Abstract
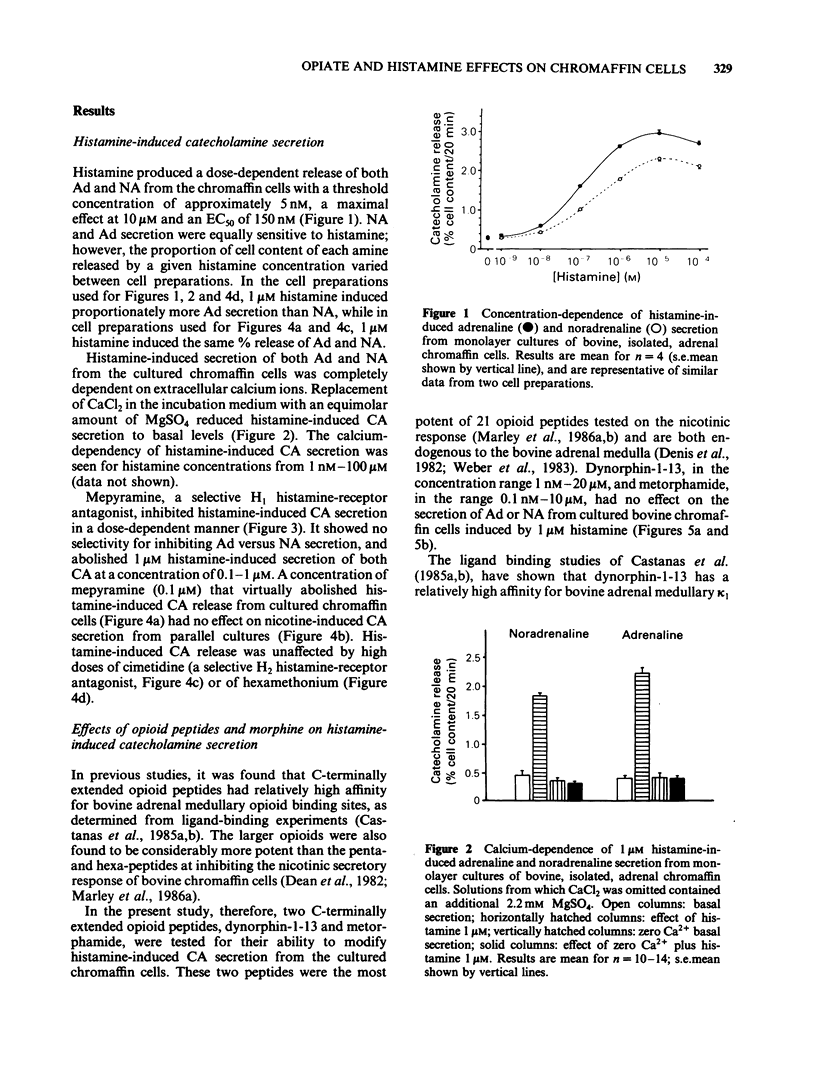
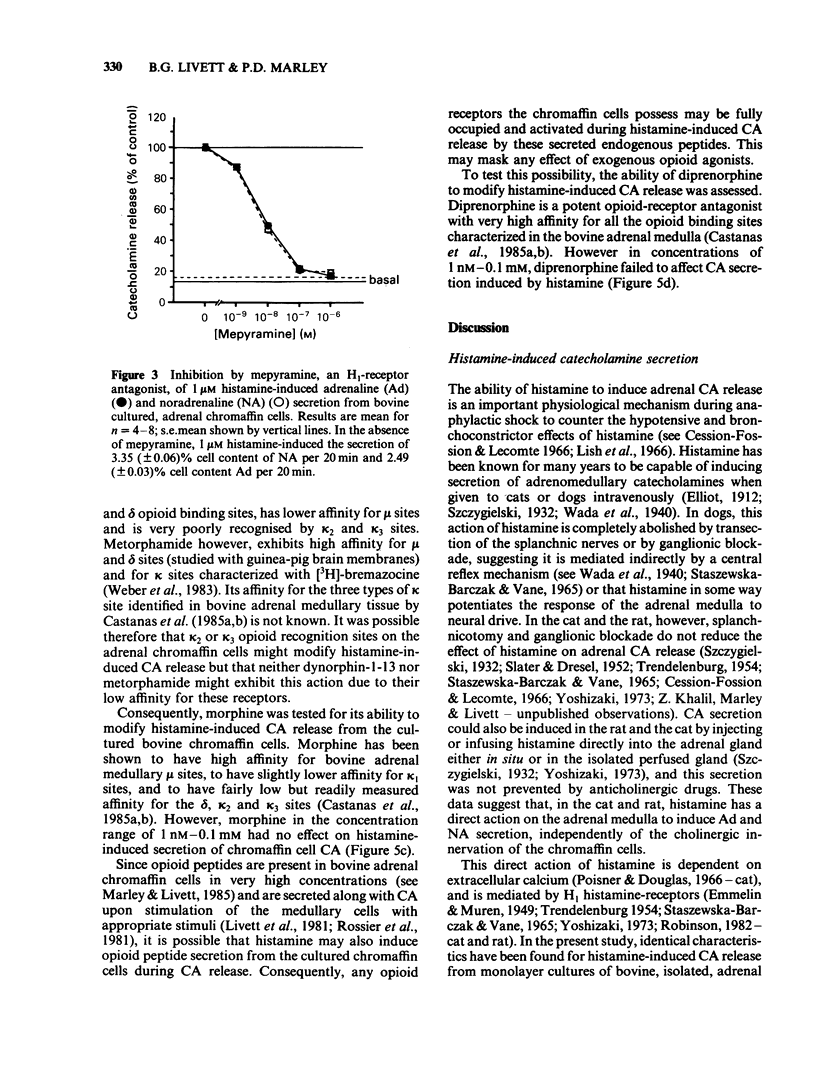
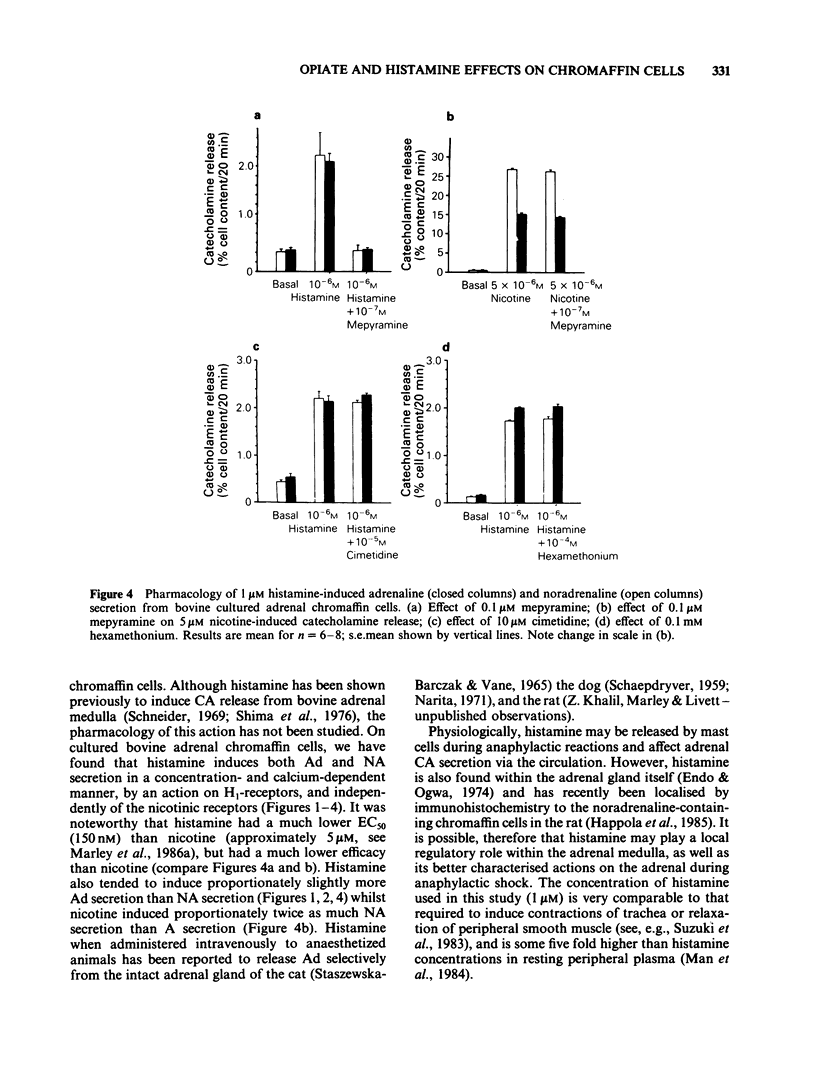
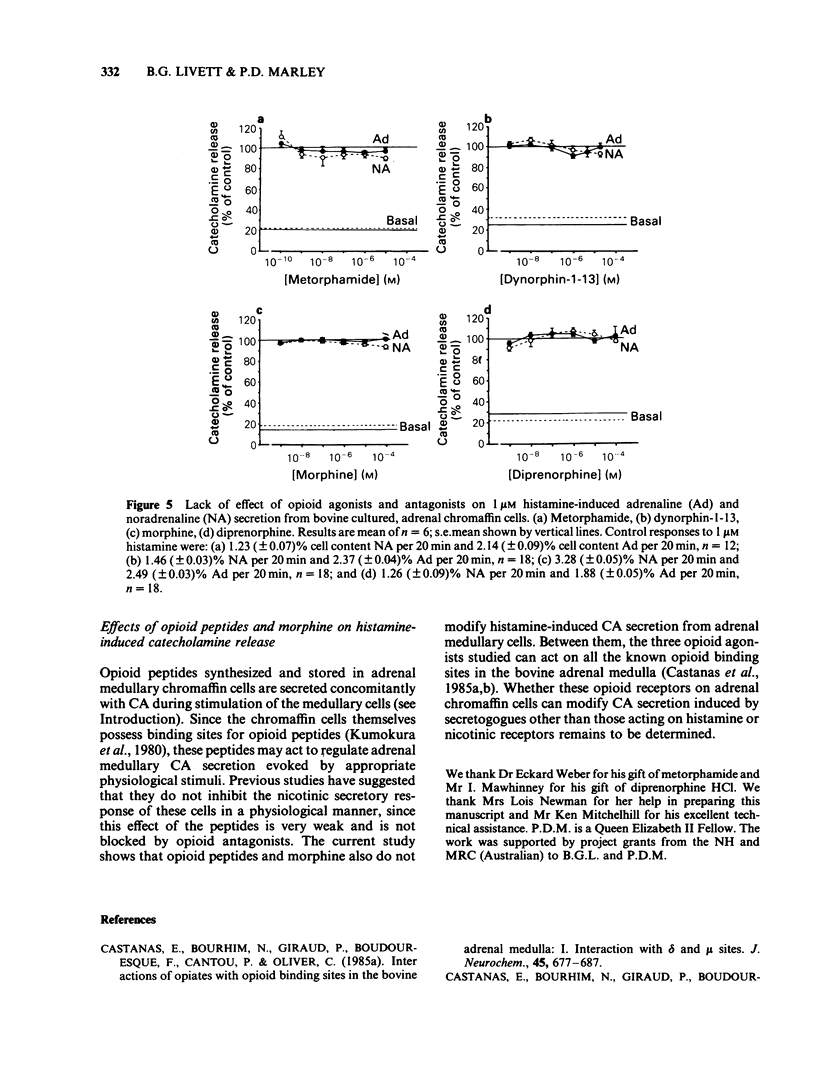
The effect of opioid peptides and morphine on histamine-induced catecholamine secretion has been studied in monolayer cultures of dispersed, bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Histamine-induced a dose-dependent secretion of both adrenaline and noradrenaline with a threshold dose of approximately 5 nM, an EC50 of 150 nM and maximal secretion at 10 microM. Catecholamine secretion induced by 1 microM histamine was completely dependent on extracellular calcium, was inhibited in a dose-dependent manner by mepyramine (1 nM-1 microM), and was unaffected by cimetidine (10 microM) and hexamethonium (0.1 mM). Dynorphin-1-13 (1 nM-20 microM), metorphamide (0.1 nM-10 microM), morphine (1 nM-0.1 mM) and diprenorphine (1 nM-0.1 mM) each had no effect on adrenaline or noradrenaline secretion induced by 1 microM histamine. The characteristics of histamine-induced catecholamine secretion from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells were similar to those reported previously for cat and rat adrenal medulla being calcium-dependent and mediated by H1 histamine-receptors. The results with opioid peptides and morphine suggest that endogenous adrenal opioid peptides do not act on the opioid binding sites found on adrenal medullary chromaffin cells to modify their secretory response to histamine.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Castanas E., Bourhim N., Giraud P., Boudouresque F., Cantau P., Oliver C. Interaction of opiates with opioid binding sites in the bovine adrenal medulla: I. Interaction with delta and mu sites. J Neurochem. 1985 Sep;45(3):677–687. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb04046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castanas E., Bourhim N., Giraud P., Boudouresque F., Cantau P., Oliver C. Interaction of opiates with opioid binding sites in the bovine adrenal medulla: II. Interaction with kappa sites. J Neurochem. 1985 Sep;45(3):688–699. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb04047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cession-Fossion A., Lecomte J. Sur les modes de stimulation de la médullo-surrénale du rat. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1966 Mar;160(1):124–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaminade M., Foutz A. S., Rossier J. Co-release of enkephalins and precursors with catecholamines from the perfused cat adrenal gland in situ. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:157–169. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chantry C. J., Seidler F. J., Slotkin T. A. Non-neurogenic mechanism for reserpine-induced release of catecholamines from the adrenal medulla of neonatal rats: possible modulation by opiate receptors. Neuroscience. 1982 Mar;7(3):673–678. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavkin C., Cox B. M., Goldstein A. Stereospecific opiate binding in bovine adrenal medulla. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 May;15(3):751–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa E., Guidotti A., Hanbauer I., Hexum T., Saiani L., Stine S., Yang H. Y. Regulation of acetylcholine receptors by endogenous cotransmitters: studies of adrenal medulla. Fed Proc. 1981 Feb;40(2):160–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa E., Guidotti A., Hanbauer I., Saiani L. Modulation of nicotinic receptor function by opiate recognition sites highly selective for Met5-enkephalin[Arg6Phe7]. Fed Proc. 1983 Sep;42(12):2946–2952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE SCHAEPDRYVER A. F. Physio-pharmacological effects on suprarenal secretion of adrenaline and noradrenaline in dogs. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1959 Aug 1;121:222–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. M., Lemaire S., Livett B. G. Evidence that inhibition of nicotine-mediated catecholamine secretion from adrenal chromaffin cells by enkephalin, beta-endorphin, dynorphin (1-13), and opiates is not mediated via specific opiate receptors. J Neurochem. 1982 Mar;38(3):606–614. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis D., Day R., Lemaire S. Dynorphin in bovine adrenal medulla. II. Isolation, partial characterization and biological activity of two distinct molecules. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1982 Jan;19(1):18–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T. R. The control of the suprarenal glands by the splanchnic nerves. J Physiol. 1912 Jul 15;44(5-6):374–409. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1912.sp001521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Ogura Y. Distribution of histamine in adrenal gland. