Abstract
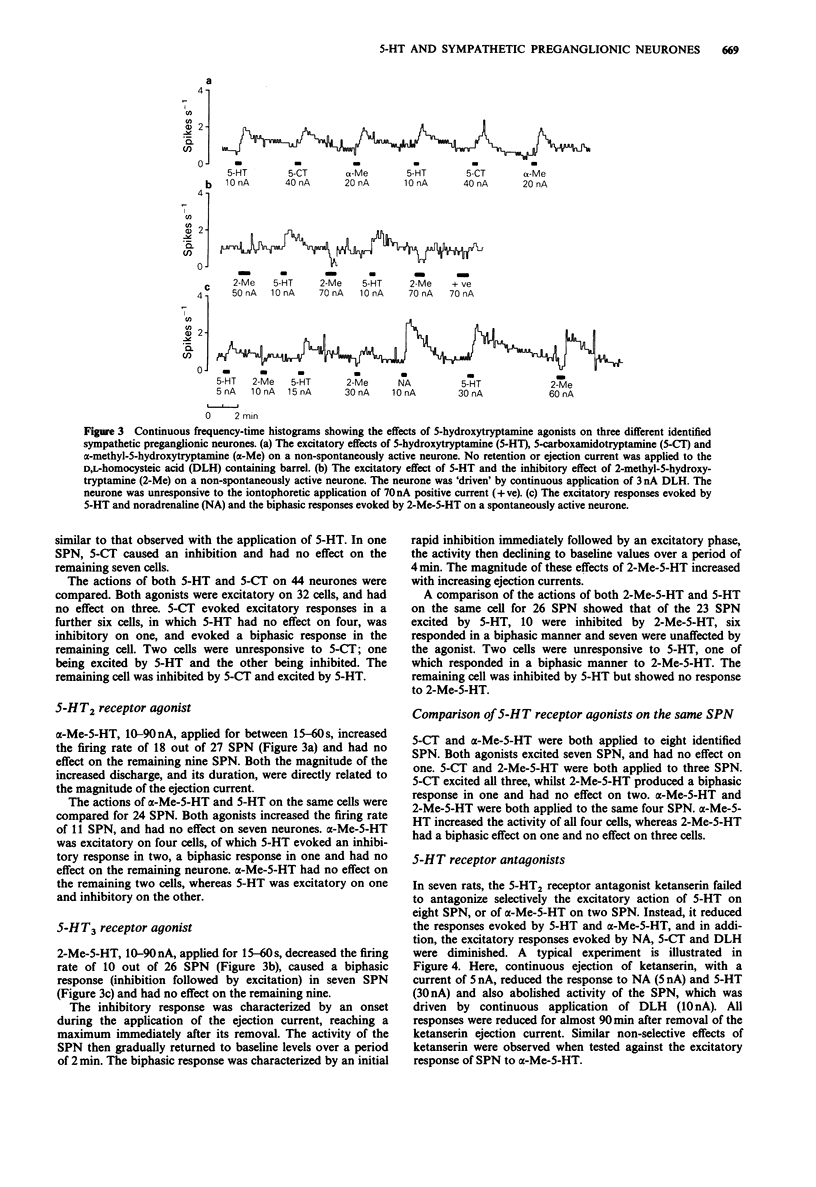
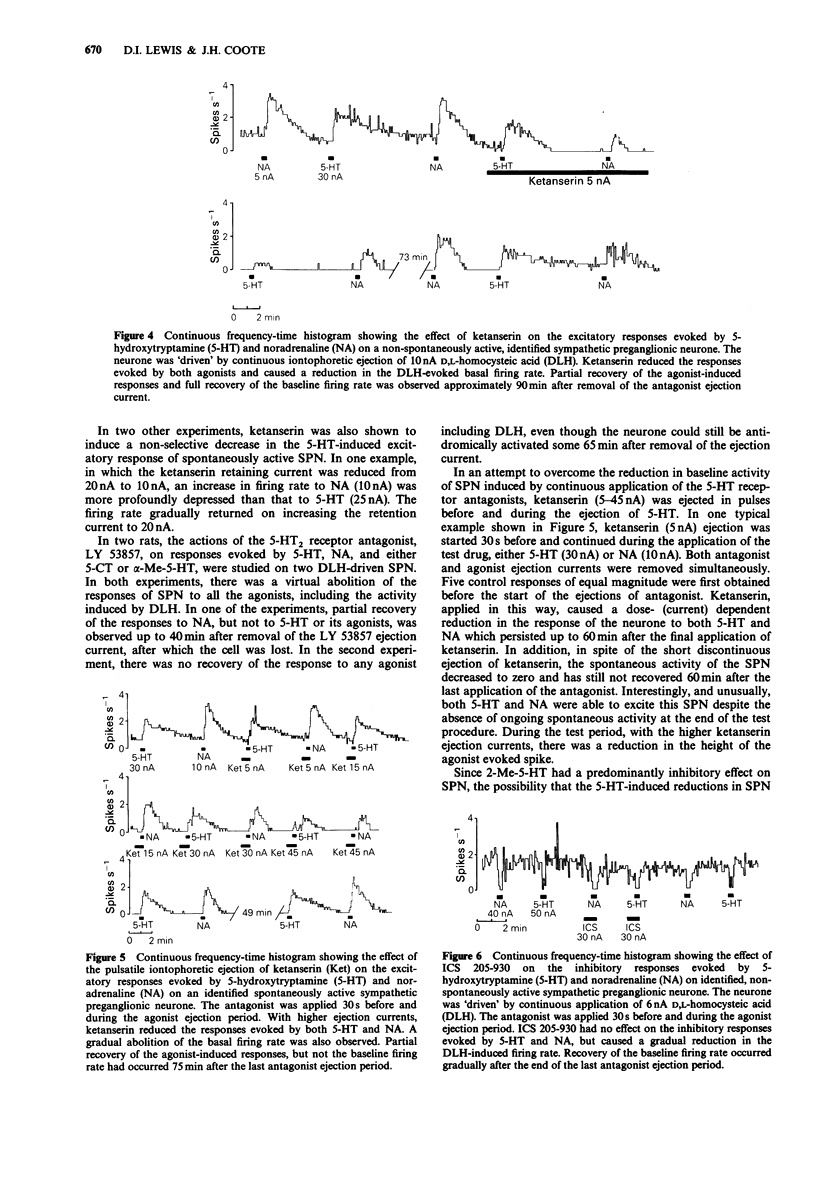
1. 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) was applied by microiontophoresis in the vicinity of identified sympathetic preganglionic neurones in the upper thoracic spinal cord of the rat, in vivo. 2. Sympathetic preganglionic neurones responded in one of three ways to 5-HT: by (a) excitation (76%), (b) inhibition (4%) or (c) in a biphasic manner (5%). 3. The excitatory responses evoked by 5-HT were mimicked by 5-carboxamidotryptamine (5-CT) and alpha-methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine (alpha-Me-5-HT). The inhibitory and biphasic responses evoked by 5-HT were mimicked by 2-methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine (2-Me-5-HT). The observed responses evoked by 5-HT and selective agonists may be different on the same cell. In several instances a single neurone excited by one agonist was inhibited by another agonist. 4. The 5-HT2-receptor antagonists, ketanserin and LY 53857, failed to abolish selectively the excitatory responses evoked by 5-HT and alpha-Me-5-HT, when applied by microiontophoresis. The antagonists non-selectively reduced the excitatory responses evoked by 5-HT, 5-CT, alpha-Me-5-HT, D,L-homocysteic acid (DLH) and noradrenaline (NA). A reduction in synaptically evoked activity was also observed. 5. The 5-HT3-receptor antagonist, ICS 205-930, failed to abolish the inhibitory responses evoked by 5-HT. 6. It was concluded that the excitatory responses evoked by 5-HT are mediated by a receptor that is neither 5-HT2 or 5-HT3, but shows similarities to the 5-HT1-like receptor profile.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacon S. J., Smith A. D. Preganglionic sympathetic neurones innervating the rat adrenal medulla: immunocytochemical evidence of synaptic input from nerve terminals containing substance P, GABA or 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1988 Sep;24(1-2):97–122. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(88)90140-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. B., Engel G., Feniuk W., Fozard J. R., Humphrey P. P., Middlemiss D. N., Mylecharane E. J., Richardson B. P., Saxena P. R. Proposals for the classification and nomenclature of functional receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine. Neuropharmacology. 1986 Jun;25(6):563–576. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(86)90207-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Kurz K. D., Mason N. R., Fuller R. W., Marzoni G. P., Garbrecht W. L. Pharmacological activity of the isomers of LY53857, potent and selective 5-HT2 receptor antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Nov;235(2):319–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell L. A., Wallis D. I. Responses to 5-hydroxytryptamine evoked in the hemisected spinal cord of the neonate rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;94(4):1101–1114. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11628.