Abstract
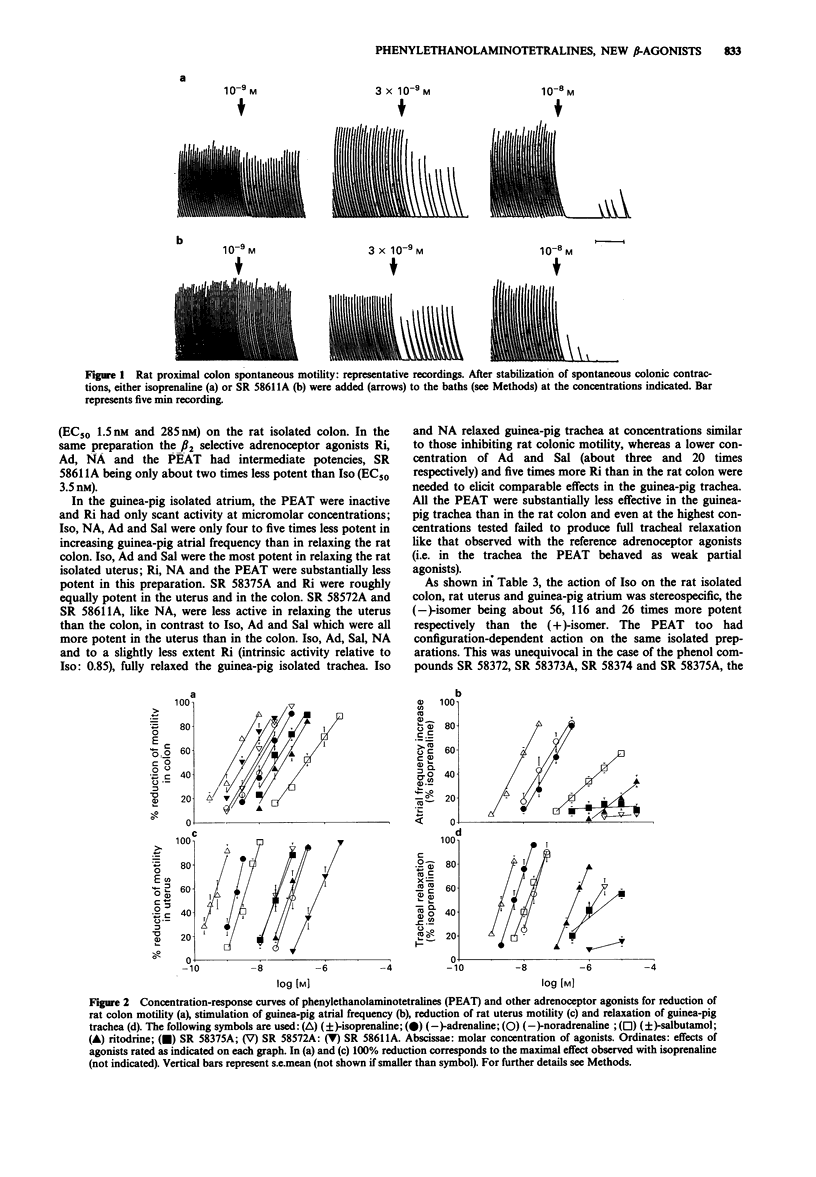
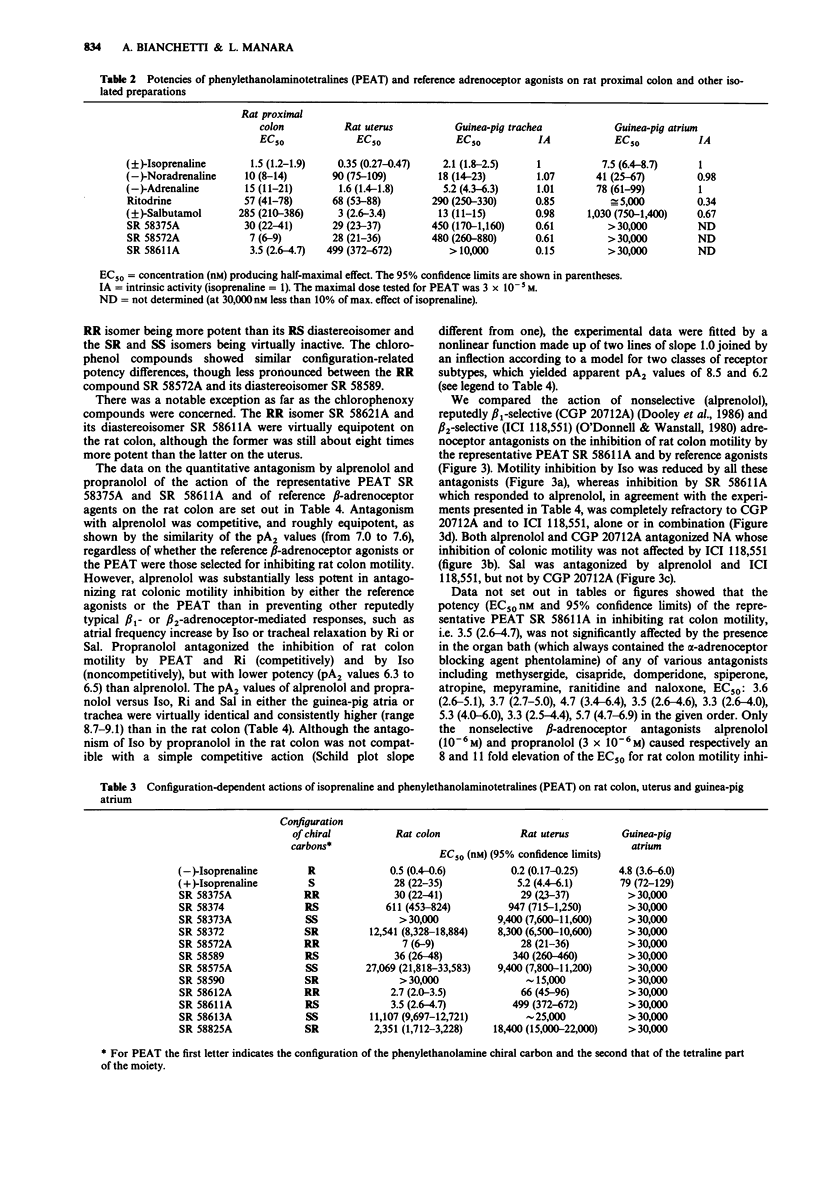
1. The new compounds phenylethanolaminotetralines (PEAT), unlike the reference beta-adrenoceptor agonists isoprenaline (Iso), ritodrine (Ri) and salbutamol (Sal), produced half-maximal inhibition of spontaneous motility of rat isolated proximal colon at substantially lower concentrations (EC50 2.7-30 nM) than those inducing beta 2-adrenoceptor-mediated responses (relaxation of guinea-pig isolated trachea and rat uterus) and had virtually no chronotropic action (EC50 greater than 3 x 10(5) M) on the guinea-pig isolated atrium (a beta 1-adrenoceptor-mediated response). 2. The nonselective beta-adrenoceptor antagonists alprenolol and propranolol prevented the inhibition of rat colon motility by the PEAT with low and different potencies (pA2 values around 7.5 and 6.5 respectively). Conversely alprenolol and propranolol had a higher and similar potency (pA2 values around 9.0) in preventing typical beta 1 or beta 2-responses (increase in atrial frequency by Iso or tracheal relaxation by Ri or Sal). 3. The selective beta-adrenoceptor antagonists CGP 20712A (beta 1) and ICI 118,551 (beta 2) either alone or in combination, did not prevent rat colon motility inhibition by the representative PEAT SR 58611A, which was also fully resistant to alpha-adrenoceptor, acetylcholine, dopamine, histamine, opioid and 5-hydroxytryptamine antagonists. 4. These results indicate that the PEAT are a new class of beta-adrenoceptor agonists and suggest that their preferential intestinal action may be accounted for by selectivity for atypical beta-adrenoceptors, abundant in the rat colon and distinct from the currently recognized beta 1 and beta 2 subtypes.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arch J. R., Ainsworth A. T., Cawthorne M. A., Piercy V., Sennitt M. V., Thody V. E., Wilson C., Wilson S. Atypical beta-adrenoceptor on brown adipocytes as target for anti-obesity drugs. Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):163–165. doi: 10.1038/309163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahouth S. W., Malbon C. C. Subclassification of beta-adrenergic receptors of rat fat cells: a re-evaluation. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;34(3):318–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley G. A., Starr J. The antinociceptive action of some beta-adrenoceptor agonists in mice. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jul;88(3):515–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10231.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond R. A., Charlton K. G., Clarke D. E. Responses to norepinephrine resistant to inhibition by alpha and beta adrenoceptor antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Feb;236(2):408–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond R. A., Clarke D. E. Agonist and antagonist characterization of a putative adrenoceptor with distinct pharmacological properties from the alpha- and beta-subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):723–734. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11698.