Abstract
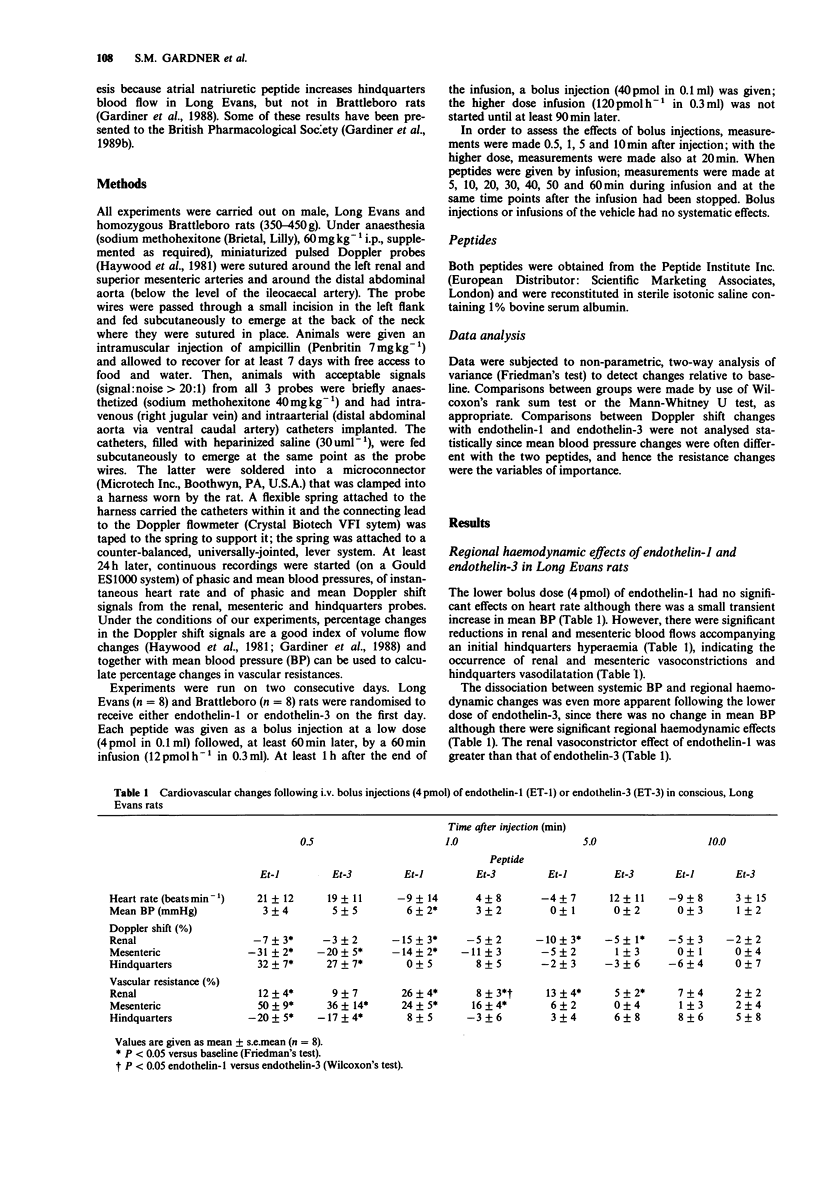
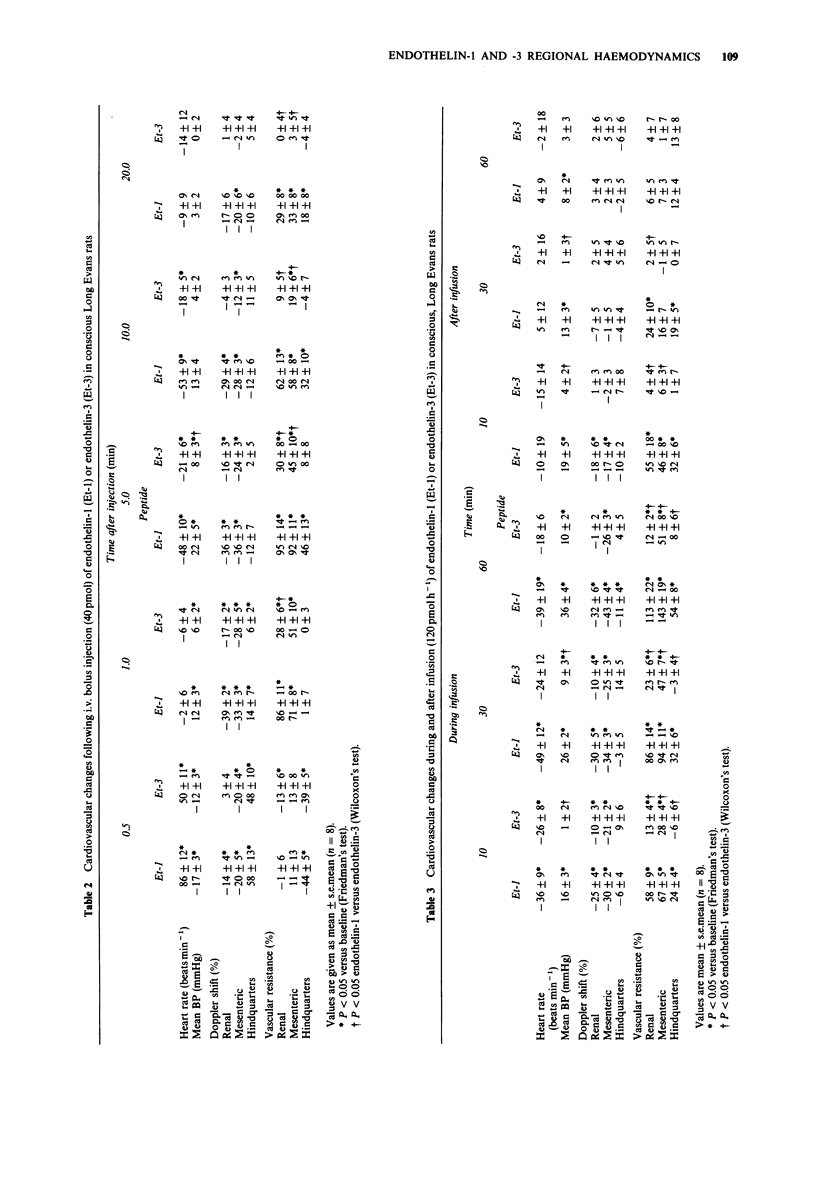
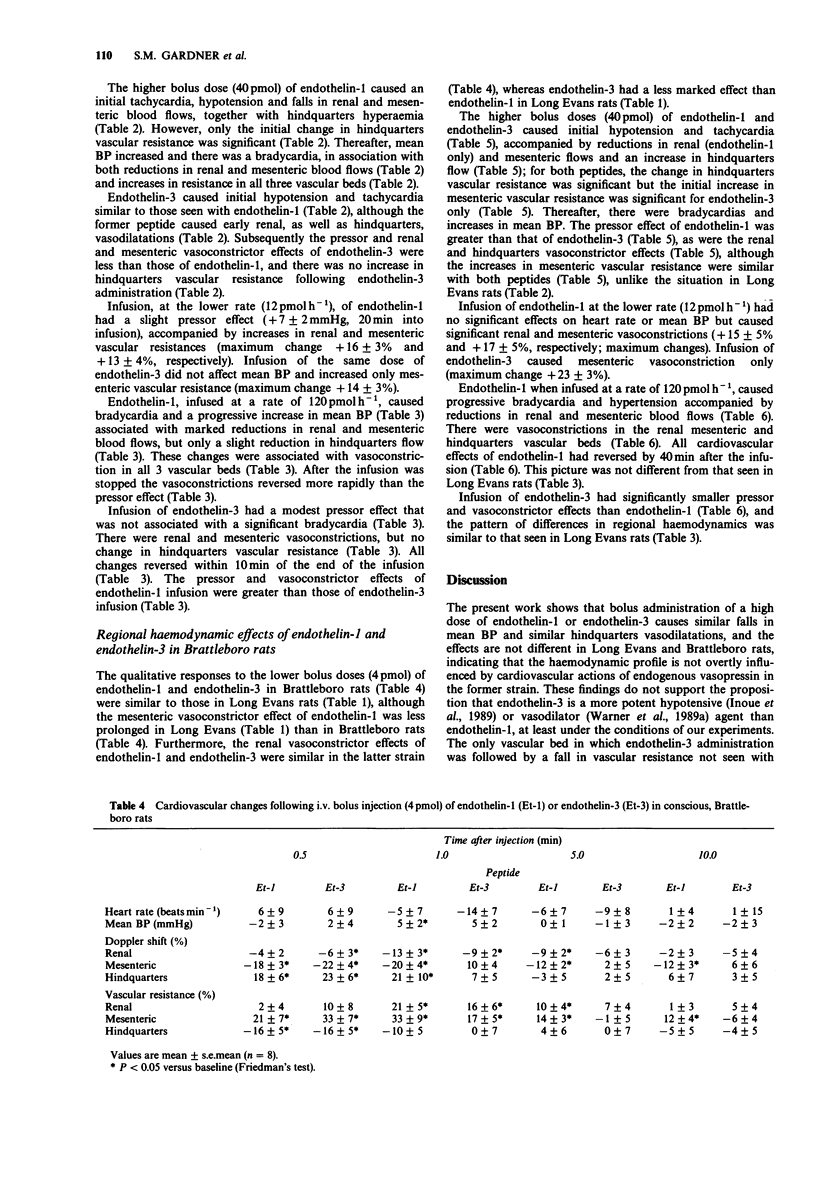
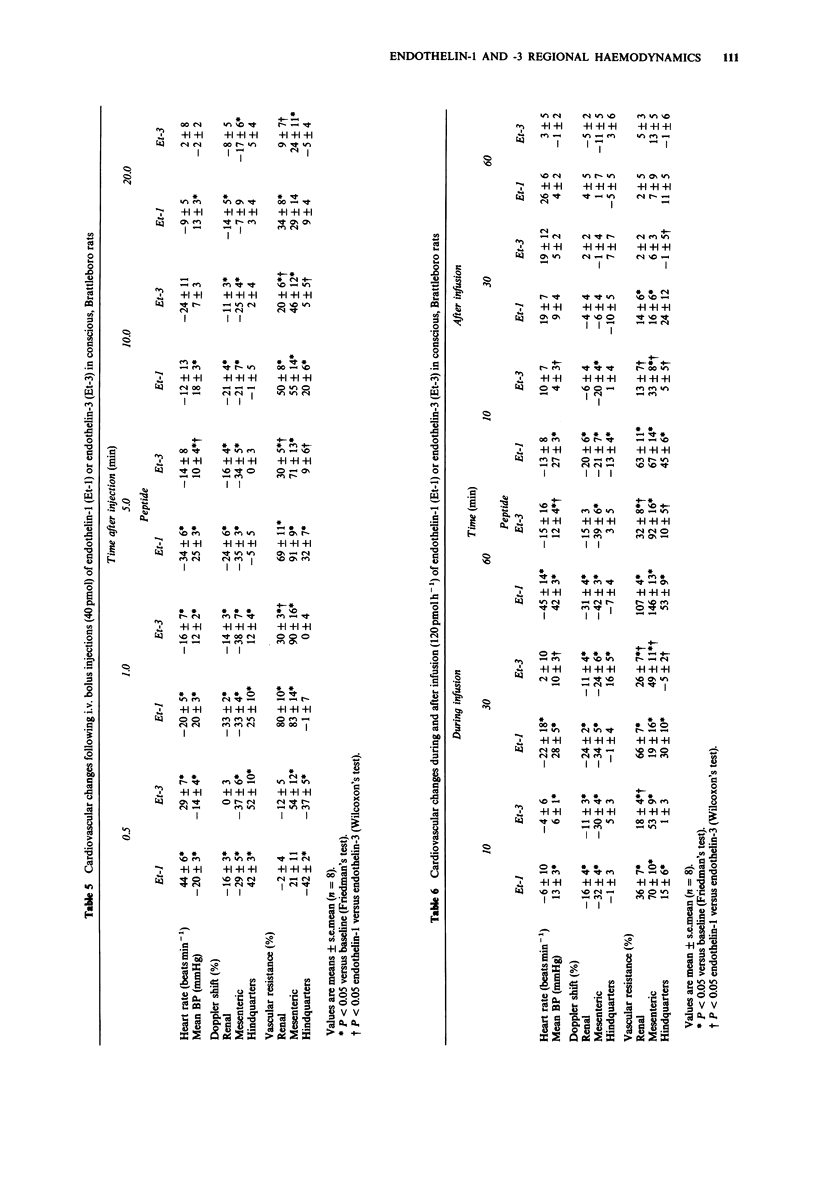
1. The regional haemodynamic effects of bolus doses (4 and 40 pmol) and infusions (12 and 120 pmol h-1) of endothelin-1 and endothelin-3 were assessed in conscious, Long Evans and Brattleboro (i.e. vasopressin-deficient) rats, chronically-instrumented with pulsed Doppler flow probes. 2. In both strains of rat the lower bolus dose of endothelin-1 caused only a slight pressor effect, but there were marked renal and mesenteric vasoconstrictions and hindquarters vasodilatation. 3. The lower bolus dose of endothelin-3 did not affect blood pressure significantly, although the changes in regional haemodynamics were qualitatively similar to those seen following endothelin-1 in Long Evans and Brattleboro rats. 4. The higher dose of endothelin-1 caused an initial hypotension accompanied by substantial hindquarters vasodilatations in Long Evans and Brattleboro rats. Subsequently, in both strains, there was a rise in blood pressure accompanied by renal, mesenteric and hindquarters vasoconstrictions. 5. The higher bolus dose of endothelin-3 caused initial hypotension and hindquarters vasodilatation similar to those seen with endothelin-1. However, the subsequent pressor effect was less with endothelin-3, as was the renal vasoconstriction, and it did not cause any increase in hindquarters vascular resistance. 