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. H., Macleod V. H., Fleetwood-Walker S., Gilbey M. P. The response of individual sympathetic preganglionic neurones to microelectrophoretically applied endogenous monoamines. Brain Res. 1981 Jun 29;215(1-2):135–145. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90497-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. H. The organisation of cardiovascular neurons in the spinal cord. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1988;110:147–285. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie M., Wilkinson L. S., Roberts M. H. Evidence for excitatory 5-HT2-receptors on rat brainstem neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;94(2):483–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M., Wilkinson L. S., Roberts M. H. Evidence for depressant 5-HT1-like receptors on rat brainstem neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;94(2):492–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11552.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dun N. J., Mo N. In vitro effects of substance P on neonatal rat sympathetic preganglionic neurones. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:321–333. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dun N. J., Mo N. Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in neonatal rat sympathetic preganglionic neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1989 Mar;410:267–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUXE K. EVIDENCE FOR THE EXISTENCE OF MONOAMINE NEURONS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. IV. DISTRIBUTION OF MONOAMINE NERVE TERMINALS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1965:SUPPL 247–247:37+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbey M. P., Coote J. H., Macleod V. H., Peterson D. F. Inhibition of sympathetic activity by stimulating in the raphe nuclei and the role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in this effect. Brain Res. 1981 Dec 7;226(1-2):131–142. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91088-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbey M. P., Peterson D. F., Coote J. H. Some characteristics of sympathetic preganglionic neurones in the rat. Brain Res. 1982 Jun 3;241(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91226-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey P. P. Peripheral 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors and their classification. Neuropharmacology. 1984 Dec;23(12B):1503–1510. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(84)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadzielawa K. Antagonism of the excitatory effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine on sympathetic preganglionic neurones and neurones activated by visceral afferents. Neuropharmacology. 1983 Jan;22(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(83)90256-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakoski J. M., Aghajanian G. K. Effects of ketanserin on neuronal responses to serotonin in the prefrontal cortex, lateral geniculate and dorsal raphe nucleus. Neuropharmacology. 