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1974 Feb;24(1):171–173. doi: 10.1254/jjp.24.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanbauer I., Govoni S., Majane E. A., Yang H. Y., Costa E. In vivo regulation of the release of met-enkephalin-like peptides from dog adrenal medulla. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1982;33:209–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häppölä O., Soinila S., Päivärinta H., Joh T. H., Panula P. Histamine-immunoreactive endocrine cells in the adrenal medulla of the rat. Brain Res. 1985 Jul 29;339(2):393–396. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumakura K., Karoum F., Guidotti A., Costa E. Modulation of nicotinic receptors by opiate receptor agonists in cultured adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):489–492. doi: 10.1038/283489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire S., Livett B., Tseng R., Mercier P., Lemaire I. Studies on the inhibitory action of opiate compounds in isolated bovine adrenal chromaffin cells: noninvolvement of stereospecific opiate binding sites. J Neurochem. 1981 Mar;36(3):886–892. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb01677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. V., Stern A. S. Biosynthesis of the enkephalins and enkephalin-containing polypeptides. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:353–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.23.040183.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lish P. M., Robbins S. I., Peters E. L. Specificity of antihistamine drugs and involvement of the adrenergic system in histamine deaths in the guinea pig. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Sep;153(3):538–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livett B. G. Adrenal medullary chromaffin cells in vitro. Physiol Rev. 1984 Oct;64(4):1103–1161. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.4.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livett B. G., Day R., Elde R. P., Howe P. R. Co-storage of enkephalins and adrenaline in the bovine adrenal medulla. Neuroscience. 1982 May;7(5):1323–1332. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)91138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livett B. G., Dean D. M., Whelan L. G., Udenfriend S., Rossier J. Co-release of enkephalin and catecholamines from cultured adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):317–319. doi: 10.1038/289317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Man W. K., Rago D., Manolas K., Welbourn R. B., Spencer J. Plasma histamine in pig: effect of food and pentagastrin. Agents Actions. 