Abstract
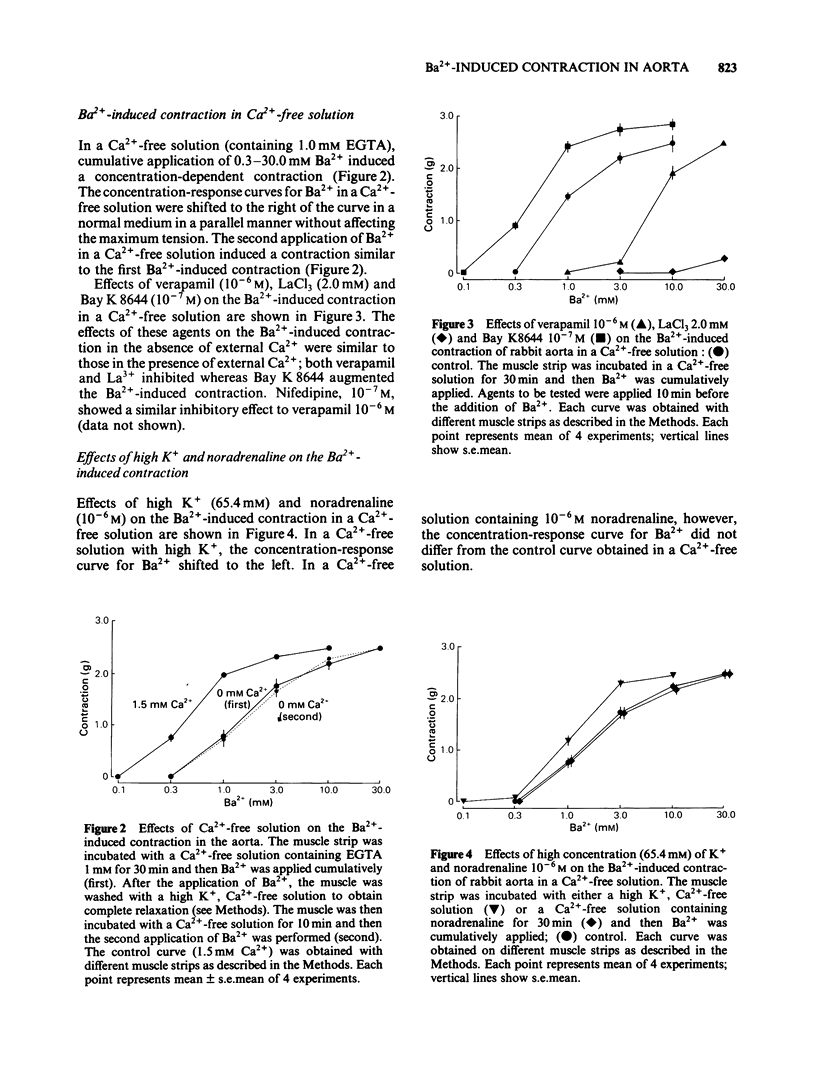
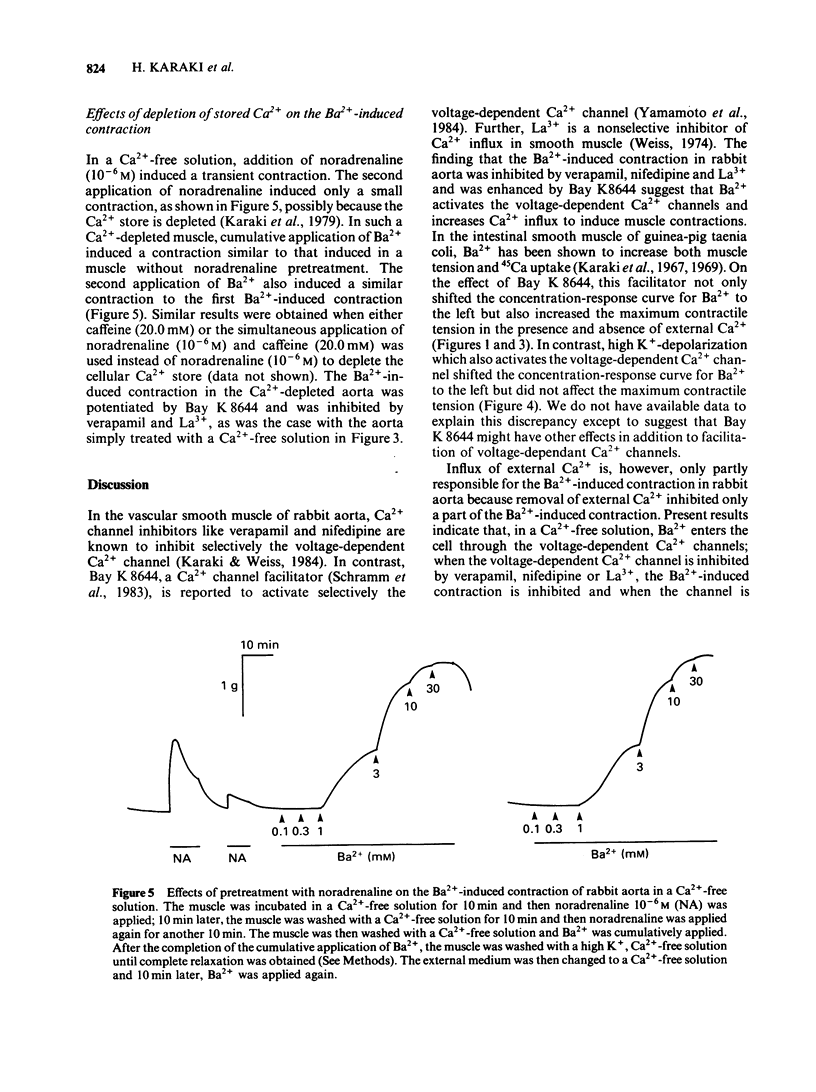
In a solution containing 1.5 mM Ca2+, cumulative application of 0.3-10.0 mM Ba2+ induced a concentration-dependent contraction of the rabbit aorta. This contraction was reduced by the Ca2+ channel inhibitors, verapamil (10(-6) M), nifedipine (10(-7) M) and lanthanum (2.0 mM), and was potentiated by the Ca2+ channel facilitator, Bay K8644 (10(-7) M). In a Ca2+-free solution containing EGTA (1.0 mM), cumulative application of Ba2+ still induced a concentration-dependent contraction, the maximum contractile tension of which was comparable to that in the presence of 1.5 mM Ca2+. The Ba2+-induced contraction which was not dependent on the external Ca2+ was also inhibited by verapamil, nifedipine and lanthanum and was potentiated by Bay K8644. A high concentration (65.4 mM) of K+ potentiated this Ba2+-induced contraction whereas noradrenaline (10(-6) M) did not have such an effect. In order to deplete the releasable Ca2+ store in the cell, the muscle strip was treated with noradrenaline (10(-6) M) and/or caffeine (20.0 mM) in a Ca2+-free solution. In such a Ca2+-depleted muscle, Ba2+ still induced a contraction of a similar magnitude to that without such treatment. Further, the second application of Ba2+ in a Ca2+-free solution induced a similar contraction to that induced by the first application of Ba2+. These results suggest that Ba2+ depolarizes the cell membrane and opens the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels resulting in a Ca2+ influx in the presence of Ca2+. In the absence of external Ca2+, Ba2+ may enter the cell through the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels and induce contraction without mobilizing the Ca2+ store which is sensitive to noradrenaline and caffeine.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bond M., Kitazawa T., Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V. Release and recycling of calcium by the sarcoplasmic reticulum in guinea-pig portal vein smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1984 Oct;355:677–695. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. Effect of calcium, barium and manganese on the action of adrenaline in the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Mar 11;172(1027):121–136. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIEL E. E. ON ROLES OF CALCIUM STRONTIUM AND BARIUM IN CONTRACTION AND EXCITABILITY OF RAT UTERINE MUSCLE. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1963 Dec 1;146:298–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deth R. C., Lynch C. J. Mobilization of a common source of smooth muscle Ca2+ by norepinephrine and methylxanthines. Am J Physiol. 1981 May;240(5):C239–C247. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1981.240.5.C239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deth R., van Breemen C. Agonist induced release of intracellular Ca2+ in the rabbit aorta. J Membr Biol. 1977 Jan 28;30(4):363–380. doi: 10.1007/BF01869677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FILO R. S., BOHR D. F., RUEGG J. C. GLYCERINATED SKELETAL AND SMOOTH MUSCLE: CALCIUM AND MAGNESIUM DEPENDENCE. Science. 1965 Mar 26;147(3665):1581–1583. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3665.1581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotta Y., Tsukui R. Effect on the guinea-pig taenia coli of the substitution of strontium or barium ions for calcium ions. Nature. 1968 Mar 2;217(5131):867–869. doi: 10.1038/217867b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karaki H., Ikeda M., Urakawa N. Effects of external calcium and some metabolic inhibitors on barium-induced tension changes in guinea pig taenia coli. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1967 Dec;17(4):603–612. doi: 10.1254/jjp.17.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karaki H., Ikeda M., Urakawa N. Movements of calcium during tension development induced by barium and high-potassium in guinea pig taenia coli. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1969 Jun;19(2):291–299. doi: 10.1254/jjp.19.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karaki H., Kubota H., Urakawa N. Mobilization of stored calcium for phasic contraction induced by norepinephrine in rabbit aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Jun 15;56(3):237–245. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karaki H., Nakagawa H., Urakawa N. Effects of calcium antagonists on release of [3H]noradrenaline in rabbit aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jun 1;101(3-4):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90154-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karaki H., Suzuki T., Urakawa N. Tris does not inhibit isolated vascular or intestinal smooth muscle contraction. Am J Physiol. 1981 Sep;241(3):H337–H341. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1981.241.3.H337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karaki H., Urakawa N. Possible role of endogenous catecholamines in the contractions induced in rabbit aorta by ouabain, sodium depletion and potassium depletion. Eur J Pharmacol. 1977 May 1;43(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(77)90161-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karaki H., Weiss G. B. Calcium channels in smooth muscle. Gastroenterology. 1984 Oct;87(4):960–970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijten P. A., van Breemen C. The effects of caffeine on the noradrenaline-sensitive calcium store in rabbit aorta. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:327–339. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUZUKI T., NISHIYAMA A., OKAMURA K. THE EFFECTS OF BARIUM ION ON THE RESTING AND ACTION POTENTIAL OF INTESTINAL SMOOTH MUSCLE CELL. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1964 Feb 25;82:87–92. doi: 10.1620/tjem.82.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm M., Thomas G., Towart R., Franckowiak G. Novel dihydropyridines with positive inotropic action through activation of Ca2+ channels. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):535–537. doi: 10.1038/303535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V., Devine C. E., Peters P. D., Hall T. A. Electron microscopy and electron probe analysis of mitochondrial cation accumulation in smooth muscle. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jun;61(3):723–742. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.3.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YUKISADA N., EBASHI F. Role of calcium in drug action on smooth muscle. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1961 Sep;11:46–53. doi: 10.1254/jjp.11.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Hwang O., Van Breemen C. Bay K8644 differentiates between potential and receptor operated Ca2+ channels. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jul 20;102(3-4):555–557. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90581-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino M., Yabu H. Single Ca channel currents in mammalian visceral smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Jul;404(3):285–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00581252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


