Abstract
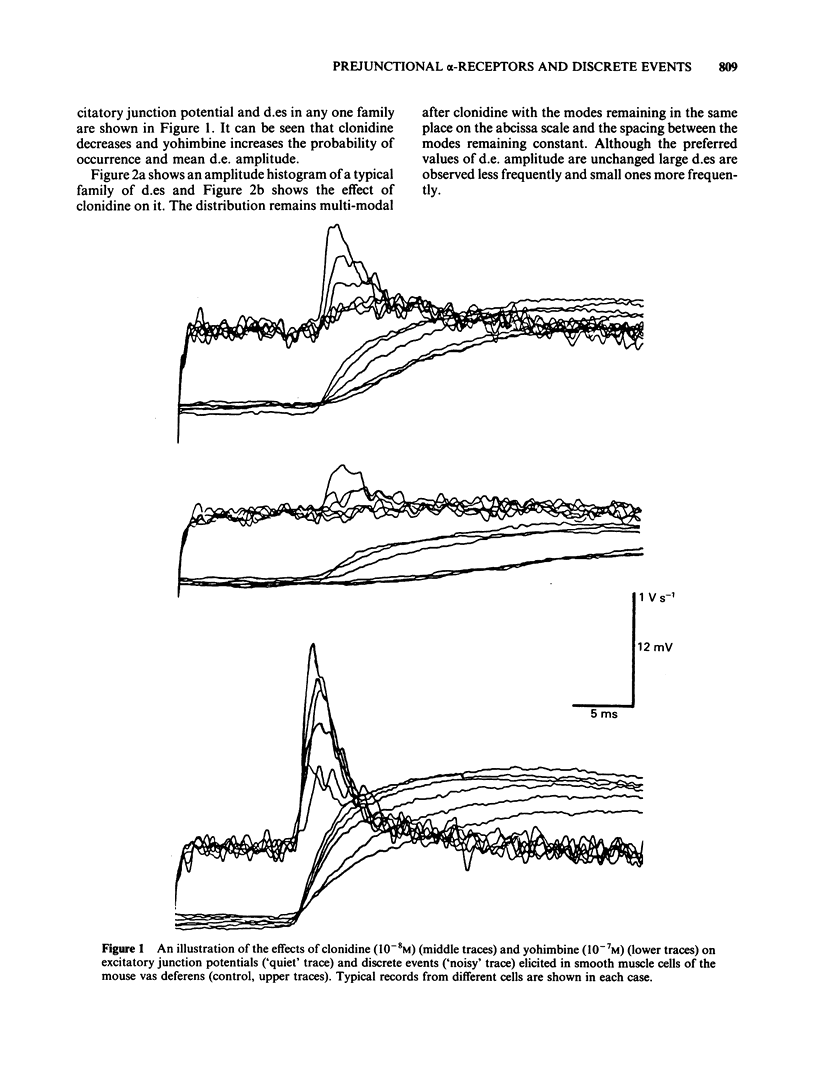
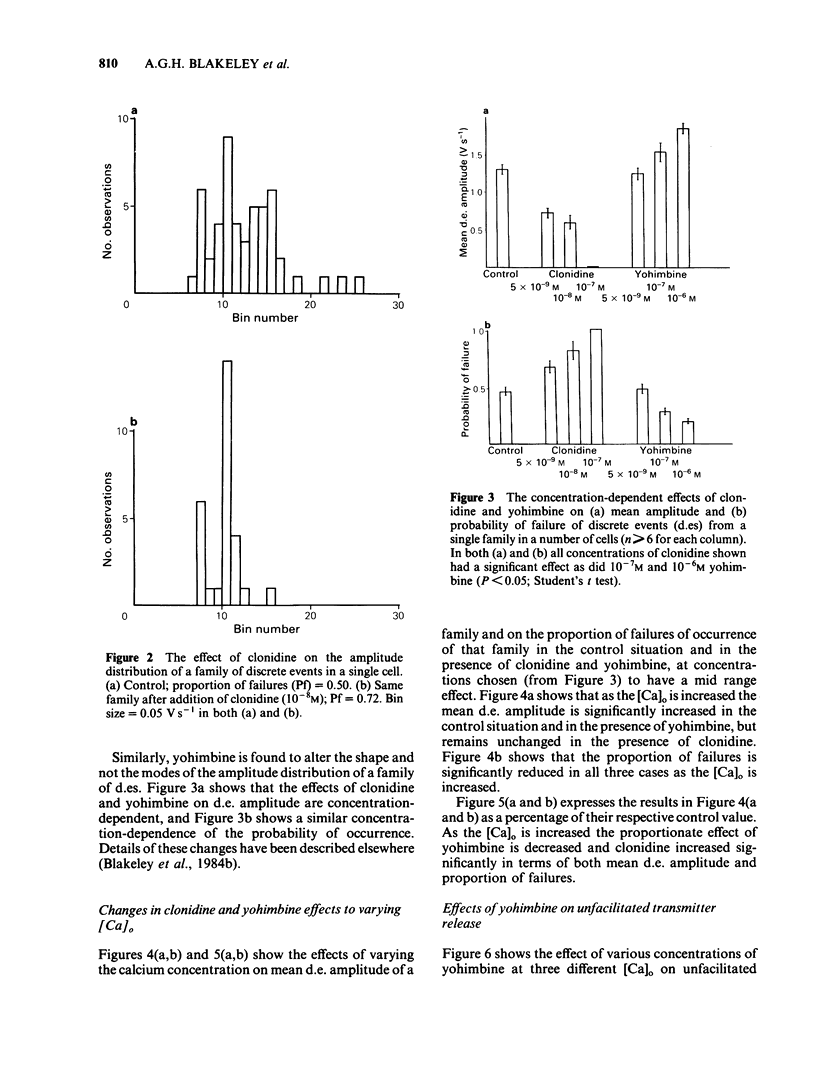
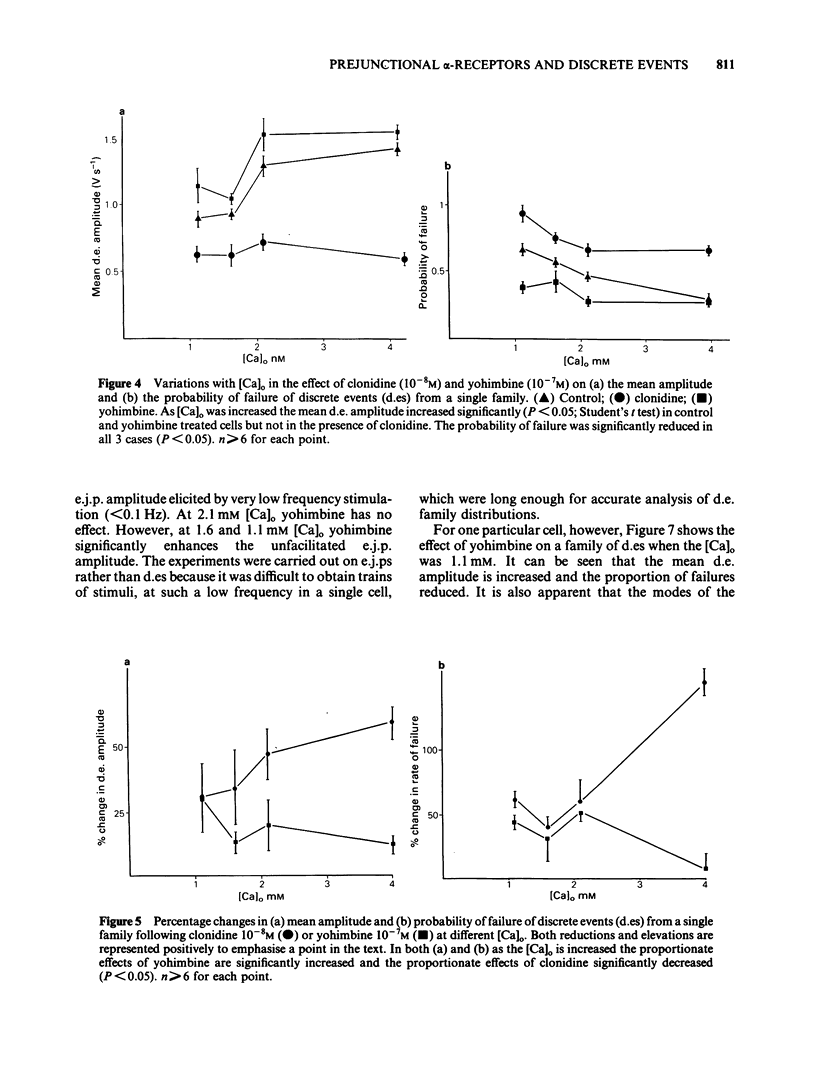
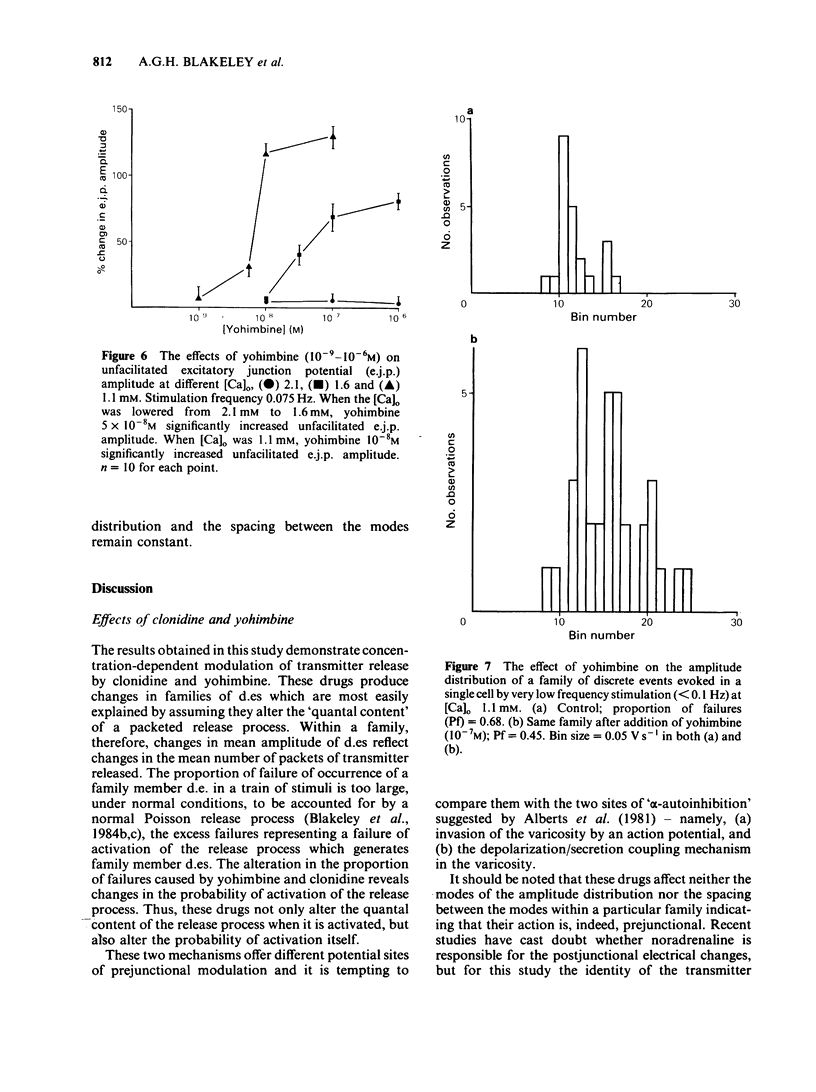
Excitatory junction potentials (e.j.ps) were recorded from mouse vas deferens and resolved into families of 'discrete events' (d.es) reflecting intermittent release of packets of transmitter from one or a few sites. Within families d.es vary in amplitude between a few preferred values unaffected by any treatments used in these experiments. As [Ca]o is raised from 1.1 to 4.0 mM there is a rise in d.e. amplitude due to an increase in the frequency of large events and a decrease in that of small. At all [Ca]o clonidine reduces d.e. amplitude by increasing failures and small events and decreasing large events. Yohimbine has opposite effects. Both drug effects are concentration-dependent in the range 5 X 10(-9) - 10(-6)M. As [Ca]o is raised from 1.1 to 4.0 mM, and therefore more natural agonist is released, clonidine becomes more effective at altering d.e. amplitude whereas yohimbine becomes less so. With very low frequency stimulation yohimbine elevates e.j.p. amplitude only if [Ca]o is below 1.6 mM. These results are not easily compatible with the notion that yohimbine breaks a 'negative feedback' control of transmitter release.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts P., Bartfai T., Stjärne L. Site(s) and ionic basis of alpha-autoinhibition and facilitation of "3H'noradrenaline secretion in guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:297–334. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angus J. A., Korner P. I. Evidence against presynaptic alpha-adrenoreceptor modulation of cardiac sympathetic transmission. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):288–291. doi: 10.1038/286288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Florin T. An electrophysiological analysis of the effect of Ca ions on neuromuscular transmission in the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Sep;55(1):97–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07616.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakeley A. G., Cunnane T. C. Packeted transmitter release in the mouse vas deferens; an electrophysiological study [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Oct;295:44P–45P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakeley A. G., Cunnane T. C., Petersen S. A. Local regulation of transmitter release from rodent sympathetic nerve terminals? J Physiol. 1982 Apr;325:93–109. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakeley A. G., Cunnane T. C. The packeted release of transmitter from the sympathetic nerves of the guinea-pig vas deferens: an electrophysiological study. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:85–96. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakeley A. G., Mathie A., Petersen S. A. Facilitation at single release sites of a sympathetic neuroeffector junction in the mouse. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:57–71. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. C., Kalsner S. An examination of the negative feedback function of presynaptic adrenoceptors in a vascular tissue. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;67(3):401–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08694.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman M. E., Surprenant A. An electrophysiological analysis of the effects of noradrenaline and alpha-receptor antagonists on neuromuscular transmission in mammalian muscular arteries. Br J Pharmacol. 1980;71(2):651–661. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsner S. Single pulse stimulation of guinea-pig vas deferens and the presynaptic receptor hypothesis. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Jun;66(2):343–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb13686.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsner S. The role of calcium in the effects of noradrenaline and phenoxybenzamine on adrenergic transmitter release from atria: no support for negative feedback of release. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Jun;73(2):363–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb10430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsner S. Yohimbine and prolongation of stimulation pulse duration alter similarly 3H-transmitter efflux in heart: an alternative to the negative feedback hypothesis. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Aug;79(4):985–992. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10545.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama H., Makita Y. Modulation of noradrenergic transmission in the guinea-pig mesenteric artery: an electrophysiological study. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:609–627. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Sixth gaddum memorial lecture, National Institute for Medical Research, Mill Hill, January 1977. Presynaptic receptors and their role in the regulation of transmitter release. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;60(4):481–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. P. The role of calcium in the release of neurotransmitter substances and hormones. Pharmacol Rev. 1970 Sep;22(3):389–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon P., Westfall D. P., Fedan J. S. Cotransmitters in the motor nerves of the guinea pig vas deferens: electrophysiological evidence. Science. 1982 Nov 12;218(4573):693–695. doi: 10.1126/science.6291151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon P., Westfall D. P. Pharmacological evidence that adenosine triphosphate and noradrenaline are co-transmitters in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1984 Feb;347:561–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Regulation of noradrenaline release by presynaptic receptor systems. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1977;77:1–124. doi: 10.1007/BFb0050157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L., Astrand P. Discrete events measure single quanta of adenosine 5'-triphosphate secreted from sympathetic nerves of guinea-pig and mouse vas deferens. Neuroscience. 1984 Sep;13(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Story D. F., McCulloch M. W., Rand M. J., Standford-Starr C. A. Conditions required for the inhibitory feedback loop in noradrenergic transmission. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):62–65. doi: 10.1038/293062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westfall T. C. Local regulation of adrenergic neurotransmission. Physiol Rev. 1977 Oct;57(4):659–728. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.4.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


