Abstract
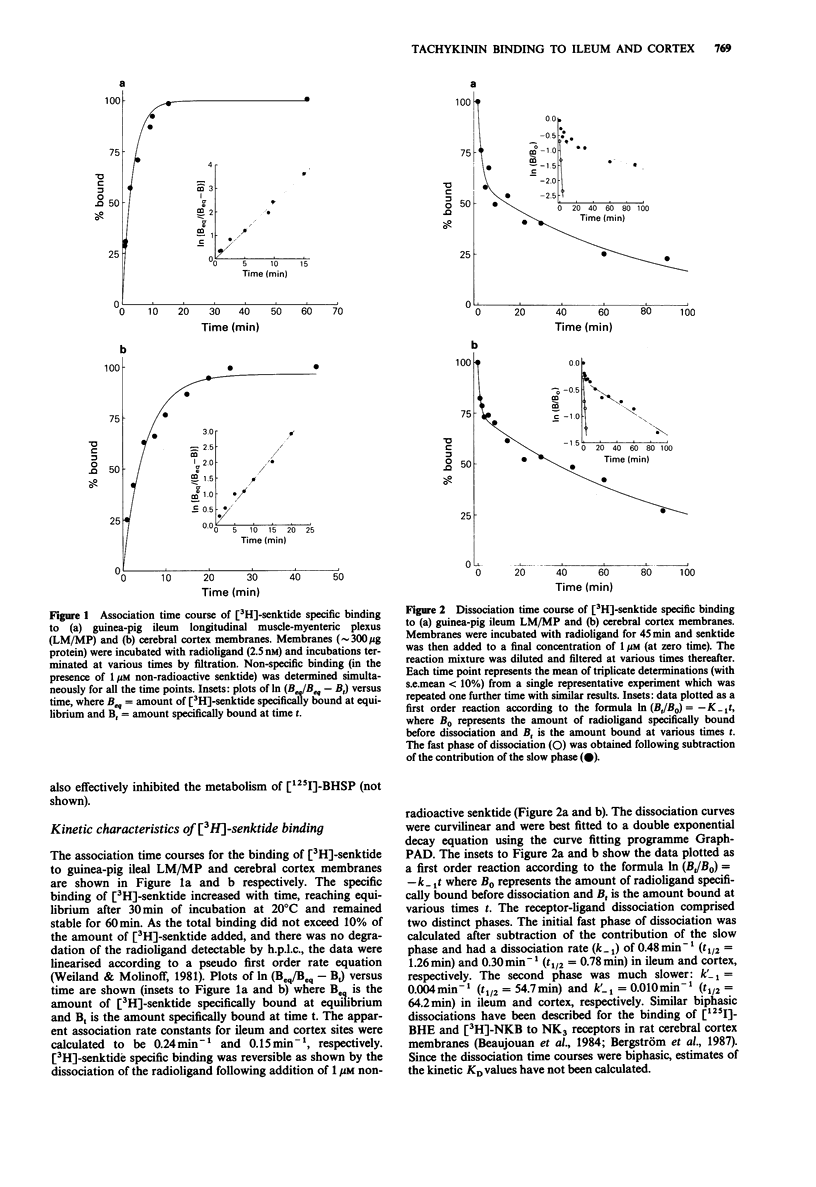
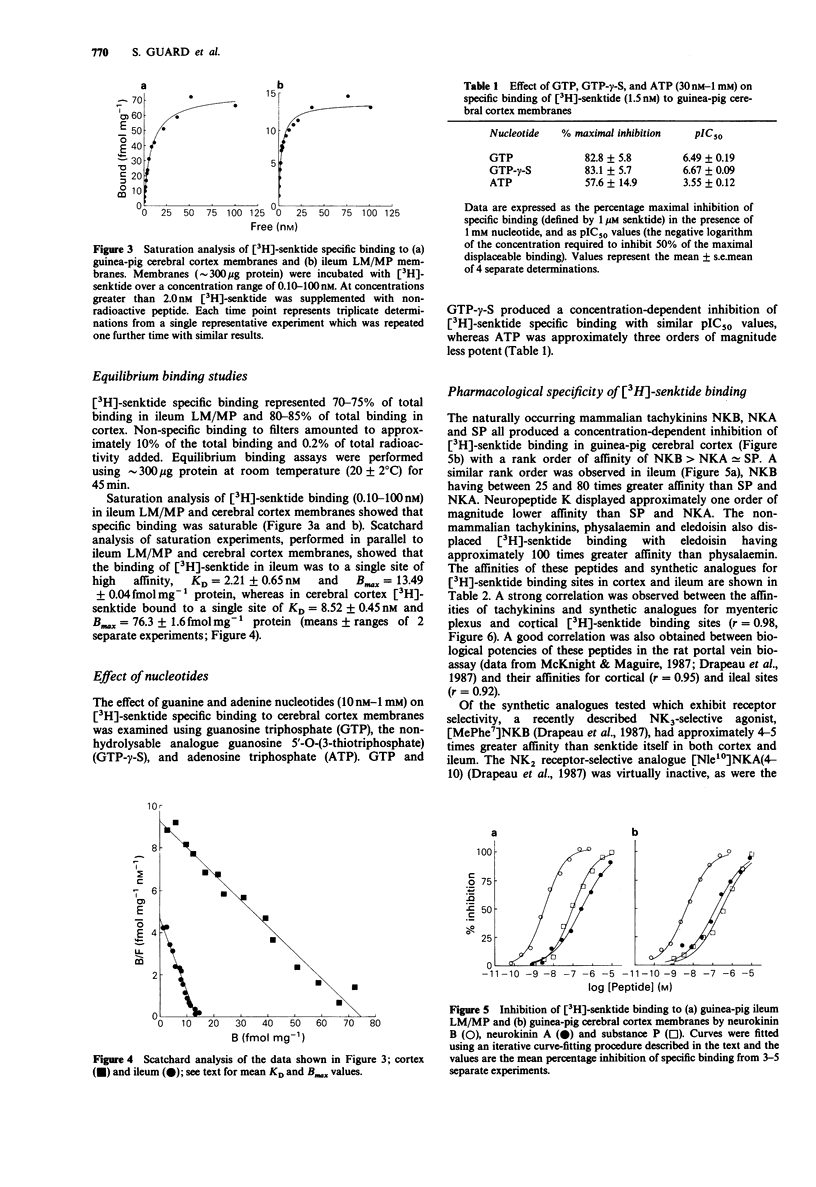
1. The binding properties and pharmacological specificity of the selective NK3 tachykinin receptor agonist [3H))-senktide [( 3H]-succinyl[Asp6,MePhe8] substance P (6-11] have been examined in homogenates of guinea-pig ileum longitudinal muscle-myenteric plexus (LM/MP) and cerebral cortex. 2. Scatchard analysis of saturation binding studies in guinea-pig ileum LM/MP and cerebral cortex membranes indicated that [3H]-senktide bound to a single site with apparent high affinity, KD = 2.21 +/- 0.65 nM; Bmax = 13.49 +/- 0.04 fmol mg-1 protein in ileum and KD = 8.52 +/- 0.45 nM; Bmax = 76.3 +/- 1.6 fmol mg-1 protein in cortex (values are means +/- ranges; n = 2). 3. The pharmacological profile for tachykinins and analogues in displacing [3H]-senktide from ileum membranes was: [MePhe7] neurokinin B greater than neurokinin B (NKB) congruent to senktide greater than eledoisin greater than substance P (SP) greater than neurokinin A(NKA) greater than physalaemin greater than [Sar9,Met(O2)11]SP greater than [Nle10]NKA(4-10) = [Glp6,L-Pro9]-SP(6-11) greater than substance P methyl ester, consistent with [3H]-senktide binding to an NK3 subtype of tachykinin receptor. A similar rank order of affinity was obtained for these peptides in displacing [3H]-senktide from cortex membranes. 4. Several tachykinin receptor agonists were tested for their ability to displace [3H]-senktide from ileal and cortical NK3 binding sites and were found to be either weak displacers (pIC50 less than 5.00) or inactive.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaujouan J. C., Torrens Y., Viger A., Glowinski J. A new type of tachykinin binding site in the rat brain characterized by specific binding of a labeled eledoisin derivative. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;26(2):248–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström L., Torrens Y., Saffroy M., Beaujouan J. C., Lavielle S., Chassaing G., Morgat J. L., Glowinski J., Marquet A. [3H]neurokinin B and 125I-Bolton Hunter eledoisin label identical tachykinin binding sites in the rat brain. J Neurochem. 1987 Jan;48(1):125–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb13136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck S. H., Burcher E., Shults C. W., Lovenberg W., O'Donohue T. L. Novel pharmacology of substance K-binding sites: a third type of tachykinin receptor. Science. 1984 Nov 23;226(4677):987–989. doi: 10.1126/science.6095447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burcher E., Buck S. H., Lovenberg W., O'Donohue T. L. Characterization and autoradiographic localization of multiple tachykinin binding sites in gastrointestinal tract and bladder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Mar;236(3):819–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burcher E., Buck S. H. Multiple tachykinin binding sites in hamster, rat and guinea-pig urinary bladder. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Sep 9;128(3):165–177. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90763-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cascieri M. A., Liang T. Binding of [125I]Bolton Hunter conjugated eledoisin to rat brain cortex membranes--evidence for two classes of tachykinin receptors in the mammalian central nervous system. Life Sci. 1984 Jul 9;35(2):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deacon C. F., Agoston D. V., Nau R., Conlon J. M. Conversion of neuropeptide K to neurokinin A and vesicular colocalization of neurokinin A and substance P in neurons of the guinea pig small intestine. J Neurochem. 1987 Jan;48(1):141–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb13138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G., D'Orléans-Juste P., Dion S., Rhaleb N. E., Rouissi N. E., Regoli D. Selective agonists for substance P and neurokinin receptors. Neuropeptides. 1987 Jul;10(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(87)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone R. L., Fosbraey P., Morton I. K. A comparison of the effects of three substance P antagonists on tachykinin-stimulated [3H]-acetylcholine release in the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;87(1):73–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10158.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Tridgett R. Comparison of the binding of radiolabelled neurokinin A and eledoisin in rat cortex synaptic membranes. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;94(2):602–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11566.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guard S., Watling K. J., Watson S. P. Characterisation of [3H]-senktide binding to NK3 tachykinin receptors in guinea-pig ileum and cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98 (Suppl):798P–798P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guard S., Watling K. J., Watson S. P. Neurokinin3-receptors are linked to inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in the guinea-pig ileum longitudinal muscle-myenteric plexus preparation. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 May;94(1):148–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guard S., Watson S. P. Evidence for neurokinin-3 receptor-mediated tachykinin release in the guinea-pig ileum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Dec 15;144(3):409–412. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90398-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanani M., Chorev M., Gilon C., Selinger Z. The actions of receptor-selective substance P analogs on myenteric neurons: an electrophysiological investigation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug 24;153(2-3):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90612-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto T., Uchida Y., Naminohira S., Sakai T. Tachykinin antagonist I: Specific, competitive and tissue-selective neurokinin B antagonists on contractile activity in smooth muscles. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1987 Dec;45(4):570–573. doi: 10.1254/jjp.45.570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer R., Gilon C., Chorev M., Selinger Z. Characterization of a neurokinin B receptor site in rat brain using a highly selective radioligand. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10257–10263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer R., Wormser U., Friedman Z. Y., Gilon C., Chorev M., Selinger Z. Neurokinin B is a preferred agonist for a neuronal substance P receptor and its action is antagonized by enkephalin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7444–7448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. M., Campbell N. J., Williams B. J., Iversen L. L. Multiple tachykinin binding sites in peripheral tissues and in brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov 4;130(3):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantyh P. W., Gates T., Mantyh C. R., Maggio J. E. Autoradiographic localization and characterization of tachykinin receptor binding sites in the rat brain and peripheral tissues. J Neurosci. 1989 Jan;9(1):258–279. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-01-00258.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantyh P. W., Mantyh C. R., Gates T., Vigna S. R., Maggio J. E. Receptor binding sites for substance P and substance K in the canine gastrointestinal tract and their possible role in inflammatory bowel disease. Neuroscience. 1988 Jun;25(3):817–837. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastrangelo D., Mathison R., Huggel H. J., Dion S., D'Orléans-Juste P., Rhaleb N. E., Drapeau G., Rovero P., Regoli D. The rat isolated portal vein: a preparation sensitive to neurokinins, particularly neurokinin B. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Feb 24;134(3):321–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90363-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Drapeau G., Dion S., D'Orléans-Juste P. Pharmacological receptors for substance P and neurokinins. Life Sci. 1987 Jan 12;40(2):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90349-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoessl A. J., Dourish C. T., Iversen S. D. The NK-3 tachykinin receptor agonist senktide elicits 5-HT-mediated behaviour following central or peripheral administration in mice and rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;94(2):285–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Iversen L. L. 3H-substance P binding to guinea-pig ileum longitudinal smooth muscle membranes. Regul Pept. 1984 Jul;8(4):273–281. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(84)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., Sandberg B. E., Hanley M. R., Iversen L. L. Tissue selectivity of substance P alkyl esters: suggesting multiple receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 28;87(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland G. A., Molinoff P. B. Quantitative analysis of drug-receptor interactions: I. Determination of kinetic and equilibrium properties. Life Sci. 1981 Jul 27;29(4):313–330. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormser U., Laufer R., Hart Y., Chorev M., Gilon C., Selinger Z. Highly selective agonists for substance P receptor subtypes. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2805–2808. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04571.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


