Abstract
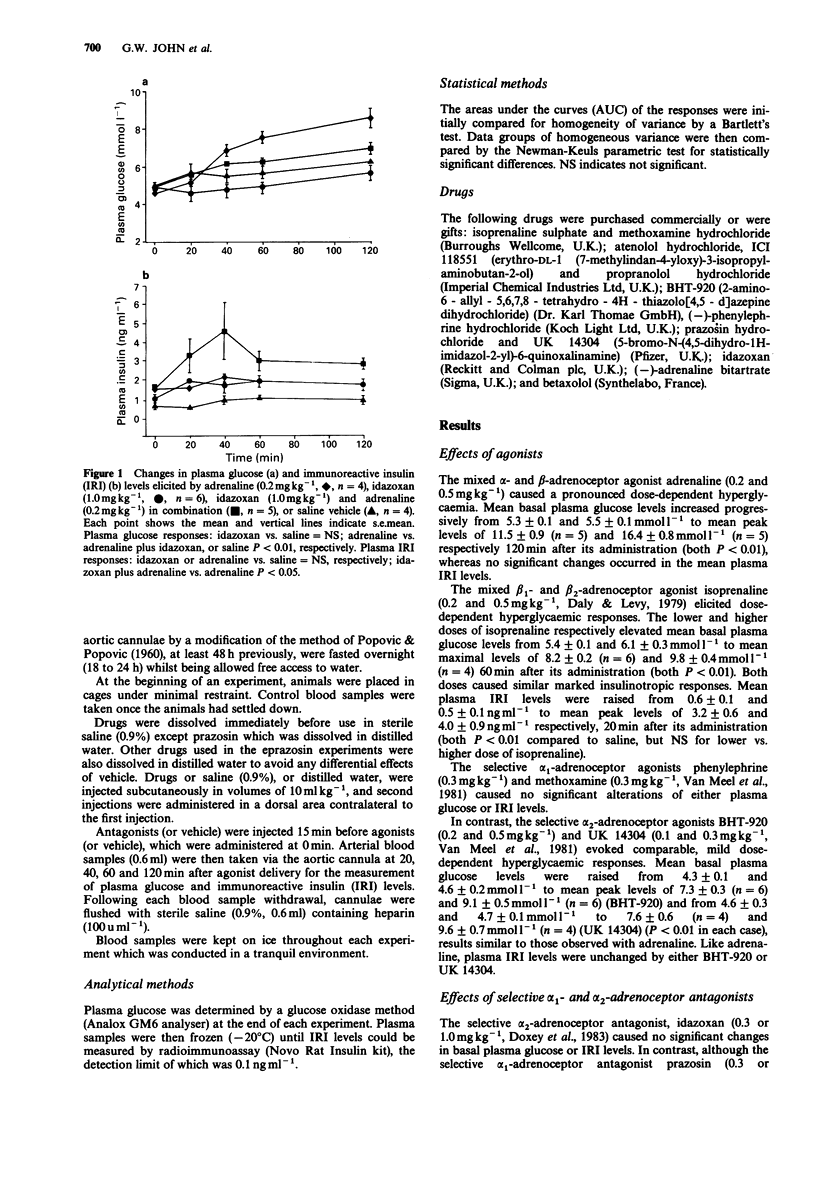
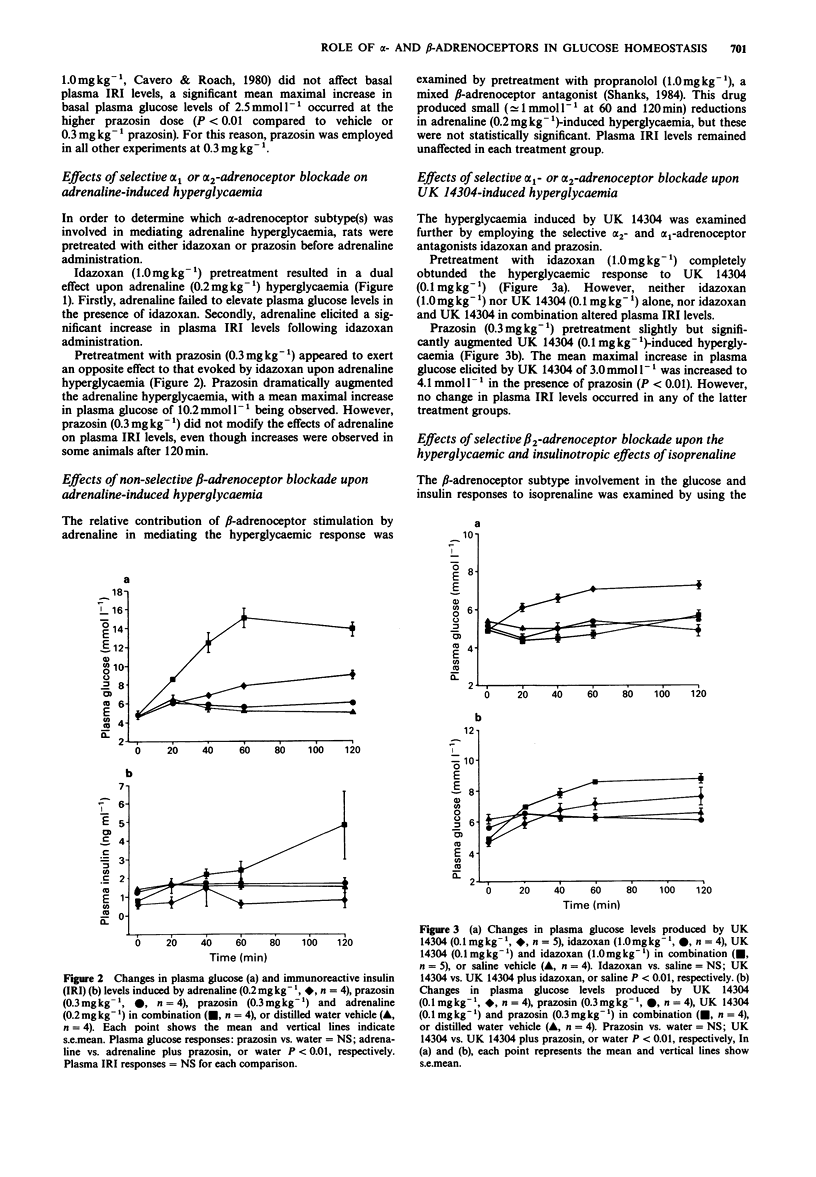
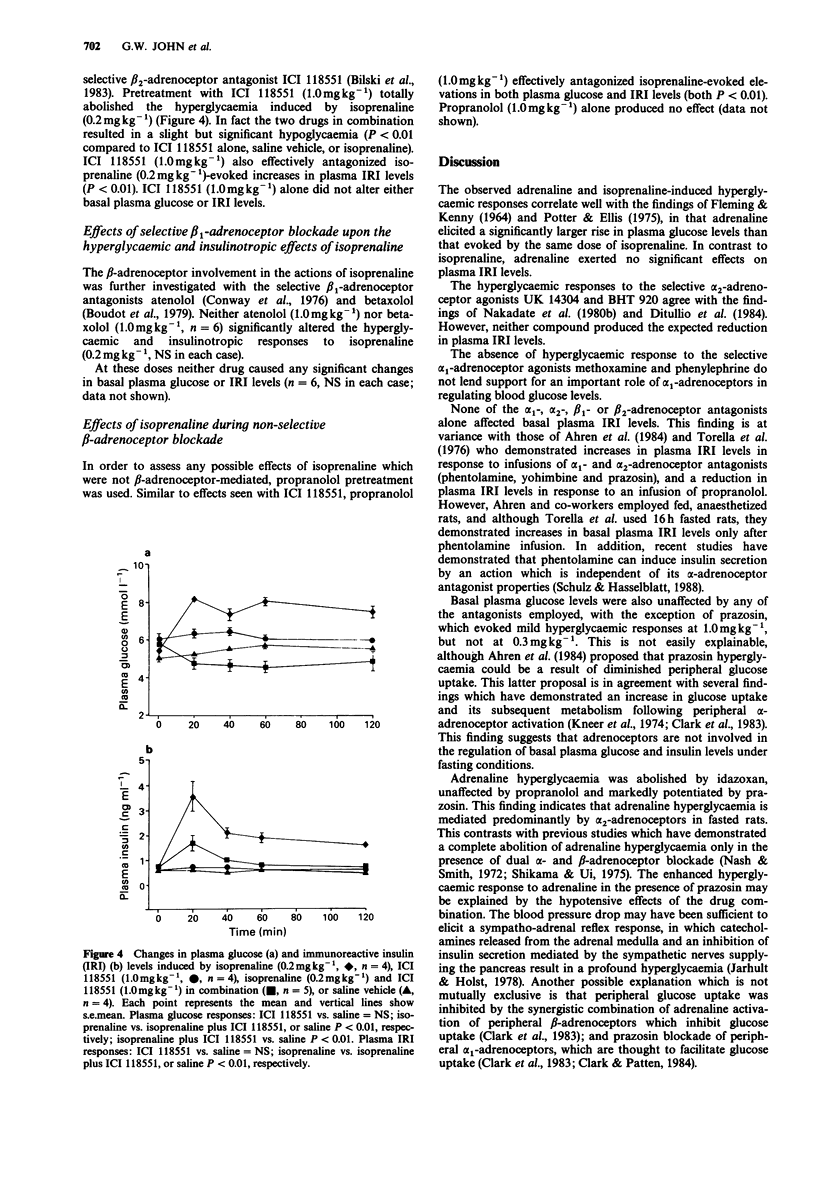
1. The role of alpha- and beta-adrenoceptor subtypes in the regulation of plasma glucose and immunoreactive insulin (IRI) levels has been investigated in normal conscious fasted rats by employing selective agonists and antagonists. 2. Adrenaline (0.2 mg kg-1)-induced hyperglycaemia was abolished by the selective alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonist idazoxan (1.0 mg kg-1), unaltered by non-selective beta-adrenoceptor blockade (propranolol, 1.0 mg kg-1) and potentiated by the selective alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist prazosin (0.3 mg kg-1). Adrenaline increased plasma IRI levels in the presence of idazoxan but not in the presence of either prazosin or propranolol. 3. The selective alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists UK 14304 (0.1 and 0.3 mg kg-1) and BHT-920 (0.2 and 0.5 mg kg-1) elicited dose-dependent hyperglycaemic responses, but did not alter plasma IRI levels. UK 14304 (0.1 mg kg-1)-evoked hyperglycaemia was blocked by idazoxan but not by prazosin. 4. The selective alpha 1-adrenoceptor agonists methoxamine (0.3 mg kg-1) and phenylephrine (0.3 mg kg-1) failed to modify either plasma glucose or IRI levels. 5. Isoprenaline (0.2 mg kg-1) elicited hyperglycaemic and insulinotropic responses which were attenuated by propranolol (1.0 mg kg-1) and the selective beta 2-adrenoceptor antagonist ICI 118551 (1.0 mg kg-1), but not by the beta 1-selective antagonists atenolol (1.0 mg kg-1) and betaxolol (1.0 mg kg-1). 6. None of the antagonists per se affected basal plasma glucose or IRI concentrations, except prazosin (1.0 mg kg-1).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahrén B., Lundquist I., Järhult J. Effects of alpha 1-, alpha 2- and beta-adrenoceptor blockers on insulin secretion in the rat. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1984 Jan;105(1):78–82. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1050078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilski A. J., Halliday S. E., Fitzgerald J. D., Wale J. L. The pharmacology of a beta 2-selective adrenoceptor antagonist (ICI 118,551). J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1983 May-Jun;5(3):430–437. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198305000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock J. U., van Zwieten P. A. The central hyperglycaemic effect of clonidine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1971 Nov-Dec;16(3):303–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(71)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boudot J. P., Cavero I., Fénard S., Lefèvre-Borg F., Manoury P., Roach A. G. Preliminary studies on SL 75212, a new potent cardioselective beta-adrenoceptor antagonist [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;66(3):445P–445P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavero I., Roach A. G. The pharmacology of prazosin, a novel antihypertensive agent. Life Sci. 1980 Oct 27;27(17):1525–1540. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90561-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. G., Patten G. S. Adrenergic control of phosphofructokinase and glycolysis in rat heart. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1984;23:127–176. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152823-2.50008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. G., Patten G. S., Filsell O. H., Rattigan S. Co-ordinated regulation of muscle glycolysis and hepatic glucose output in exercise by catecholamines acting via alpha-receptors. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jul 11;158(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80664-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway F. J., Fitzgerald J. D., McAinsh J., Rowlands D. J., Simpson W. T. Human pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies on the atenolo (ICI 66,082), a new cardioselective beta-adrenoceptor blocking drug. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Apr;3(2):267–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1976.tb00602.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coore H. G., Randle P. J. Regulation of insulin secretion studied with pieces of rabbit pancreas incubated in vitro. Biochem J. 1964 Oct;93(1):66–78. doi: 10.1042/bj0930066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiTullio N. W., Cieslinski L., Matthews W. D., Storer B. Mechanisms involved in the hyperglycemic response induced by clonidine and other alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Jan;228(1):168–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Roach A. G., Smith C. F. Studies on RX 781094: a selective, potent and specific antagonist of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;78(3):489–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb08809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEMING W. W., KENNY A. D. THE EFFECT OF FASTING ON THE HYPERGLYCAEMIC RESPONSES TO CATECHOL AMINES IN RATS. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Apr;22:267–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb02032.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman B. L., Tayo F. M. Effect of ICI 66082, a beta-adrenoceptor blocking drug on blood glucose in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1975 Mar;31(1):115–121. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(75)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms H. H., Gooren L., Spoelstra A. J., Hesse C., Verschoor L. Blockade of isoprenaline-induced changes in plasma free fatty acids, immunoreactive insulin levels and plasma renin activity in healthy human subjects, by propranolol, pindolol, practolol, atenolol, metoprolol and acebutolol. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Jan;5(1):19–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb01593.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. B., De Lean A., Wood C. L., Schocken D. D., Lefkowitz R. J. Alpha-adrenergic receptor subtypes: quantitative assessment by ligand binding. Life Sci. 1979 May 7;24(19):1739–1745. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90061-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail N. A., El-Denshary E. S., Idahl L. A., Lindström P., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Effects of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists on insulin secretion, calcium uptake, and rubidium efflux in mouse pancreatic islets. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Jun;118(2):167–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07257.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Järhult J., Holst J. J. Reflex adrenergic control of endocrine pancreas evoked by unloading of carotid baroreceptors in cats. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 Oct;104(2):188–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneto A., Miki E., Kosaka K. Effect of beta and beta2 adrenoreceptor stimulants infused intrapancreatically on glucagon and insulin secretion. Endocrinology. 1975 Nov;97(5):1166–1173. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-5-1166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo S. H., Kamaka J. K., Lum B. K. Adrenergic receptor mechanisms involved in the hyperglycemia and hyperlactic-acidemia produced by sympathomimetic amines in the cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Aug;202(2):301–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer J., Panten U., Zielmann S. Effects of alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists on clonidine-induced inhibition of insulin secretion by isolated pancreatic islets. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):415–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11014.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loubatières A., Mariani M. M., Sorel G., Savi L. The action of beta-adrenergic blocking and stimulating agents on insulin secretion. Characterization of the type of beta receptor. Diabetologia. 1971 Jun;7(3):127–132. doi: 10.1007/BF01212541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist I., Ericson L. E. beta-Adrenergic insulin release and adrenergic innervation of mouse pancreatic islets. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Oct 6;193(1):73–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00221602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakadate T., Nakaki T., Muraki T., Kato R. Adrenergic regulation of blood glucose levels: possible involvement of postsynaptic alpha-2 type adrenergic receptors regulating insulin release. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Oct;215(1):226–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakadate T., Nakaki T., Muraki T., Kato R. Regulation of plasma insulin level by alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Aug 8;65(4):421–424. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90347-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaki T., Nakadate T., Kato R. Alpha 2-adrenoceptors modulating insulin release from isolated pancreatic islets. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Aug;313(2):151–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00498572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash C. B., Smith R. D. Blood sugar responses to epinephrine in the dog in the presence of dual adrenergic blockade. Eur J Pharmacol. 1972 Jan;17(1):34–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(72)90265-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPOVIC V., POPOVIC P. Permanent cannulation of aorta and vena cava in rats and ground squirrels. J Appl Physiol. 1960 Jul;15:727–728. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.4.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr A receptor mechanism for the inhibition of insulin release by epinephrine in man. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jan;46(1):86–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI105514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr Beta adrenergic stimulation of insulin release in man. Diabetes. 1967 Mar;16(3):150–155. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.3.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter D. E., Ellis S. Isoproterenol- and epinephrine-induced changes in blood glucose and tissue glycogen levels in normal and diabetic rats: the influence of alteration in endogenous insulin levels and state of nourishment. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 May;193(2):576–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz A., Hasselblatt A. Phentolamine, a deceptive tool to investigate sympathetic nervous control of insulin release. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;337(6):637–643. doi: 10.1007/BF00175789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skikama H., Ui M. Adrenergic receptor and epinephrine-induced hyperglycemia and glucose tolerance. Am J Physiol. 1975 Oct;229(4):962–966. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.4.962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe G. A., Bradshaw J. E., Gleeson R. M., Grunstein H. S., Nicholson M. V. The central vs. peripheral effects of clonidine on ACTH, corticosterone and glucose release. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 May 20;111(3):401–403. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90651-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struthers A. D., Brown D. C., Brown M. J., Schumer B., Bloom S. R. Selective alpha 2 receptor blockade facilitates the insulin response to adrenaline but not to glucose in man. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1985 Nov;23(5):539–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1985.tb01114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torella R., Giugliano D., Improta L., Giordano C., Grazioli A., D'onofrio F. Adrenergic control of basal insulin and glucose in the rat. Farmaco Prat. 1977 May;32(5):238–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meel J. C., de Jonge A., Timmermans P. B., van Zwieten P. A. Selectivity of some alpha adrenoceptor agonists for peripheral alpha-1 and alpha-2 adrenoceptors in the normotensive rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Dec;219(3):760–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


