Abstract
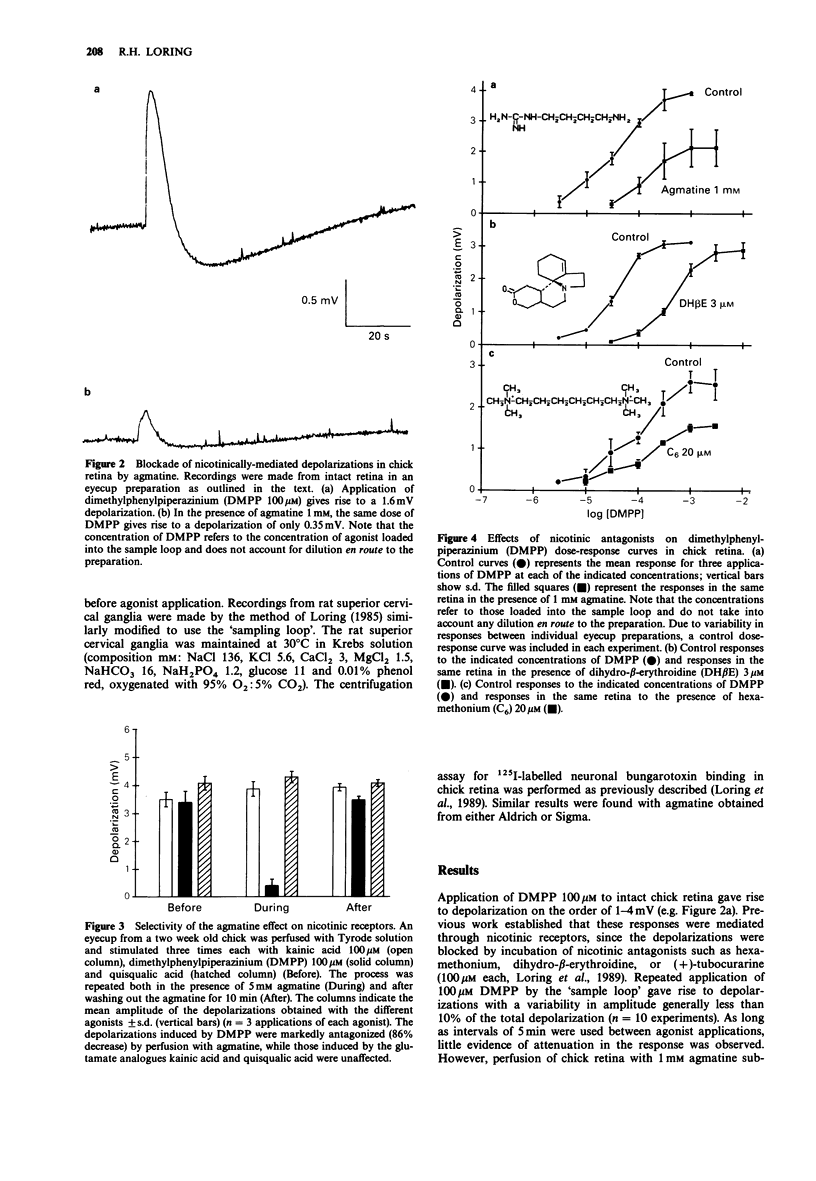
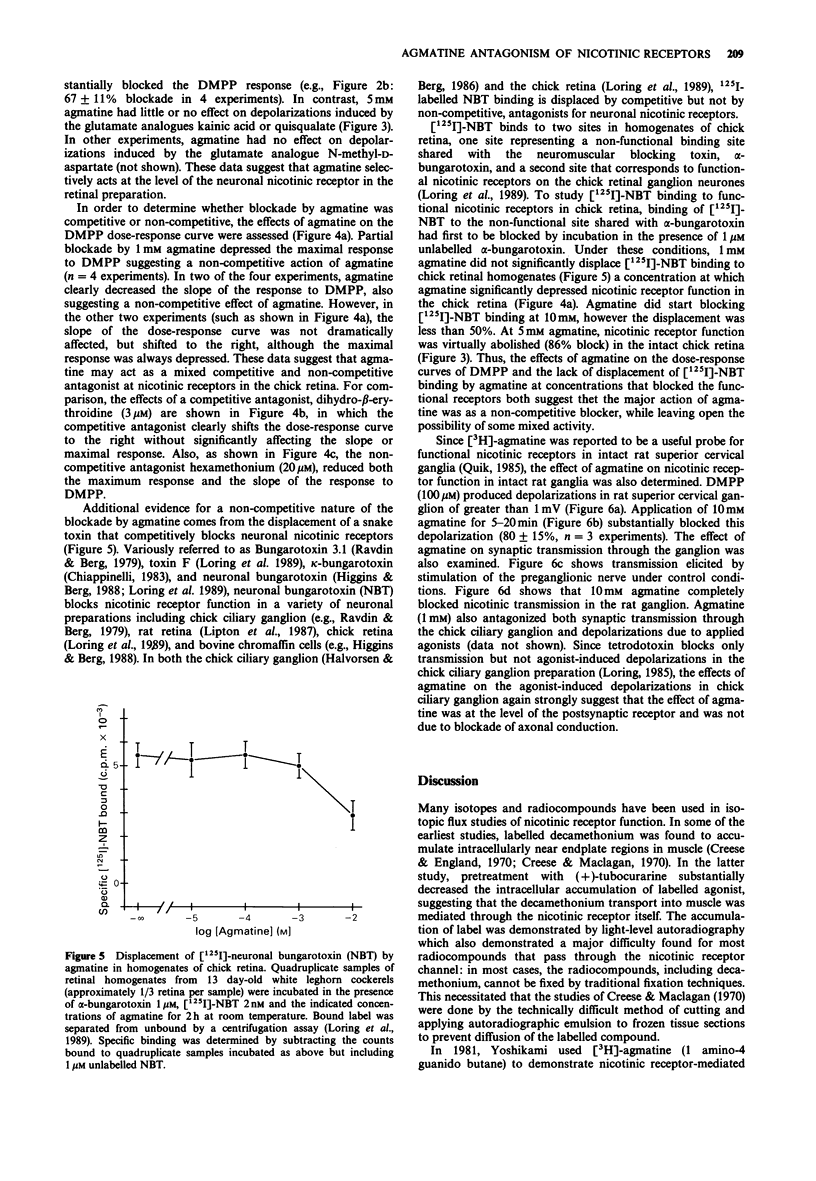
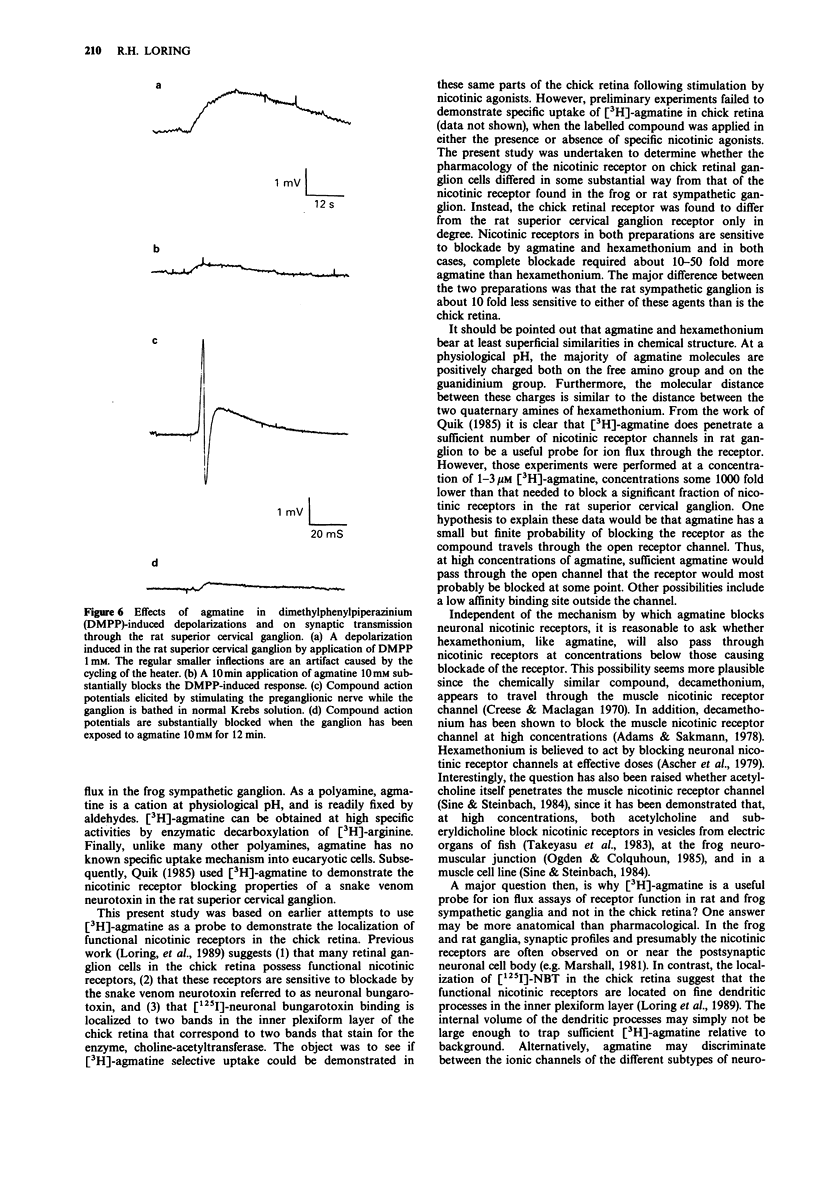
1. Tritiated agmatine has been used by others in ion flux methods to measure nicotinic receptor function in neurones. However, as shown here, agmatine blocks nicotinic receptor function in both the chick retina and the rat superior cervical ganglion at high concentrations. 2. In intact chick retina, agmatine 1 mM decreases dimethylphenylpiperazinium (DMPP)-induced depolarizations measured in the optic nerve by approximately 70%, while having little effect on responses induced by glutamate analogues. DMPP dose-response curves are reduced in a manner consistent with a non-competitive effect of agmatine, and agmatine at 1 mM does not prevent binding of 125I-labelled neuronal bungarotoxin, a snake venom neurotoxin that competitively binds and blocks functional nicotinic receptors in chick retinal homogenates. 3. Agmatine (10 mM) substantially blocks both DMPP-induced depolarizations of rat superior cervical ganglion and synaptic transmission through the ganglion. Others have established that [3H]-agmatine will pass through nicotinic receptor channels in the rat ganglion. These data suggest that agmatine acts both as a cation and as a weak channel blocker at neuronal nicotinic receptors.
Full text
PDF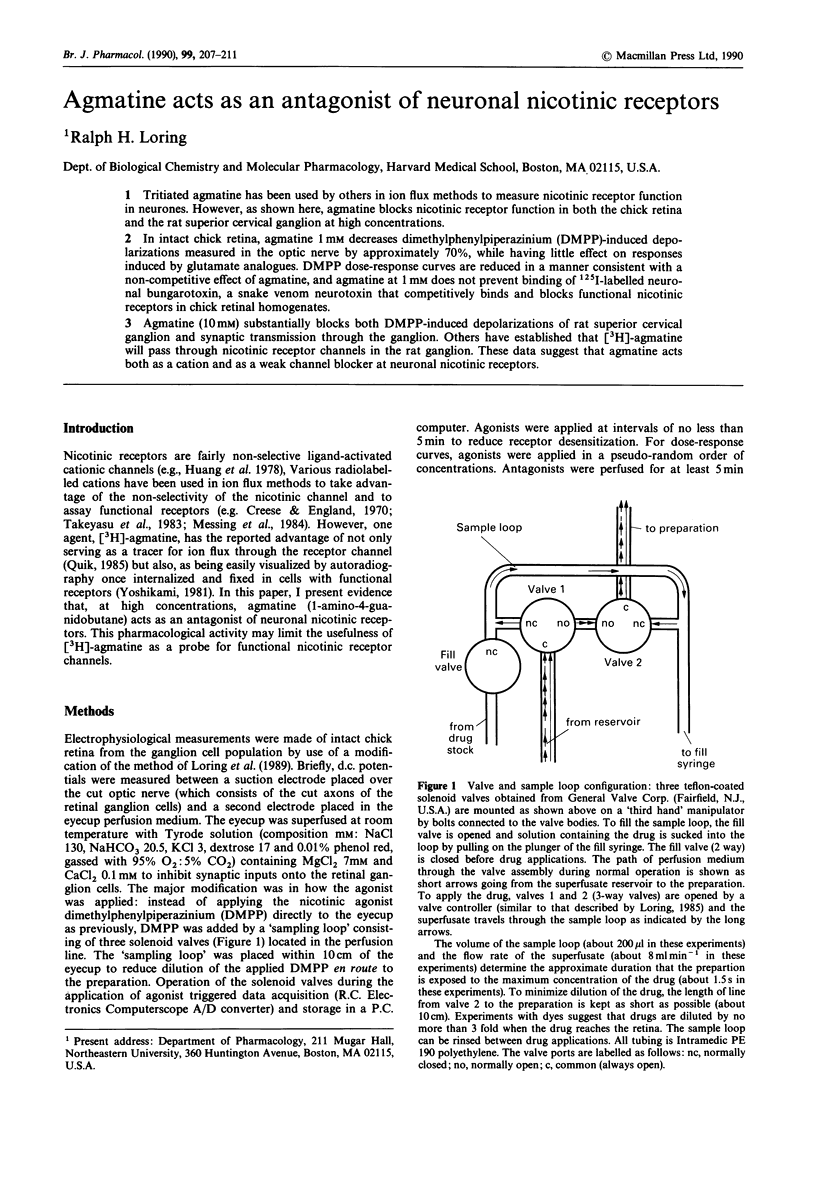