1985 Apr;24(4):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(85)90130-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leysen J. E., Awouters F., Kennis L., Laduron P. M., Vandenberk J., Janssen P. A. Receptor binding profile of R 41 468, a novel antagonist at 5-HT2 receptors. Life Sci. 1981 Mar 2;28(9):1015–1022. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90747-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewy A. D., McKellar S. Serotonergic projections from the ventral medulla to the intermediolateral cell column in the rat. Brain Res. 1981 Apr 27;211(1):146–152. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall R. B. Effects of putative neurotransmitters on sympathetic preganglionic neurons. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:553–564. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.003005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall R. B. Serotonergic excitation of sympathetic preganglionic neurons: a microiontophoretic study. Brain Res. 1983 Dec 19;289(1-2):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki T., Coote J. H., Dun N. J. Excitatory and inhibitory effects of epinephrine on neonatal rat sympathetic preganglionic neurons in vitro. Brain Res. 1989 Sep 11;497(1):108–116. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90976-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson B. P., Engel G., Donatsch P., Stadler P. A. Identification of serotonin M-receptor subtypes and their specific blockade by a new class of drugs. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):126–131. doi: 10.1038/316126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. H., Davies M., Girdlestone D., Foster G. A. Effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine agonists and antagonists on the responses of rat spinal motoneurones to raphe obscurus stimulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;95(2):437–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11664.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi H., Lewis D. I., Coote J. H. Effects of activating spinal alpha-adrenoreceptors on sympathetic nerve activity in the rat. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1988 Jun;23(1):69–78. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(88)90168-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A., Crist J. Electrophysiological characterization of functionally distinct 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors on guinea-pig submucous plexus. Neuroscience. 1988 Jan;24(1):283–295. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90331-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yusof A. P., Coote J. H. Excitatory and inhibitory actions of intrathecally administered 5-hydroxytryptamine on sympathetic nerve activity in the rat. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1988 Apr;22(3):229–236. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(88)90111-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


