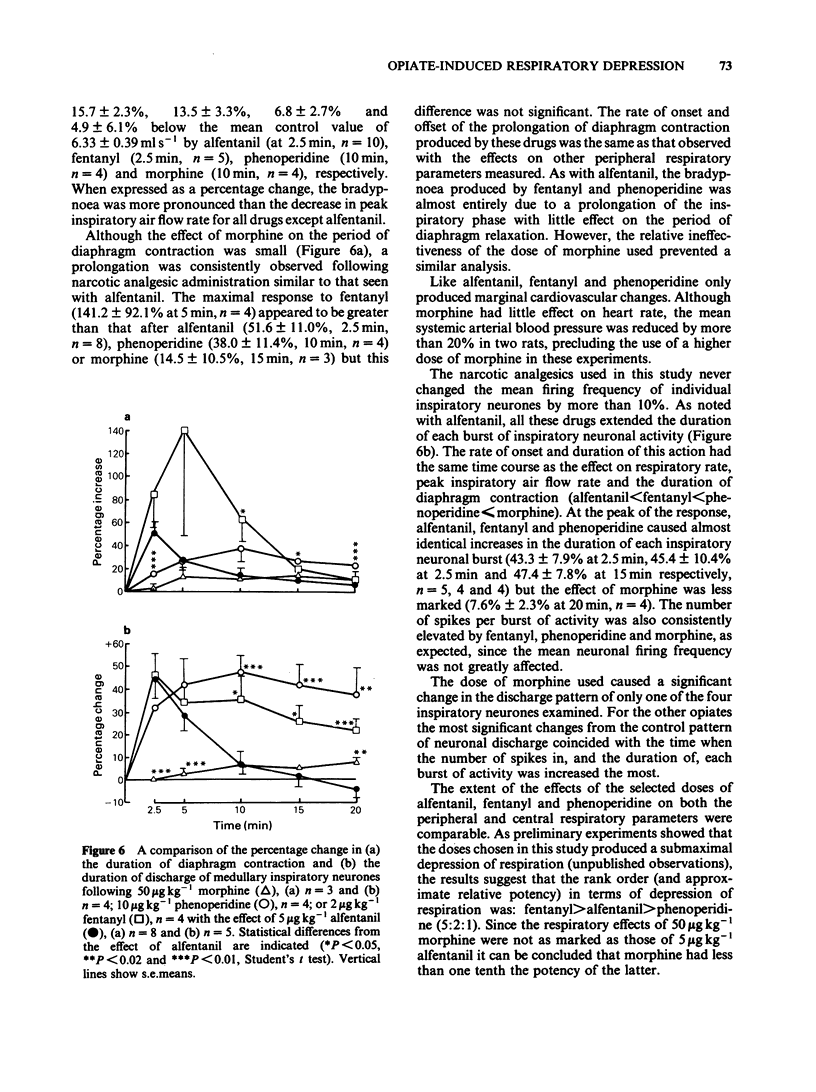
Abstract
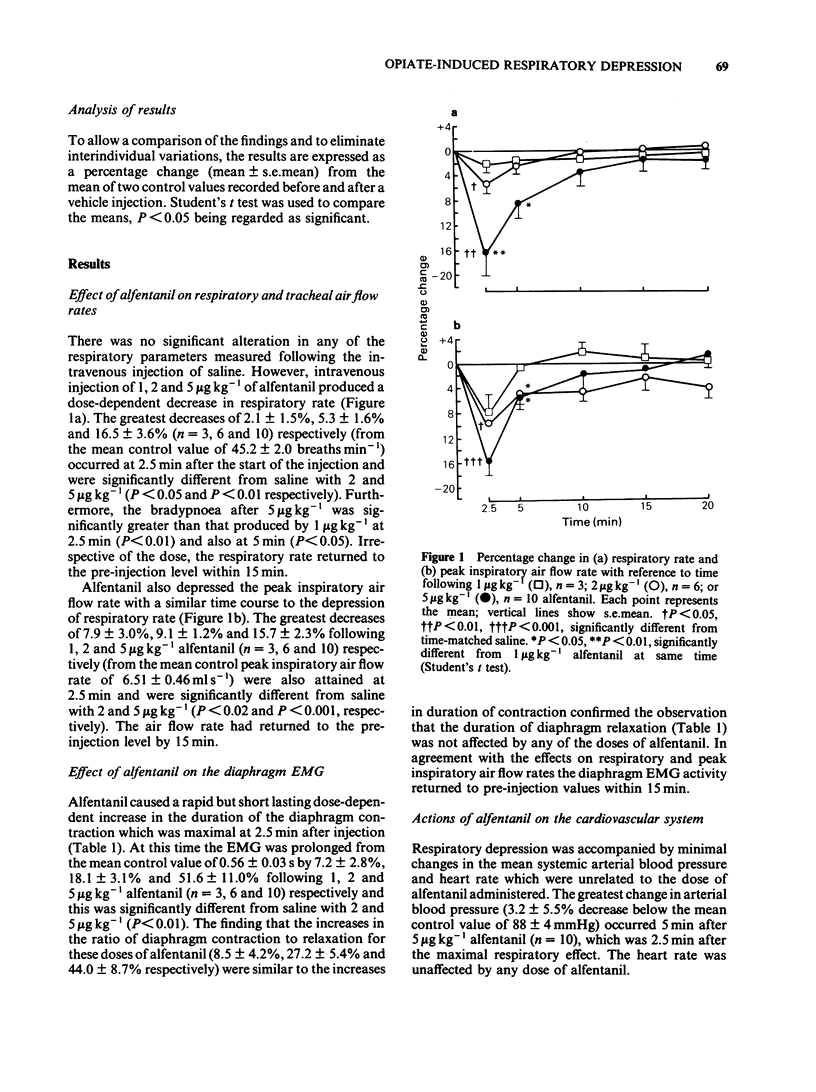
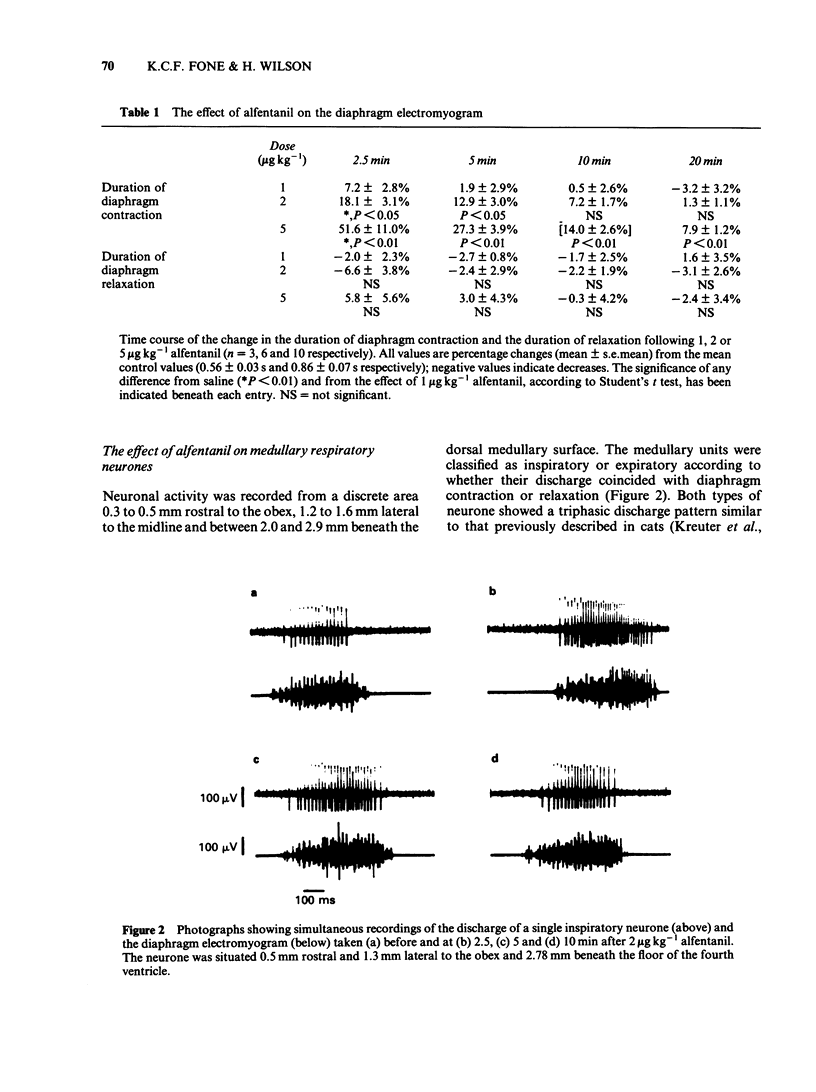
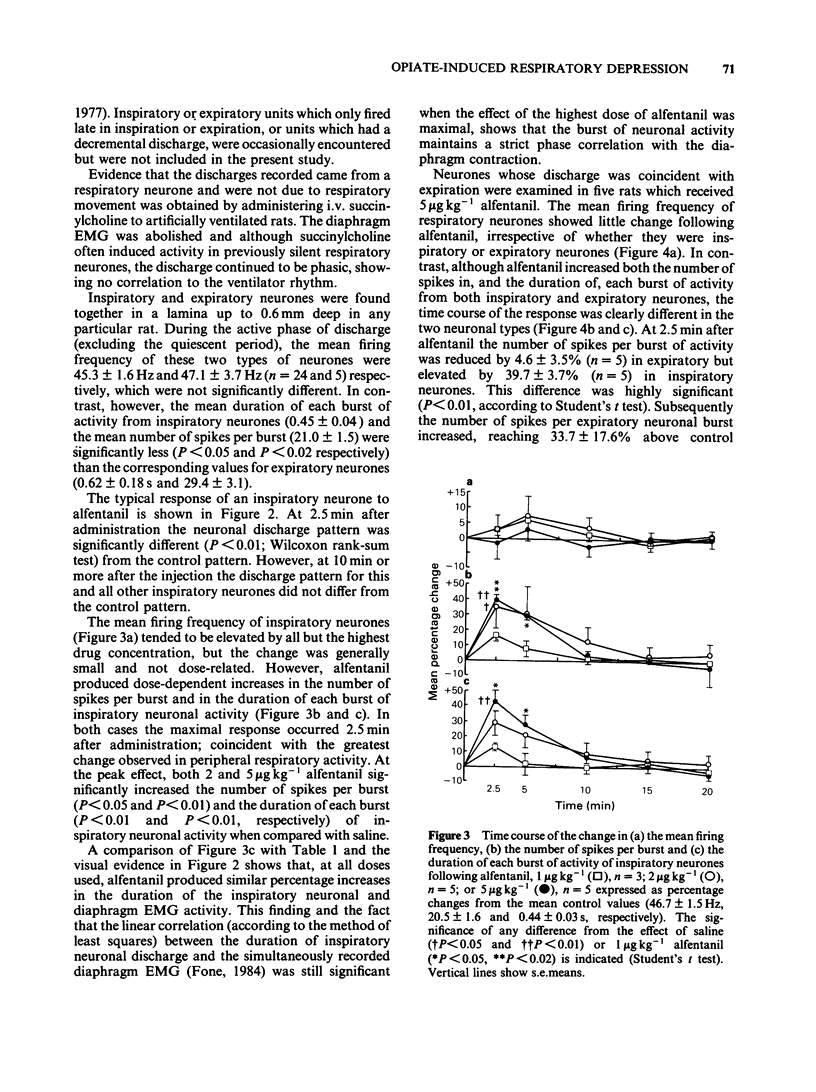
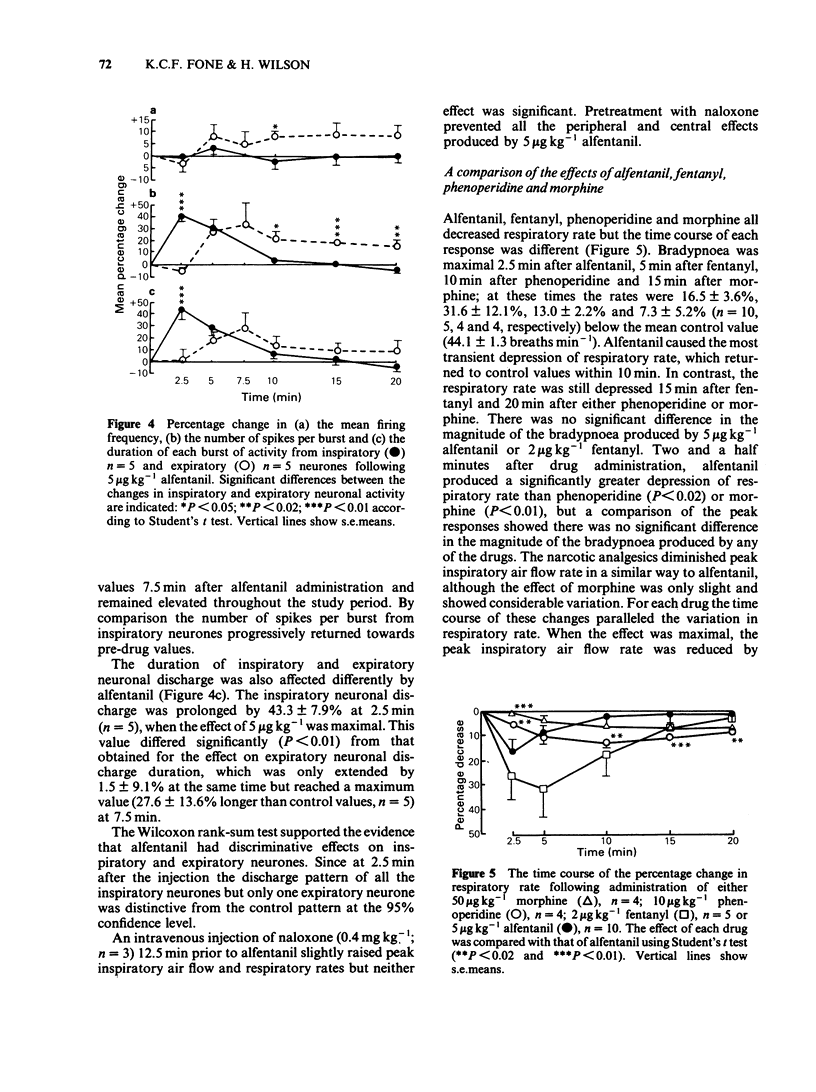
The effects of intravenous injections of alfentanil, fentanyl, phenoperidine or morphine on respiratory and peak inspiratory air flow rate, the diaphragm electromyogram (EMG), the activity recorded extracellularly from respiratory neurones located in the ventral respiratory group and the cardiovascular system were examined in anaesthetized rats. Alfentanil produced dose-dependent changes in peripheral and central respiratory parameters, which were prevented by naloxone pretreatment. Minimal effects were produced on the cardiovascular system. The bradypnoea was principally due to a prolongation of the inspiratory phase and was accompanied by a comparable decrease in the peak inspiratory air flow rate. Alfentanil prolonged the discharge duration of inspiratory neurones such that it still maintained a strict phase correlation with the diaphragm EMG, but changes in firing frequency were inconsistent and negligible. The action on expiratory neuronal discharge was analogous to that on inspiratory neuronal discharge but delayed in onset. Hypotension produced by morphine limited the dose used but the respiratory responses to morphine and other selected narcotic analgesics were otherwise similar to that of alfentanil, differing mainly in time-course and magnitude. From the respiratory parameters assessed, the order of duration of effect was morphine greater than phenoperidine greater than fentanyl greater than alfentanil and the relative potencies were 0.1, 0.5, 2.5 and 1 respectively. The selective prolongation of inspiration and the immediate action on inspiratory neurones suggests that systemically administered narcotic analgesics may alter the mechanisms within the central respiratory rhythm generator which determine the cessation of inspiration.