Abstract
1. The vasoconstrictor effects of endothelin-1 were studied in perfused mesenteric vascular beds (MVB) and aortic rings of 14-16 week-old spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) and age-matched Wistar Kyoto rats (WKY). 2. Reactivity to endothelin-1 was increased in MVBs of SHR, as indicated by the maximum perfusion pressure obtained (264 +/- 8 and 141 +/- 9 mmHg respectively) (P less than 0.001), whereas sensitivity was not significantly different between the two strains (EC50 171 +/- 21 and 102 +/- 19, respectively). 3. In aortic rings, in contrast, reactivity to endothelin-1 was reduced in SHR as compared to WKY, whereas sensitivity was similar (EC50 0.78 +/- 0.08 and 0.87 +/- 0.09 nM). 4. As with endothelin-1, reactivity to noradrenaline and potassium chloride was increased in MVBs, but not in aortic rings of SHR. Endothelin-1 was 30 times more potent than noradrenaline in MVBs of SHR, and 15 times more potent than noradrenaline in aortic rings. 5. In both strains, nifedipine and nitrendipine almost completely blocked potassium-induced contractions in MVB and aortic rings, respectively, whereas contractions induced by endothelin-1 or noradrenaline were only partially inhibited. 6. It is concluded that calcium influx via the voltage-operated calcium channel is only partially responsible for the vasoconstrictor action of endothelin-1 in MVBs and aortic rings of SHR and WKY rats. The increased reactivity of the MVB of SHR to endothelin-1 at this stage of the hypertensive process is most likely to be the result of a change in vascular structure rather than due to a primary hypertensive mechanism.
Full text
PDF
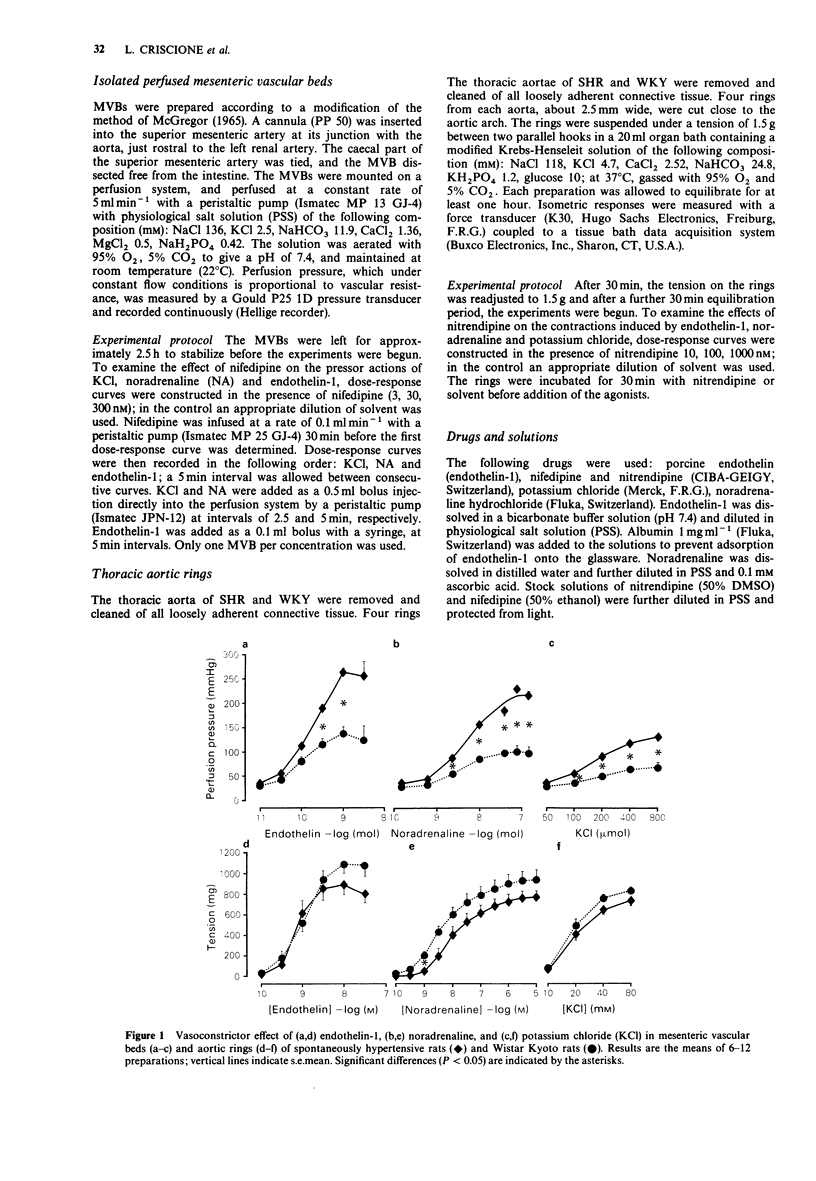
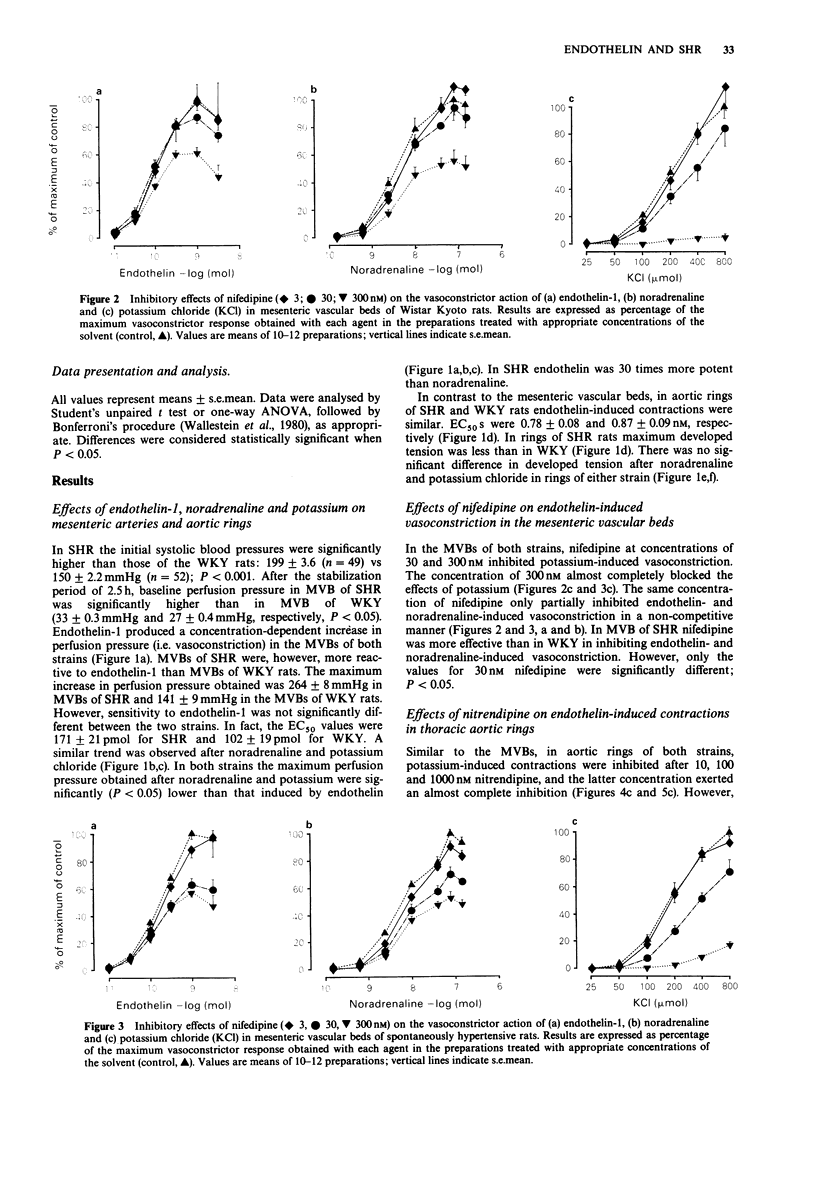
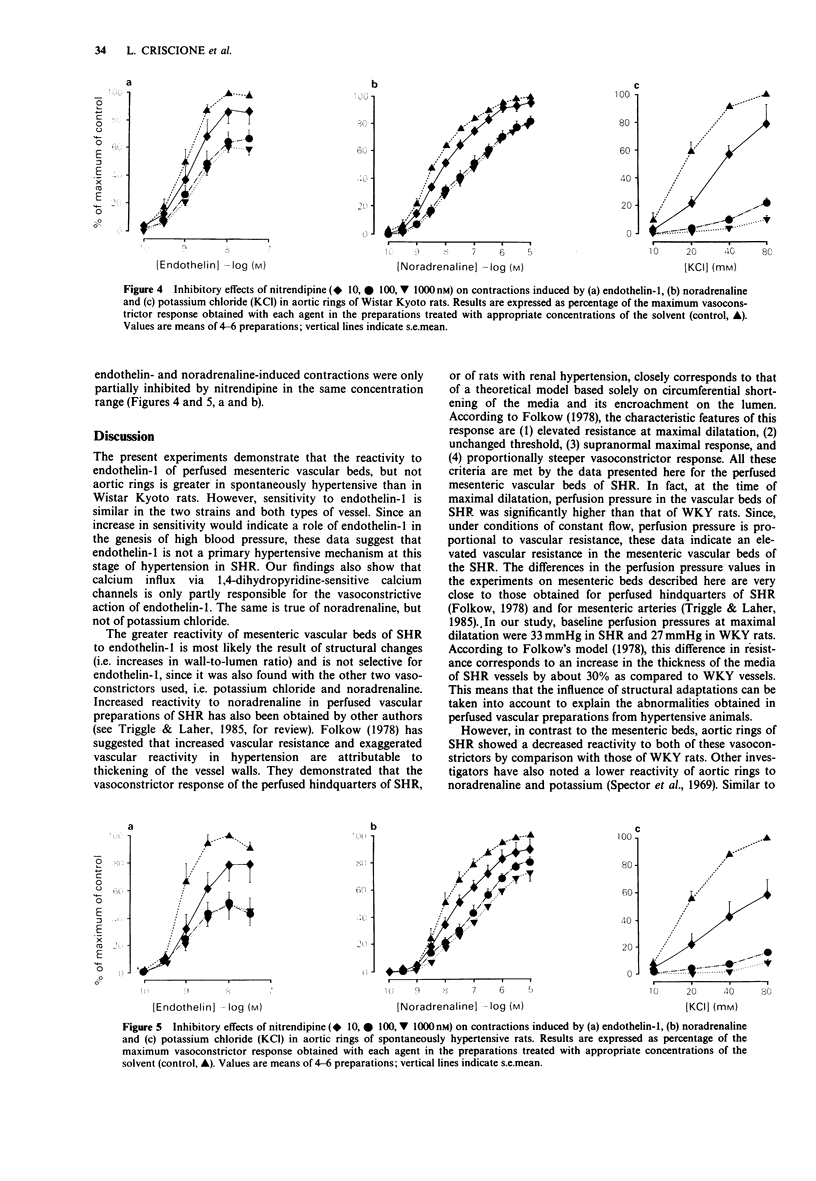


