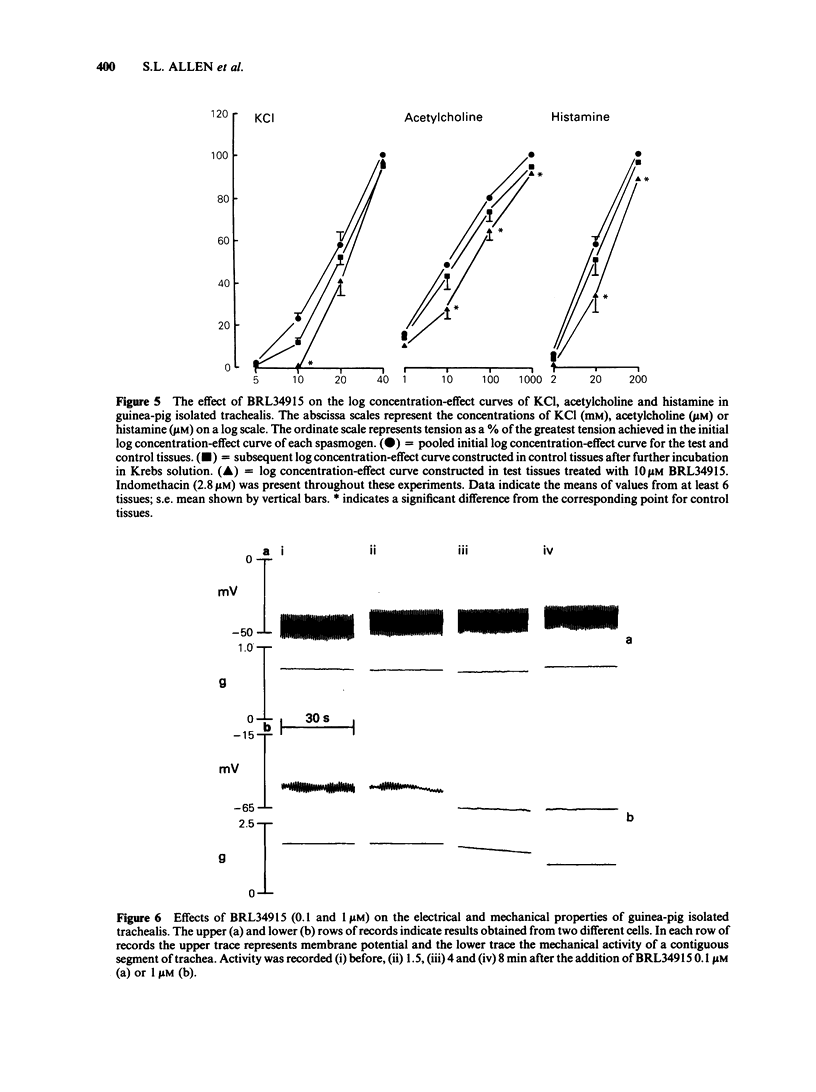
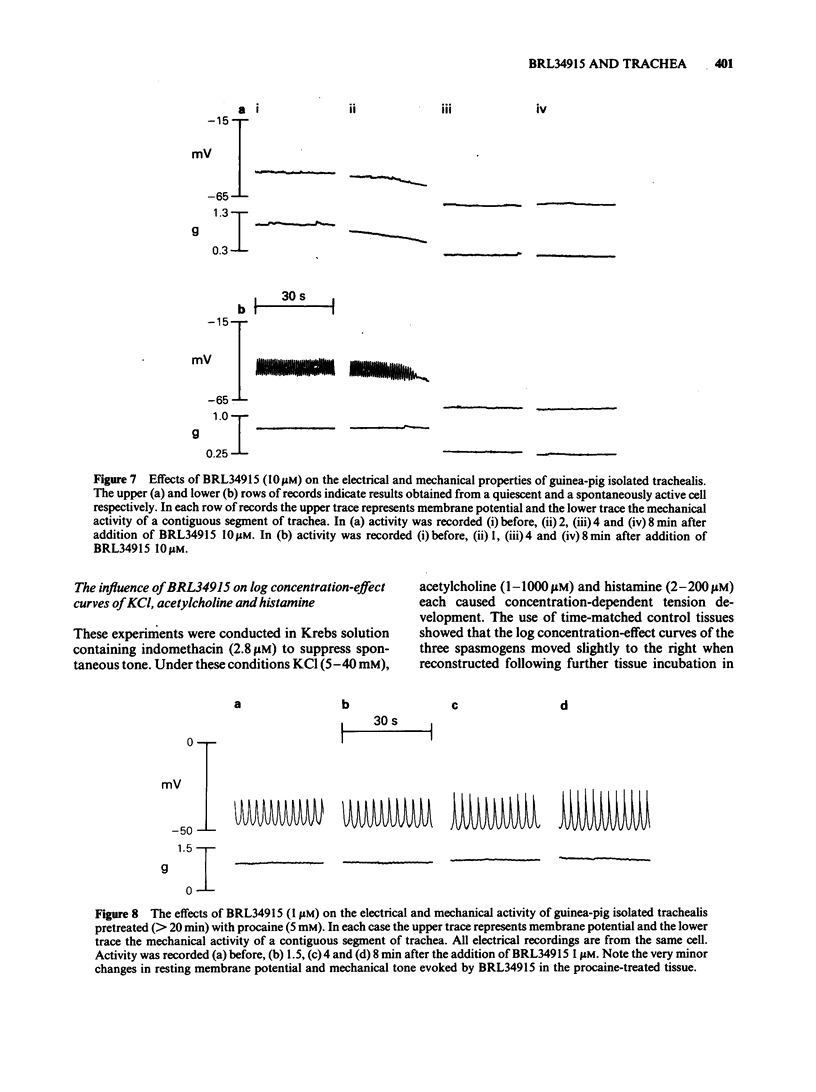
BRL34915 (0.1-10 microM) suppressed the spontaneous tone of guinea-pig isolated trachealis in a concentration-dependent manner. BRL34915 was not antagonized by propranolol (1 microM). In trachea where spontaneous tone was suppressed by indomethacin (2.8 microM) but subsequently restored to the same level with acetylcholine or histamine, the relaxant potency of BRL34915 was reduced. In Krebs solution containing K+ (120 mM), isolated trachealis muscle developed near-maximal tension. The relaxant effects of BRL34915 were virtually abolished in this medium. Concentration-effect curves for KCl, acetylcholine and histamine were constructed in tissues treated with indomethacin (2.8 microM). BRL34915 (10 microM) depressed the foot of the concentration-effect curve for KCl and caused minor rightward shifts in the concentration-effect curves of acetylcholine and histamine. Four K+-channel inhibitors were tested. Apamin (0.1 microM) did not modify the action of BRL34915. Tetraethylammonium (8 mM) had little effect but procaine (5 mM) and 4-aminopyridine (5 mM) each significantly inhibited the relaxant action of BRL34915. Intracellular electrophysiological recording showed that BRL34915 (0.1 microM) caused very minor relaxation and little, if any, electrical change. Higher concentrations (1-10 microM) evoked relaxation, suppression of spontaneous electrical slow waves and marked hyperpolarization of the trachealis cells. In the presence of TEA (8 mM) or procaine (5 mM) the hyperpolarization induced by BRL34915 was significantly reduced. In trachealis skinned of its plasma membranes, tension development induced by Ca2+ (20 microM) was unaffected either by BRL34915 (10 microM) or by nicorandil (1 mM). In studies of the efflux of 86Rb+ from muscle-rich strips of trachea, BRL34915 (1 and 10 microM) increased the efflux rate constant. It is concluded that BRL34915 evokes relaxation of the trachealis by a mechanism that involves neither beta-adrenoceptor activation nor direct reduction of the sensitivity of the intracellular contractile machinery to cytosolic free Ca2+. The action of BRL34915 may depend on the opening of K+ channels in the plasma membrane which are permeable to 86Rb+. The opening of these channels, or the effects of their opening, may be reduced by K+-channel inhibitors such as 4-aminopyridine, procaine and TEA but not by apamin.