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atweh S. F., Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. I. Spinal cord and lower medulla. Brain Res. 1977 Mar 18;124(1):53–67. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90863-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bill D. J., Hartley J. E., Stephens R. J., Thompson A. M. The antinociceptive activity of meptazinol depends on both opiate and cholinergic mechanisms. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 May;79(1):191–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10512.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Pleuvry B. J., Kay B. Respiratory effects of a new opiate analgesic, R 39209, in the rabbit: comparison with fentanyl. Br J Anaesth. 1980 Nov;52(11):1101–1106. doi: 10.1093/bja/52.11.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. I. Neurogenesis of respiratory rhythm in the mammal. Physiol Rev. 1979 Oct;59(4):1105–1173. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.4.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Aubioul J., Van Gerven W., Van de Water A., Xhonneux R., Reneman R. S. Cardiovascular and some respiratory effects of high doses of alfentanil in dogs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Apr 13;100(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90317-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denavit-Saubié M., Champagnat J., Zieglgänsberger W. Effects of opiates and methionine-enkephalin on pontine and bulbar respiratory neurones of the cat. Brain Res. 1978 Oct 20;155(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90305-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS A. G. J., NASMYTH P. A., STEWART H. C. The fall of blood pressure caused by intravenous morphine in the rat and the cat. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1952 Dec;7(4):542–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1952.tb00720.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden A. I., Feuerstein G. Hypothalamic regulation of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems: role of specific opiate receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Aug;79(4):997–1002. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flórez J., Hurlé M. A., Mediavilla A. Respiratory responses to opiates applied to the medullary ventral surface. Life Sci. 1982 Nov 15;31(20-21):2189–2192. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90115-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flórez J., McCarthy L. E., Borison H. L. A comparative study in the cat of the respiratory effects of morphine injected intravenously and into the cerebrospinal fluid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Oct;163(2):448–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HABER E., KOHN K. W., NGAI S. H., HOLADAY D. A., WANG S. C. Localization of spontaneous respiratory neuronal activities in the medulla oblongata of the cat: a new location of the expiratory center. Am J Physiol. 1957 Aug;190(2):350–355. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.190.2.350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassen A. H., Feuerstein G., Faden A. I. Selective cardiorespiratory effects mediated by mu opioid receptors in the nucleus ambiguus. Neuropharmacology. 1984 Apr;23(4):407–415. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(84)90248-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewson G., Bradley P. B. The effects of anilidopiperidine analgesics on single respiratory and non-respiratory neurones in the brain stem of the rat. Life Sci. 1982 Nov 15;31(20-21):2335–2338. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay B., Pleuvry B. Human volunteer studies of Alfentanyl (R39209), a new short-acting narcotic analgesic. Anaesthesia. 