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Folkow B. The fourth Volhard lecture: cardiovascular structural adaptation; its role in the initiation and maintenance of primary hypertension. Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl. 1978 Dec;4:3s–22s. doi: 10.1042/cs055003s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Zawadzki J. V. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):373–376. doi: 10.1038/288373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie M. N., Owasoyo J. O., McMurtry I. F., O'Brien R. F. Sustained coronary vasoconstriction provoked by a peptidergic substance released from endothelial cells in culture. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Feb;236(2):339–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryglewski R. J., Botting R. M., Vane J. R. Mediators produced by the endothelial cell. Hypertension. 1988 Dec;12(6):530–548. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.12.6.530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey K. A., Rubanyi G., Paul R. J., Highsmith R. F. Characterization of a coronary vasoconstrictor produced by cultured endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):C550–C556. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.5.C550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Yoshimi H., Takata S., Watanabe T. X., Kumagai S., Nakajima K., Sakakibara S. Cellular mechanism of action by a novel vasoconstrictor endothelin in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 15;154(3):868–875. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karaki H. Use of tension measurements to delineate the mode of action of vasodilators. J Pharmacol Methods. 1987 Aug;18(1):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(87)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama M., Kanaide H., Abe S., Hirano K., Kai H., Nakamura M. Endothelin-induced Ca-independent contraction of the porcine coronary artery. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 May 15;160(3):1302–1308. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGREGOR D. D. THE EFFECT OF SYMPATHETIC NERVE STIMULATION OF VASOCONSTRICTOR RESPONSES IN PERFUSED MESENTERIC BLOOD VESSELS OF THE RAT. J Physiol. 1965 Mar;177:21–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden P. A., Danthuluri N. R., Brenner B. M., Ballermann B. J., Brock T. A. Endothelin action on vascular smooth muscle involves inositol trisphosphate and calcium mobilization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 16;158(1):86–93. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80180-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama K., Ishii K., Kato H. Effect of Ca-antagonists on the contraction of cerebral and peripheral arteries produced by electrical and mechanical stimuli. Gen Pharmacol. 1983;14(1):111–113. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(83)90076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resink T. J., Scott-Burden T., Bühler F. R. Endothelin stimulates phospholipase C in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 30;157(3):1360–1368. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Ohashi M., Metz M. Z., Bing R. J. Inhibitory effect of a calcium antagonist (diltiazem) on aortic and coronary contractions in rabbits. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1982 Dec;14(12):741–744. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(82)90187-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector S., Fleisch J. H., Maling H. M., Brodie B. B. Vascular smooth muscle reactivity in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Science. 1969 Dec 5;166(3910):1300–1301. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3910.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomobe Y., Miyauchi T., Saito A., Yanagisawa M., Kimura S., Goto K., Masaki T. Effects of endothelin on the renal artery from spontaneously hypertensive and Wistar Kyoto rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug 2;152(3):373–374. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90736-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triggle C. R., Laher I. A review of changes in vascular smooth muscle functions in hypertension: isolated tissue versus in vivo studies. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1985 Apr;63(4):355–365. doi: 10.1139/y85-065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Renterghem C., Vigne P., Barhanin J., Schmid-Alliana A., Frelin C., Lazdunski M. Molecular mechanism of action of the vasoconstrictor peptide endothelin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 30;157(3):977–985. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80970-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallenstein S., Zucker C. L., Fleiss J. L. Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res. 1980 Jul;47(1):1–9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.47.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb R. C., Bohr D. F. Recent advances in the pathogenesis of hypertension: consideration of structural, functional, and metabolic vascular abnormalities resulting in elevated arterial resistance. Am Heart J. 1981 Aug;102(2):251–264. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8703(81)80016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Endothelin, a novel endothelium-derived peptide. Pharmacological activities, regulation and possible roles in cardiovascular control. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 15;38(12):1877–1883. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90484-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Breemen C., Siegel B. The mechanism of alpha-adrenergic activation of the dog coronary artery. Circ Res. 1980 Mar;46(3):426–429. doi: 10.1161/01.res.46.3.426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


