Abstract
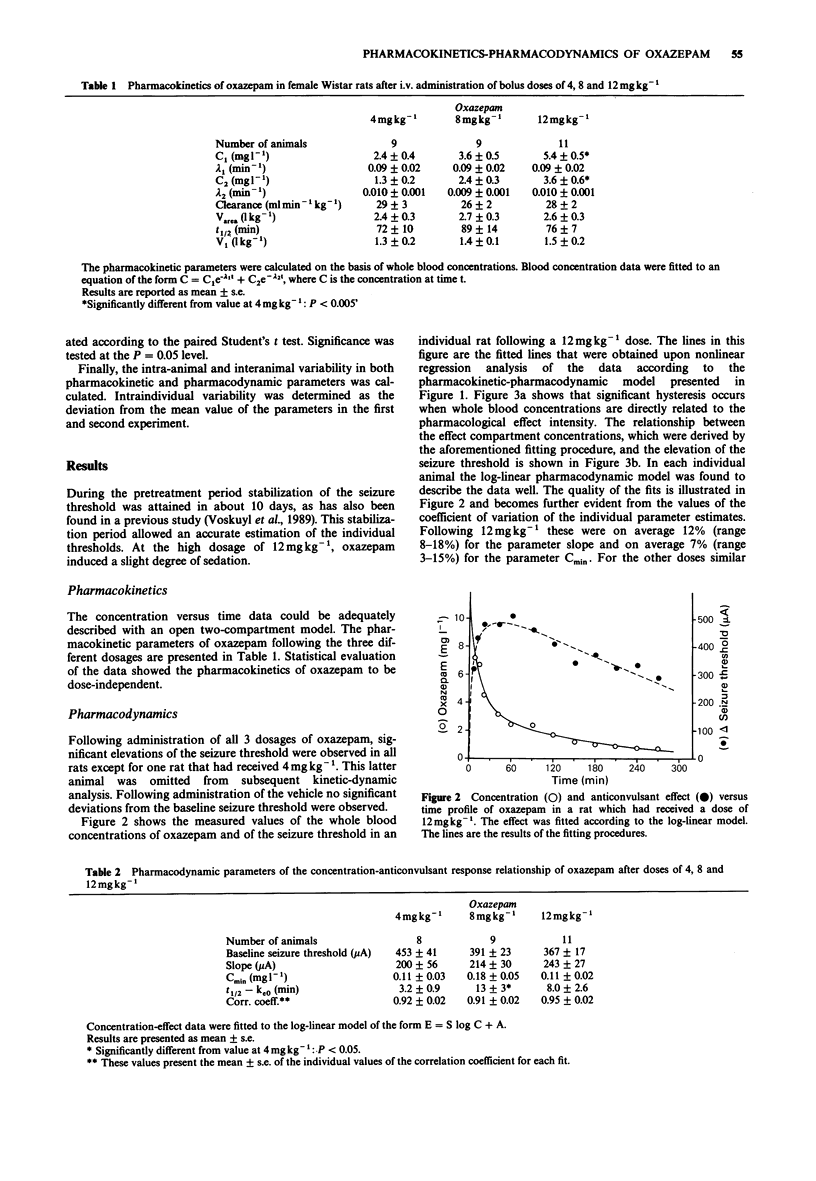
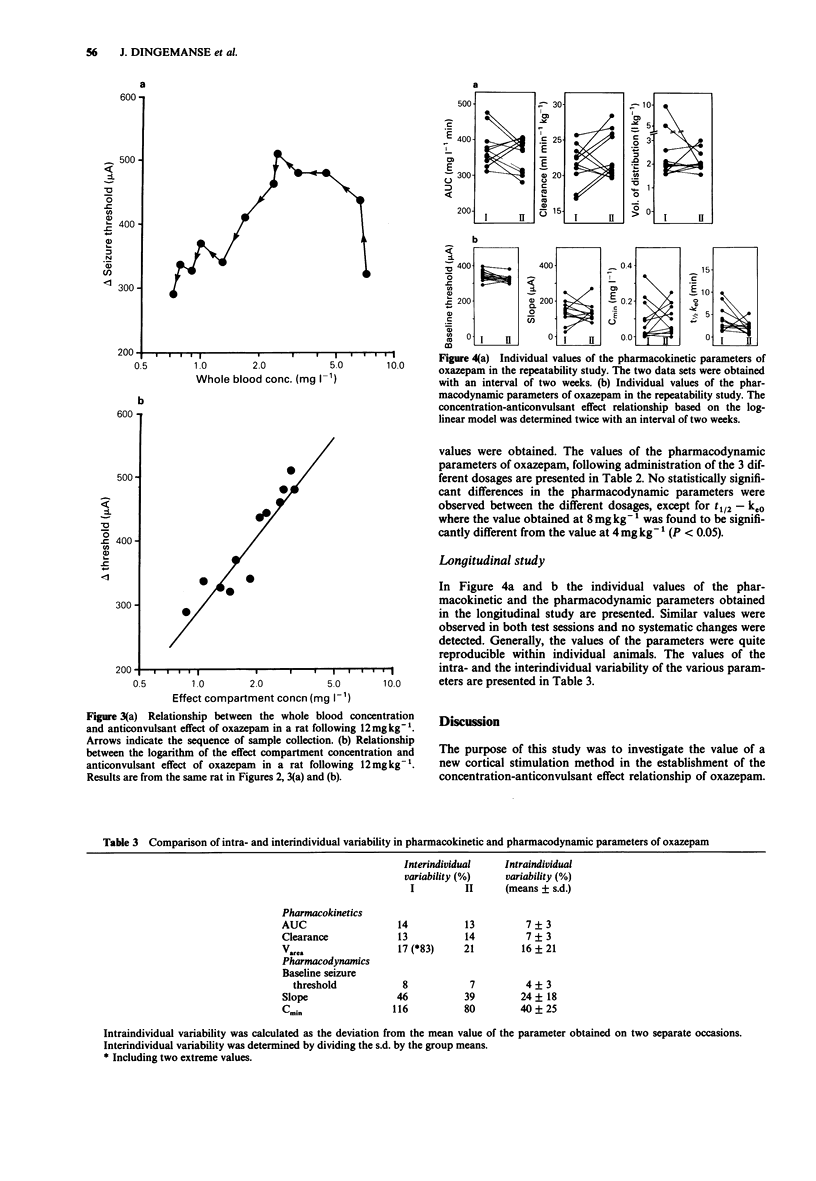
1. The purpose of this investigation was to examine in vivo drug-concentration anticonvulsant effect relationships of oxazepam in individual rats following administration of a single dose. 2. Whole blood concentration vs time profiles of oxazepam were determined following administration of doses of 4, 8 and 12 mg kg-1. The pharmacokinetics could be described by an open 2-compartment pharmacokinetic model. Following 12 mg kg-1 the values (mean +/- s.e., n = 11) of clearance and volume of distribution were 28 +/- 2 ml min-1 kg-1 and 2.6 +/- 0.31 kg-1, respectively, and were not significantly different from the values obtained at the other doses. 3. The anticonvulsant effect was quantitated by a new technique which allows repetitive determination of the convulsive threshold by direct cortical stimulation within one rat. Significant dose-dependent elevations of the seizure threshold were observed. 4. By pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modelling, a log-linear relationship was found between concentration and anticonvulsant effect. Following 12 mg kg-1 the values (mean +/- s.e., n = 11) of the pharmacodynamic parameters slope and minimal effective concentration (Cmin) were 243 +/- 27 microA and 0.11 +/- 0.02 mg l-1, respectively and not significantly different from the values obtained at the other doses. 5. In a repeatability study the pharmacodynamic parameters were determined twice on two different occasions with an interval of two weeks in the same group of 11 rats. The inter-animal variability in the pharmacodynamic parameter slope was 46%, whereas the intra-animal variability was 24 +/- 18%.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braestrup C., Nielsen M. Anxiety. Lancet. 1982 Nov 6;2(8306):1030–1034. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingemanse J., Danhof M., Breimer D. D. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling of CNS drug effects: an overview. Pharmacol Ther. 1988;38(1):1–52. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(88)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingemanse J., Sollie F. A., Breimer D. D., Danhof M. Pharmacokinetic modeling of the anticonvulsant response of oxazepam in rats using the pentylenetetrazol threshold concentration as pharmacodynamic measure. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1988 Apr;16(2):203–228. doi: 10.1007/BF01062261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingemanse J., Thomassen D., Mentink B. H., Danhof M. Strategy to assess the role of (inter)active metabolites in pharmacodynamic studies in-vivo: a model study with heptabarbital. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;40(8):552–557. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1988.tb05301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis R. J. ELSMOS--an extended least squares modelling system in FORTRAN IV for mini- or micro-computer implementation. Comput Programs Biomed. 1984 Feb-Apr;18(1-2):43–49. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(84)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigh J. R., Gent J. P., Calvert R. Plasma concentrations of clobazam and its N-desmethyl metabolite; protection against pentetrazol-induced convulsions in mice. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;36(9):636–638. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1984.tb04917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariton C., Jadot G., Mesdjian E., Mandel P. Diazepam: kinetic profiles in various brain areas, plasma and erythrocytes after chronic administration in the rat. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 1985 Apr-Jun;10(2):105–111. doi: 10.1007/BF03189703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
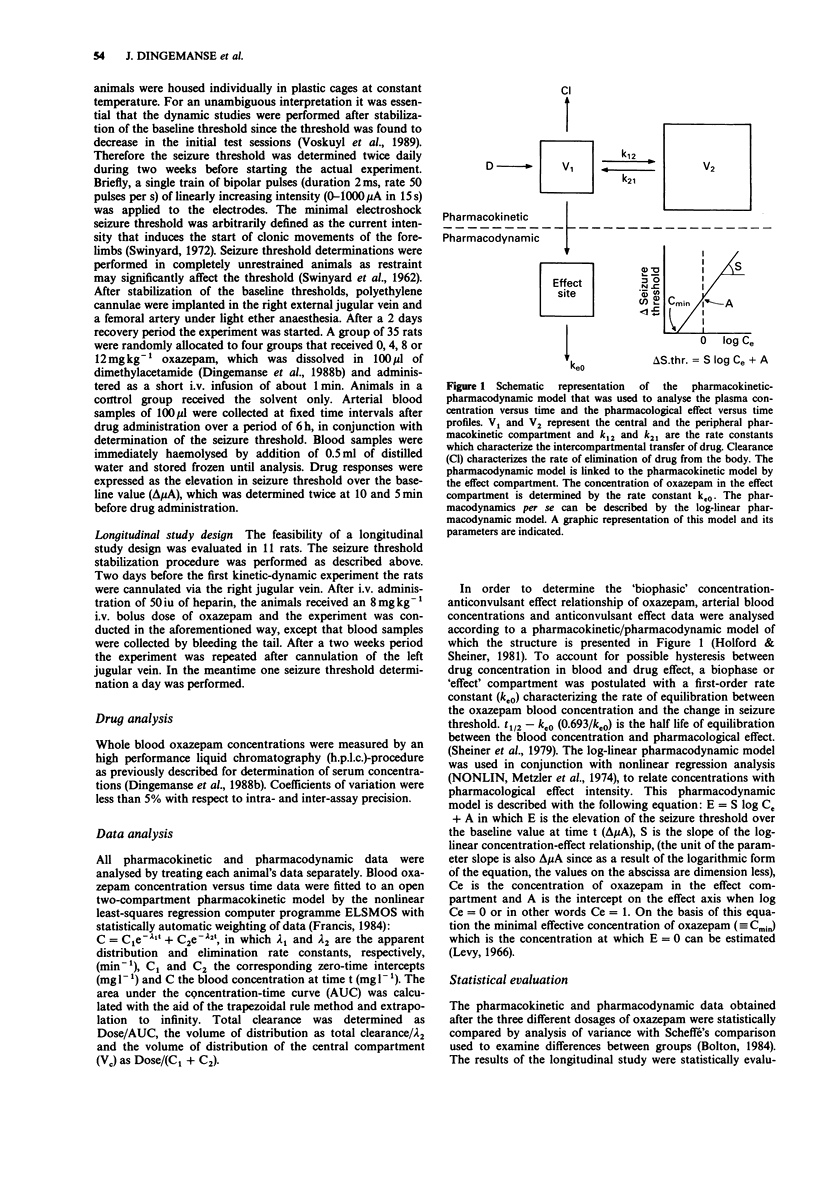
- Holford N. H., Sheiner L. B. Understanding the dose-effect relationship: clinical application of pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic models. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1981 Nov-Dec;6(6):429–453. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198106060-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igari Y., Sugiyama Y., Sawada Y., Iga T., Hanano M. Prediction of diazepam disposition in the rat and man by a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1983 Dec;11(6):577–593. doi: 10.1007/BF01059058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz U., Antonin K. H., Bieck P. R. Pharmacokinetics and plasma binding of diazepam in man, dog, rabbit, guinea pig and rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Oct;199(1):67–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz U. Estimation of the blood-plasma concentration ratio of diazepam in the rat. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1985 Jun;13(3):347–348. doi: 10.1007/BF01065659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy G. Kinetics of pharmacologic effects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1966 May-Jun;7(3):362–372. doi: 10.1002/cpt196673362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWINYARD E. A., RADHAKRISHNAN N., GOODMAN L. S. Effect of brief restraint on the convulsive threshold of mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962 Dec;138:337–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiner L. B., Stanski D. R., Vozeh S., Miller R. D., Ham J. Simultaneous modeling of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: application to d-tubocurarine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979 Mar;25(3):358–371. doi: 10.1002/cpt1979253358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanski D. R., Ham J., Miller R. D., Sheiner L. B. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of d-tubocurarine during nitrous oxide-narcotic and halothane anesthesia in man. Anesthesiology. 1979 Sep;51(3):235–241. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197909000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. M., Bennett G. D., Abbott L. C., Finnell R. H. Seizure control following administration of anticonvulsant drugs in the quaking mouse. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov 26;118(1-2):163–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90675-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voskuyl R. A., Dingemanse J., Danhof M. Determination of the threshold for convulsions by direct cortical stimulation. Epilepsy Res. 1989 Mar-Apr;3(2):120–129. doi: 10.1016/0920-1211(89)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOLLEY D. E., TIMIRAS P. S. Estrous and circadian periodicity and electroshock convulsions in rats. Am J Physiol. 1962 Feb;202:379–382. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.2.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. G. Kinetics of pharmacologic response. I. Proposed relationships between response and drug concentration in the intact animal and man. J Theor Biol. 1968 Aug;20(2):173–201. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(68)90188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