1984 Apr;14(3-4):529–533. doi: 10.1007/BF01973864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marley P. D., Mitchelhill K. I., Livett B. G. Effects of opioid peptides containing the sequence of Met5-enkephalin or Leu5-enkephalin on nicotine-induced secretion from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1986 Jan;46(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb12918.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marley P. D., Mitchelhill K. I., Livett B. G. Metorphamide, a novel endogenous adrenal opioid peptide, inhibits nicotine-induced secretion from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Brain Res. 1986 Jan 15;363(1):10–17. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90653-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marley P., Livett B. G. Neuropeptides in the autonomic nervous system. CRC Crit Rev Clin Neurobiol. 1985;1(3):201–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poisner A. M., Douglas W. W. The need for calcium in adrenomedullary secretion evoked by biogenic amines, polypeptides, and muscarinic agents. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Oct;123(1):62–64. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossier J., Dean D. M., Livett B. G., Udenfriend S. Enkephalin congeners and precursors are synthesized and released by primary cultures of adrenal chromaffin cells. Life Sci. 1981 Feb 16;28(7):781–789. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLATER I. H., DRESEL P. E. The pressor effect of histamine after autonomic ganglionic blockade. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1952 May;105(1):101–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiani L., Guidotti A. Opiate receptor-mediated inhibition of catecholamine release in primary cultures of bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1982 Dec;39(6):1669–1676. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider F. H. Secretion from the cortex-free bovine adrenal medulla. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Oct;37(2):371–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb10574.