Abstract
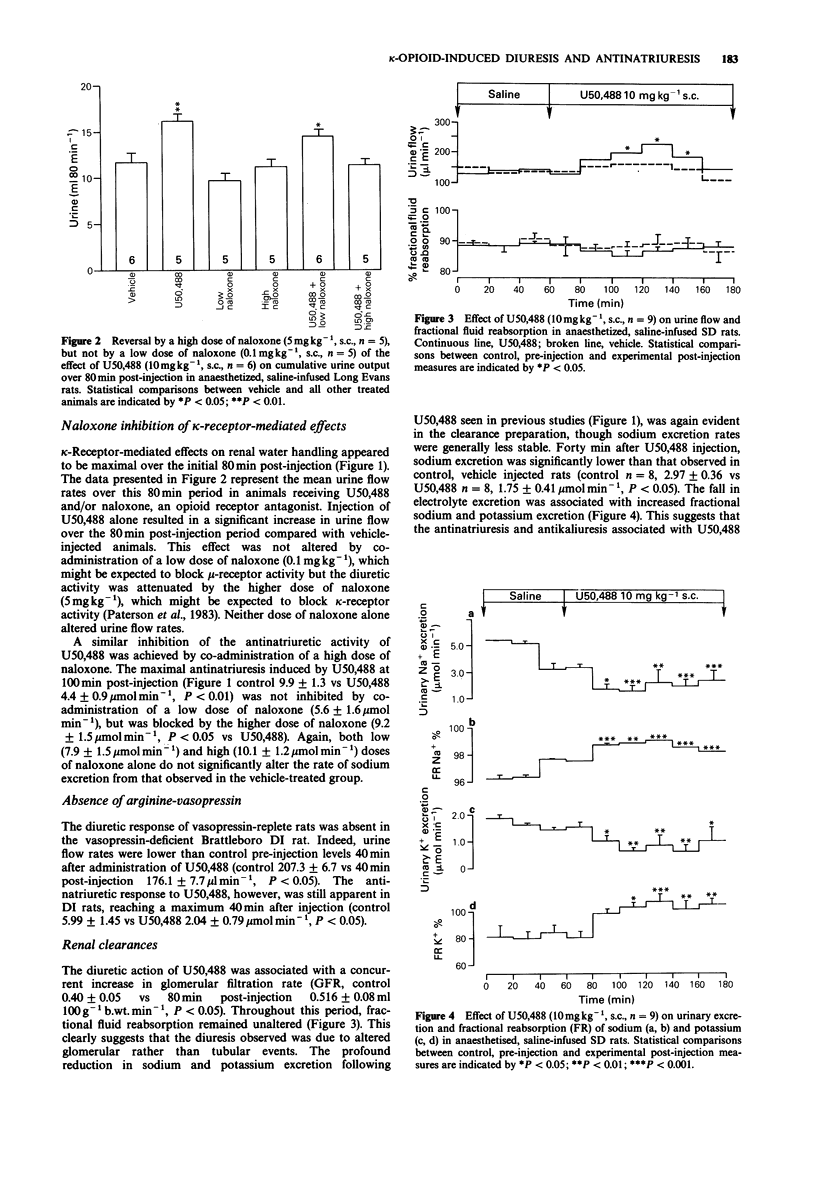
1. Subcutaneous injection of the kappa-opioid agonists U50,488 (10 mg kg-1) and tifluadom (3.5 mg kg-1) into Inactin-anaesthetized, saline-infused rats was associated with a diuresis, antinatriuresis and antikaliuresis which lasted for up to 2 h. A high (5 mg kg-1), but not low (0.1 mg kg-1), dose of naloxone blocked the renal effects of U50,488. 2. U50,488 administration in anaesthetized, vasopressin-deficient Brattleboro DI rats was associated with an attenuated diuresis, though the antinatriuretic response remained intact. 3. The diuretic action of U50,488 was associated with an increase in glomerular filtration rate while fractional fluid reabsorption remained steady. In contrast, fractional sodium and potassium reabsorption were increased. 4. These data suggest that kappa-opioid agonists alter renal handling of both water and electrolytes. This appears to be mediated by two separate mechanisms: increased fluid loss largely reflects altered glomerular events while the fall in electrolyte excretion results from altered tubular handling.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashton N., Balment R. J., Blackburn T. P. Kappa-opioid-induced changes in renal water and electrolyte management and endocrine secretion. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;97(3):769–776. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12015.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton N., Balment R. J. Neurohypophysial hormone influence on renal function in the New Zealand genetically hypertensive rat. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1988 Jul;118(3):422–428. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1180422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balment R. J., Brimble M. J., Forsling M. L., Kelly L. P., Musabayane C. T. A synergistic effect of oxytocin and vasopressin on sodium excretion in the neurohypophysectomized rat. J Physiol. 1986 Dec;381:453–464. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn T. P., Borkowski K. R., Friend J., Rance M. J. On the mechanisms of kappa-opioid-induced diuresis. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;89(3):593–598. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb11160.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blantz R. C., Pelayo J. C. In vivo actions of angiotensin II on glomerular function. Fed Proc. 1983 Nov;42(14):3071–3074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. J., Follenfant R. L., Smith T. W. Evaluation of opioid-induced antinociceptive effects in anaesthetized and conscious animals. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;95(1):275–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb16574.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. M. Plasma corticosterone changes in response to central or peripheral administration of kappa and sigma opiate agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jun;233(3):863–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsling M. L., Brimble M. J., Balment R. J. The influence of vasopressin on oxytocin-induced changes in urine flow in the male rat. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1982 Jun;100(2):216–220. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1000216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSMITH C., RECTOR F. C., Jr, SELDIN D. W. Evidence for a direct effect of serum sodium concentration on sodium reabsorption. J Clin Invest. 