1980 Oct;35(10):952–956. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1980.tb04992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay B., Stephenson D. K. Alfentanyl (R39209): initial clinical experience with a new narcotic analgesic. Anaesthesia. 1980 Dec;35(12):1197–1201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1980.tb05078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuter F., Richter D. W., Camerer H., Senekowitsch R. Morphological and electrical description of medullary respiratory neurons of the cat. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Nov 25;372(1):7–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00582200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. E., Duffin J. The medullary respiratory neurons: a review. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1984 Feb;62(2):161–182. doi: 10.1139/y84-028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill E. G. The lateral respiratory neurones of the medulla: their associations with nucleus ambiguus, nucleus retroambigualis, the spinal accessory nucleus and the spinal cord. Brain Res. 1970 Nov 11;24(1):11–28. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. A. Location and function of medullary respiratory neurons. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Jun;115(6 Pt 2):209–216. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.S.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin-Surun M. P., Boudinot E., Gacel G., Champagnat J., Roques B. P., Denavit-Saubie M. Different effects of mu and delta opiate agonists on respiration. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Feb 17;98(2):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90594-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin-Surun M. P., Gacel G., Champagnat J., Denavit-Saubie M., Roques B. P. Pharmacological identification of delta and mu opiate receptors on bulbar respiratory neurons. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Feb 17;98(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90595-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON J. R. Single unit activity in medullary respiratory centers of cat. J Neurophysiol. 1959 Sep;22:590–598. doi: 10.1152/jn.1959.22.5.590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NGAI S. H. Effects of morphine and meperidine on the central respiratory mechanisms in the cat; the action of levallorphan in antagonizing these effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1961 Jan;131:91–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pokorski M., Grieb P., Wideman J. Opiate system influences central respiratory chemosensors. Brain Res. 1981 Apr 27;211(1):221–226. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90088-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebel P. S., Bovill J. G., van der Haven A. Cardiovascular effects of alfentanil anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth. 1982 Nov;54(11):1185–1190. doi: 10.1093/bja/54.11.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Kuhar M. J., Uhl G. R., Snyder S. H. Opioid peptide enkephalin: immunohistochemical mapping in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2167–2171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webber C. L., Jr, Peiss C. N. Interaction of respiratory cell discharge patterns and spontaneous resporatory rate. Am J Physiol. 1975 May;228(5):1384–1392. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.5.1384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamir N., Palkovits M., Brownstein M. J. Distribution of immunoreactive dynorphin in the central nervous system of the rat. Brain Res. 1983 Nov 28;280(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