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultzberg M., Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Terenius L., Brandt J., Elde R. P., Goldstein M. Enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in gland cells and nerve terminals of the adrenal medulla. Neuroscience. 1978;3(12):1169–1186. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shima S., Kawashima Y., Hirai M., Kouyama Studies on cyclic nucleotides in the adrenal gland. V. Adenylate cyclase in the adrenal medulla. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1976 Dec;26(6):711–717. doi: 10.1254/jjp.26.711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staszewska-Barczak J., Vane J. R. The release of catechol amines from the adrenal medulla by histamine. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1965 Dec;25(3):728–742. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1965.tb01795.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Yamauchi N., Miyamoto T., Muranaka M. Gold-induced reduction in reactivity to histamine in isolated guinea pig tracheal rings. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983 Nov;72(5 Pt 1):469–474. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(83)90583-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRENDELENBURG U. The action of histamine and pilocarpine on the superior cervical ganglion and the adrenal glands of the cat. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1954 Dec;9(4):481–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1954.tb00865.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Kilpatrick D. L. Biochemistry of the enkephalins and enkephalin-containing peptides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Mar;221(2):309–323. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90149-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Esch F. S., Böhlen P., Paterson S., Corbett A. D., McKnight A. T., Kosterlitz H. W., Barchas J. D., Evans C. J. Metorphamide: isolation, structure, and biologic activity of an amidated opioid octapeptide from bovine brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7362–7366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizaki T. Effect of histamine, bradykinin and morphine on adrenaline release from rat adrenal gland. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1973 Oct;23(5):695–699. doi: 10.1254/jjp.23.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