6. Infusion of endothelin-1 at the lower rate (12 pmol h-1) caused renal and mesenteric vasoconstrictions in both strains of rat, whereas endothelin-3 at this rate caused only mesenteric vasoconstriction. 7. Infusion of endothelin-1 at the higher rate (120 pmol h-1) caused progressive hypertension and vasoconstrictions in all three vascular beds studied; these were similar in both strains of rat.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eglen R. M., Michel A. D., Sharif N. A., Swank S. R., Whiting R. L. The pharmacological properties of the peptide, endothelin. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug;97(4):1297–1307. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12592.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner S. M., Compton A. M., Bennett T. Regional haemodynamic effects of depressor neuropeptides in conscious, unrestrained, Long Evans and Brattleboro rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;95(1):197–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb16565.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner S. M., Compton A. M., Bennett T. Regional hemodynamic effects of endothelin-1 in conscious, unrestrained, Wistar rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1989;13 (Suppl 5):S202–S204. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198900135-00057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haywood J. R., Shaffer R. A., Fastenow C., Fink G. D., Brody M. J. Regional blood flow measurement with pulsed Doppler flowmeter in conscious rat. Am J Physiol. 1981 Aug;241(2):H273–H278. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1981.241.2.H273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue A., Yanagisawa M., Kimura S., Kasuya Y., Miyauchi T., Goto K., Masaki T. The human endothelin family: three structurally and pharmacologically distinct isopeptides predicted by three separate genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2863–2867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minkes R. K., Coy D. H., Murphy W. A., McNamara D. B., Kadowitz P. J. Effects of porcine and rat endothelin and an analog on blood pressure in the anesthetized cat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 30;164(3):571–575. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90266-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minkes R. K., Kadowitz P. J. Differential effects of rat endothelin on regional blood flow in the cat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 8;165(1):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90784-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spokes R. A., Ghatei M. A., Bloom S. R. Studies with endothelin-3 and endothelin-1 on rat blood pressure and isolated tissues: evidence for multiple endothelin receptor subtypes. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1989;13 (Suppl 5):S191–S192. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198900135-00053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner T. D., de Nucci G., Vane J. R. Rat endothelin is a vasodilator in the isolated perfused mesentery of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan 17;159(3):325–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90167-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winquist R. J., Scott A. L., Vlasuk G. P. Enhanced release of atrial natriuretic factor by endothelin in atria from hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 1989 Jul;14(1):111–114. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.14.1.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. E., Fozard J. R. Regional vasodilation is a prominent feature of the haemodynamic response to endothelin in anaesthetized, spontaneously hypertensive rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct 11;155(1-2):201–203. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90425-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Inoue A., Ishikawa T., Kasuya Y., Kimura S., Kumagaye S., Nakajima K., Watanabe T. X., Sakakibara S., Goto K. Primary structure, synthesis, and biological activity of rat endothelin, an endothelium-derived vasoconstrictor peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6964–6967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Nucci G., Thomas R., D'Orleans-Juste P., Antunes E., Walder C., Warner T. D., Vane J. R. Pressor effects of circulating endothelin are limited by its removal in the pulmonary circulation and by the release of prostacyclin and endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9797–9800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