Full text
PDF


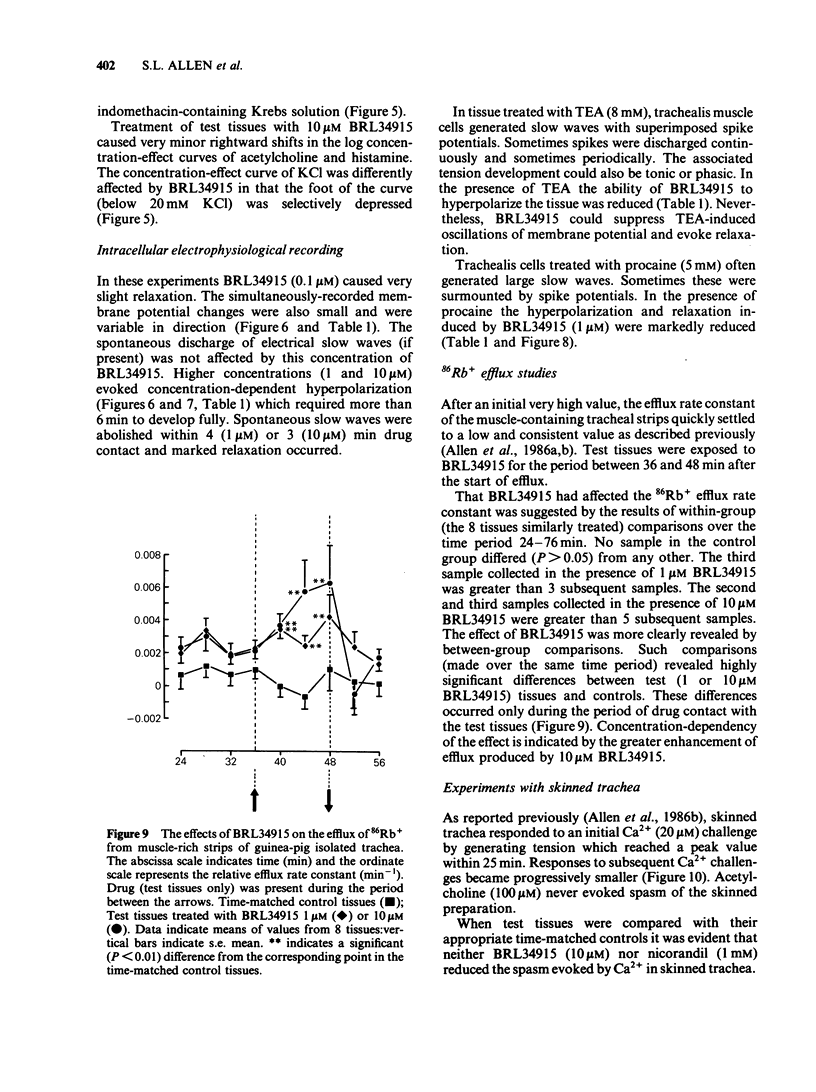
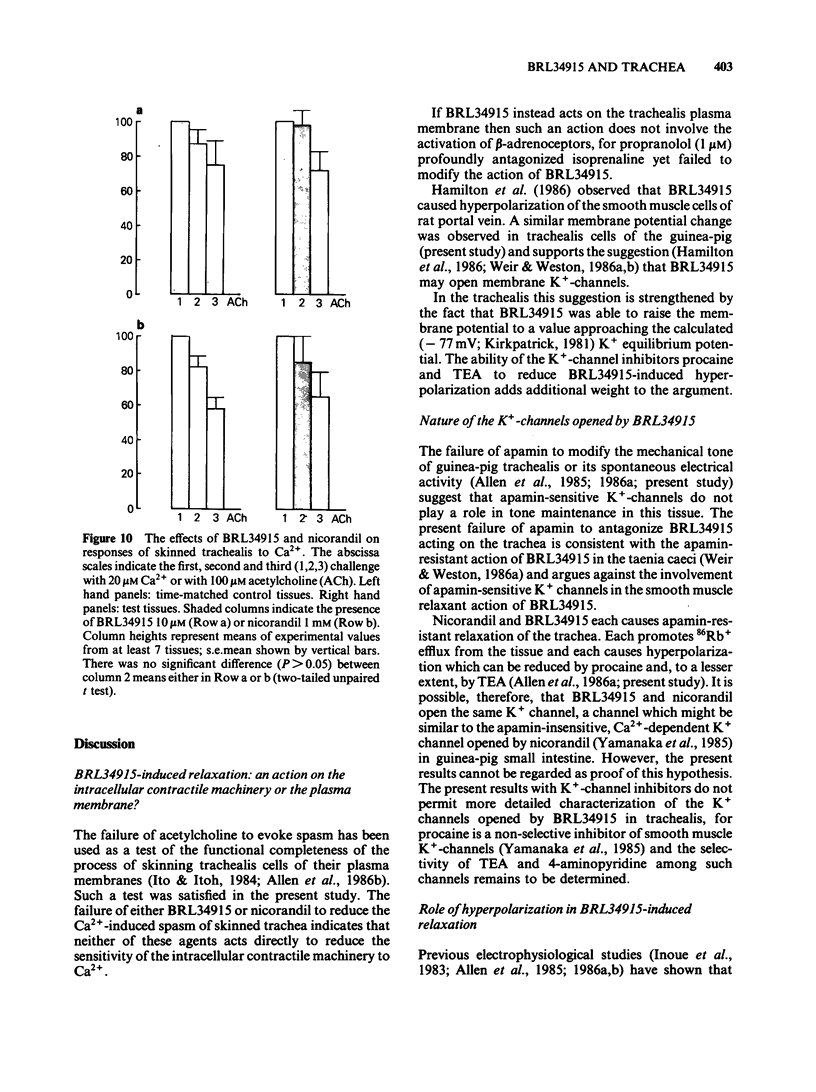


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akasaka K., Konno K., Ono Y., Mue S., Abe C. Electromyographic study of bronchial smooth muslce in bronchial asthma. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1975 Sep;117(1):55–59. doi: 10.1620/tjem.117.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen S. L., Beech D. J., Foster R. W., Morgan G. P., Small R. C. Electrophysiological and other aspects of the relaxant action of isoprenaline in guinea-pig isolated trachealis. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Dec;86(4):843–854. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb11106.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen S. L., Cortijo J., Foster R. W., Morgan G. P., Small R. C., Weston A. H. Mechanical and electrical aspects of the relaxant action of aminophylline in guinea-pig isolated trachealis. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jun;88(2):473–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10226.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen S. L., Foster R. W., Morgan G. P., Small R. C. The relaxant action of nicorandil in guinea-pig isolated trachealis. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;87(1):117–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10163.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. S., Small R. C. Evidence of poor conduction of muscle excitation in the longitudinal axis of guinea-pig isolated trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 May;79(1):75–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10498.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R. W., Small R. C., Weston A. H. Evidence that the spasmogenic action of tetraethylammonium in guinea-pig trachealis is both direct and dependent on the cellular influx of calcium ion. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 May;79(1):255–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10519.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. C., Weir S. W., Weston A. H. Comparison of the effects of BRL 34915 and verapamil on electrical and mechanical activity in rat portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):103–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09476.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Ito Y., Takeda K. The effects of 2-nicotinamidoethyl nitrate on smooth muscle cells of the dog mesenteric artery and trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Nov;80(3):459–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Itoh T. Effects of isoprenaline on the contraction-relaxation cycle in the cat trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;83(3):677–686. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16221.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir S. W., Weston A. H. Effect of apamin on responses to BRL 34915, nicorandil and other relaxants in the guinea-pig taenia caeci. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):113–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09477.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir S. W., Weston A. H. The effects of BRL 34915 and nicorandil on electrical and mechanical activity and on 86Rb efflux in rat blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):121–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09478.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka K., Furukawa K., Kitamura K. The different mechanisms of action of nicorandil and adenosine triphosphate on potassium channels of circular smooth muscle of the guinea-pig small intestine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;331(1):96–103. doi: 10.1007/BF00498857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