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Sakmann B. Decamethonium both opens and blocks endplate channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2994–2998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher P., Large W. A., Rang H. P. Studies on the mechanism of action of acetylcholine antagonists on rat parasympathetic ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1979 Oct;295:139–170. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese R., England J. M. Decamethonium in depolarized muscle and the effects of tubocurarine. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):345–361. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese R., Maclagan J. Entry of decamethonium in rat muscle studied by autoradiography. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):363–386. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halvorsen S. W., Berg D. K. Identification of a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor on neurons using an alpha-neurotoxin that blocks receptor function. J Neurosci. 1986 Nov;6(11):3405–3412. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-11-03405.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins L. S., Berg D. K. Cyclic AMP-dependent mechanism regulates acetylcholine receptor function on bovine adrenal chromaffin cells and discriminates between new and old receptors. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1157–1165. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. Y., Catterall W. A., Ehrenstein G. Selectivity of cations and nonelectrolytes for acetylcholine-activated channels in cultured muscle cells. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Apr;71(4):397–410. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.4.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A., Aizenman E., Loring R. H. Neural nicotinic acetylcholine responses in solitary mammalian retinal ganglion cells. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Sep;410(1-2):37–43. doi: 10.1007/BF00581893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loring R. H. A method for recording agonist-induced depolarizations in small autonomic ganglia. J Neurosci Methods. 1985 Jan;12(3):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(85)90007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loring R. H., Aizenman E., Lipton S. A., Zigmond R. E. Characterization of nicotinic receptors in chick retina using a snake venom neurotoxin that blocks neuronal nicotinic receptor function. J Neurosci. 1989 Jul;9(7):2423–2431. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-07-02423.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall L. M. Synaptic localization of alpha-bungarotoxin binding which blocks nicotinic transmission at frog sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1948–1952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing A., Bizzini B., Gonatas N. K. Concanavalin A inhibits nicotinic acetylcholine receptor function in cultured chick ciliary ganglion neurons. Brain Res. 1984 Jun 15;303(2):241–249. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91210-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden D. C., Colquhoun D. Ion channel block by acetylcholine, carbachol and suberyldicholine at the frog neuromuscular junction. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Sep 23;225(1240):329–355. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quik M. Inhibition of nicotinic receptor mediated ion fluxes in rat sympathetic ganglia by BGT II-S1 a potent phospholipase. Brain Res. 1985 Jan 28;325(1-2):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90304-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin P. M., Berg D. K. Inhibition of neuronal acetylcholine sensitivity by alpha-toxins from Bungarus multicinctus venom. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):2072–2076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Steinbach J. H. Agonists block currents through acetylcholine receptor channels. Biophys J. 1984 Aug;46(2):277–283. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84022-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbach J. H., Ifune C. How many kinds of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor are there? Trends Neurosci. 1989 Jan;12(1):3–6. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeyasu K., Udgaonkar J. B., Hess G. P. Acetylcholine receptor: evidence for a voltage-dependent regulatory site for acetylcholine. Chemical kinetic measurements in membrane vesicles using a voltage clamp. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 6;22(25):5973–5978. doi: 10.1021/bi00294a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikami D. Transmitter sensitivity of neurons assayed by autoradiography. Science. 1981 May 22;212(4497):929–930. doi: 10.1126/science.6262911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