1962 Apr;41:850–859. doi: 10.1172/JCI104542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huidobro-Toro J. P., Parada S. Kappa-opiates and urination: pharmacological evidence for an endogenous role of the kappa-opiate receptor in fluid and electrolyte balance. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Dec 15;107(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa I., Brenner B. M. Glomerular actions of angiotensin II. Am J Med. 1984 May 31;76(5B):43–49. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90882-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar S., Kim H. S., Wood P. L. Kappa opiate agonists modulate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Aug;238(2):429–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Paterson S. J., Robson L. E. Characterization of the kappa-subtype of the opiate receptor in the guinea-pig brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Aug;73(4):939–949. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb08749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahti R. A., Collins R. J. Opiate effects on plasma corticosteroids: relationship to dysphoria and self-administration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1982 Jul;17(1):107–109. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(82)90270-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leander J. D. A kappa opioid effect: increased urination in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jan;224(1):89–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leander J. D. Further study of kappa opioids on increased urination. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Oct;227(1):35–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. Inhibition of ADH release in the rat by narcotic antagonists. Neuroendocrinology. 1975;19(3):241–251. doi: 10.1159/000122444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson S. J., Robson L. E., Kosterlitz H. W. Classification of opioid receptors. Br Med Bull. 1983 Jan;39(1):31–36. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirion R., Finkel M. S., Mendelsohn F. A., Zamir N. Localization of opiate binding sites in kidney and adrenal gland of the rat. Life Sci. 1983;33 (Suppl 1):299–302. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90502-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schor N., Ichikawa I., Brenner B. M. Mechanisms of action of various hormones and vasoactive substances on glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. Kidney Int. 1981 Oct;20(4):442–451. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slizgi G. R., Ludens J. H. Studies on the nature and mechanism of the diuretic activity of the opioid analgesic ethylketocyclazocine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Mar;220(3):585–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slizgi G. R., Taylor C. J., Ludens J. H. Effects of the highly selective kappa opioid, U-50, 488, on renal function in the anesthetized dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Sep;230(3):641–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonvoigtlander P. F., Lahti R. A., Ludens J. H. U-50,488: a selective and structurally novel non-Mu (kappa) opioid agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jan;224(1):7–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. L., Charleson S. E., Lane D., Hudgin R. L. Multiple opiate receptors: differential binding of mu, kappa and delta agonists. Neuropharmacology. 1981 Dec;20(12A):1215–1220. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(81)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