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristow M., Sherrod T. R., Green R. D. Analysis of beta receptor drug interactions in isolated rabbit atrium, aorta, stomach and trachea. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 Jan;171(1):52–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckner C. K., Christopherson R. C. Adrenergic receptors of rat esophageal smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 May;189(2):467–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. Catecholamine action on smooth muscle. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Mar;39(1):49–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croci T., Cecchi R., Tarantino A., Aureggi G., Bianchetti A., Boigegrain R., Manara L. Inhibition of rat colon motility by stimulation of atypical beta-adrenoceptors with new gut-specific agents. Pharmacol Res Commun. 1988 Feb;20(2):147–151. doi: 10.1016/s0031-6989(88)80007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley D. J., Bittiger H., Reymann N. C. CGP 20712 A: a useful tool for quantitating beta 1- and beta 2-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct 14;130(1-2):137–139. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek B. A., Bjellin L. A., Lundgren B. T. Beta-adrenergic control of motility in the rat colon. I. Evidence for functional separation of the beta 1- and beta 2-adrenoceptor-mediated inhibition of colon activity. Gastroenterology. 1986 Feb;90(2):400–407. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90939-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek B. A., Nahorski S. R. Beta-adrenergic control of motility in the rat colon. II. Proportions of beta 1- and beta 2-adrenoceptors identified with 125I-(-)pindolol binding. Gastroenterology. 1986 Feb;90(2):408–413. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90940-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek B. Studies on mechanisms for beta-adrenoceptor mediated inhibition of colon motility. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1985;546:1–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emorine L. J., Marullo S., Briend-Sutren M. M., Patey G., Tate K., Delavier-Klutchko C., Strosberg A. D. Molecular characterization of the human beta 3-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1118–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.2570461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frielle T., Kobilka B., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Human beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors: structurally and functionally related receptors derived from distinct genes. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Jul;11(7):321–324. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90095-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Costa M. The adrenergic innervation of the gastrointestinal tract. Ergeb Physiol. 1974;69(0):2–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giudice A., Croci T., Bianchetti A., Manara L. Inhibition of rat colonic motility and cardiovascular effects of new gut-specific beta-adrenergic phenylethanolaminotetralines. Life Sci. 1989;44(19):1411–1417. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90399-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grivegnée A. R., Fontaine J., Reuse J. Effect of dopamine on dog distal colon in-vitro. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;36(7):454–457. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1984.tb04424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms H. H., Zaagsma J., de Vente J. Differentiation of beta-adrenoceptors in right atrium, diaphragm and adipose tissue of the rat, using stereoisomers of propranolol, alprenolol, nifenalol and practolol. Life Sci. 1977 Jul 1;21(1):123–128. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90432-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaumann A. J., Lobnig B. M. Mode of action of (-)-pindolol on feline and human myocardium. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Sep;89(1):207–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb11137.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenakin T. P. The classification of drugs and drug receptors in isolated tissues. Pharmacol Rev. 1984 Sep;36(3):165–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenakin T. P. Theoretical and practical problems with the assessment of intrinsic efficacy of agonists: efficacy of reputed beta-1 selective adrenoceptor agonists for beta-2 adrenoceptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Nov;223(2):416–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korth M. Effects of several phosphodiesterase-inhibitors on guinea-pig myocardium. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1978 Mar;302(1):77–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00586601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY B., TOZZI S. THE ADRENERGIC RECEPTIVE MECHANISM OF THE RAT UTERUS. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Nov;142:178–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lands A. M., Arnold A., McAuliff J. P., Luduena F. P., Brown T. G., Jr Differentiation of receptor systems activated by sympathomimetic amines. Nature. 1967 May 6;214(5088):597–598. doi: 10.1038/214597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemoine H., Kaumann A. J. A model for the interaction of competitive antagonists with two receptor-subtypes characterized by a Schild-plot with apparent slope unity. Agonist-dependent enantiomeric affinity ratios for bupranolol in tracheae but not in right atria of guinea pigs. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;322(2):111–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00512383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libert F., Parmentier M., Lefort A., Dinsart C., Van Sande J., Maenhaut C., Simons M. J., Dumont J. E., Vassart G. Selective amplification and cloning of four new members of the G protein-coupled receptor family. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):569–572. doi: 10.1126/science.2541503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyrenäs E., Abrahamsson H. Beta adrenergic influence on oesophageal peristalsis in man. Gut. 1986 Mar;27(3):260–266. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.3.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyrenäs E., Abrahamsson H., Dotevall G. Rectosigmoid motility response to beta-adrenoceptor stimulation in patients with the irritable bowel syndrome. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1985 Dec;20(10):1163–1168. doi: 10.3109/00365528509089270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay D. How should values of pA2 and affinity constants for pharmacological competitive antagonists be estimated? J Pharm Pharmacol. 1978 May;30(5):312–313. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1978.tb13237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neely J., Catchpole B. Ileus: the restoration of alimentary-tract motility by pharmacological means. Br J Surg. 1971 Jan;58(1):21–28. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800580104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell S. R., Wanstall J. C. Evidence that ICI 118, 551 is a potent, highly Beta 2-selective adrenoceptor antagonist and can be used to characterize Beta-adrenoceptor populations in tissues. Life Sci. 1980 Aug 25;27(8):671–677. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell S. R., Wanstall J. C. Potency and selectivity in vitro of compounds related to isoprenaline and orciprenaline on beta-adrenoceptors in the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Nov;52(3):407–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb08610.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell S. R., Wanstall J. C. The importance of choice of agonist in studies designed to predict beta 2 : beta 1 adrenoceptor selectivity of antagonists from pA2 values on guinea-pig trachea and atria. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Sep;308(3):183–190. doi: 10.1007/BF00501381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omini C., Folco G., Sautebin L., Nava G., Mandelli V., Berti F. beta-Adrenoceptor activation induces prostaglandin E2 generation in guinea-pig trachea. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jun 19;72(2-3):227–231. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90277-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri G., Szenohradszky J., Porszasz-Gibiszer K. Sympatholytic treatment of "paralytic" ileus. Surgery. 1971 Sep;70(3):359–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raper C. Adrenoceptor classification. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1987 May;14(5):401–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1987.tb00990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. Localization of adrenergic receptors in guinea pig ileum and rabbit jejunum to cholinergic neurons and to smooth muscle cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1977 Feb;99(2):190–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1977.tb10370.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Wilson S., Piercy V., Sennitt M. V., Arch J. R. The rat lipolytic beta-adrenoceptor: studies using novel beta-adrenoceptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 May 4;100(3-4):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaagsma J., Nahorski S. R. Is the adipocyte beta-adrenoceptor a prototype for the recently cloned atypical 'beta 3-adrenoceptor'? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jan;11(1):3–7. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90032-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


