Abstract
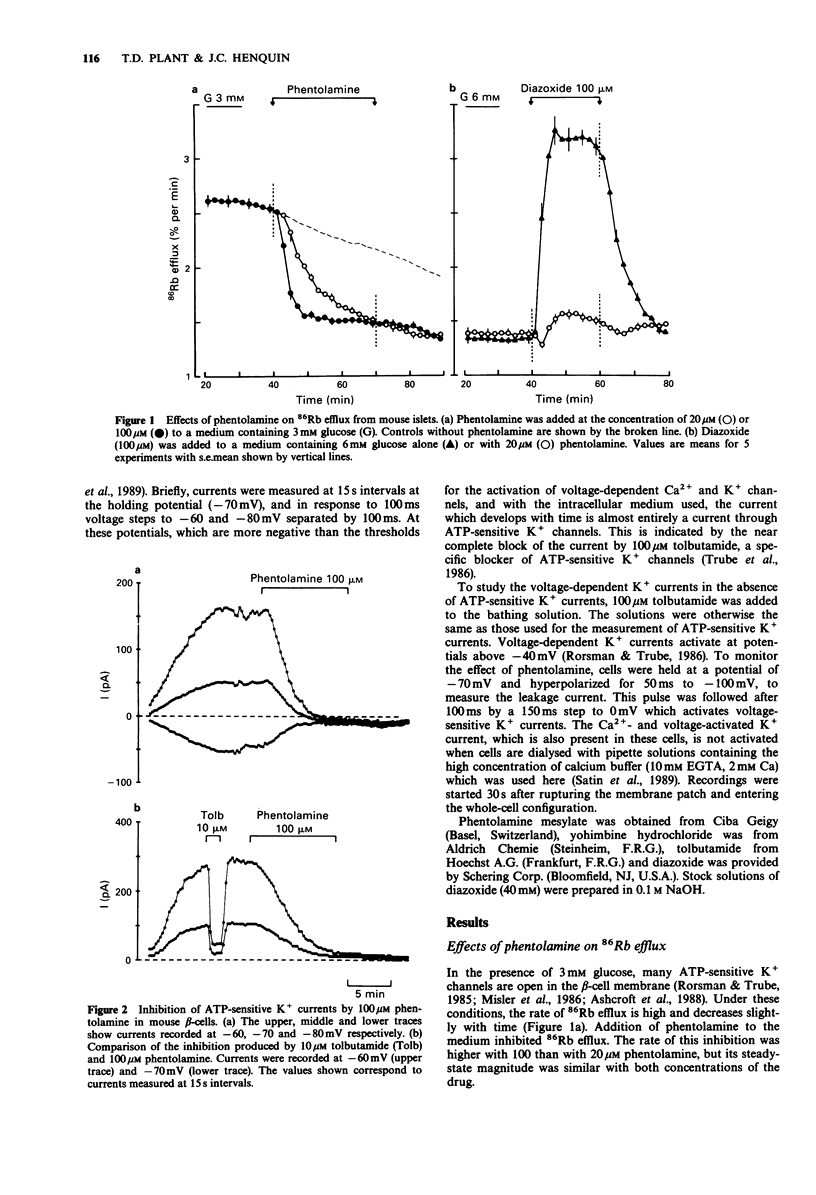
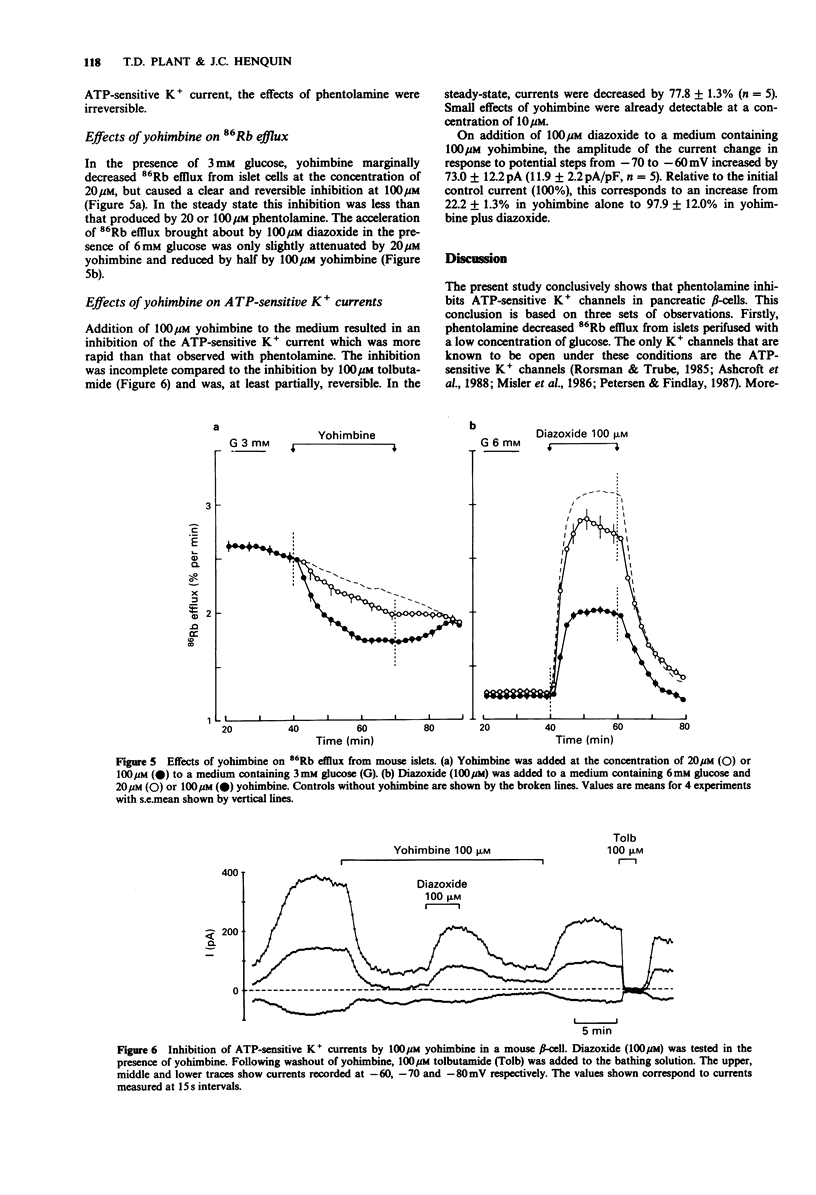
1. The effects of phentolamine and yohimbine on adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP)-sensitive K+ channels were studied in normal mouse beta-cells. 2. In the presence of 3 mM glucose, many ATP-sensitive K+ channels are open in the beta-cell membrane. Under these conditions, phentolamine inhibited 86Rb efflux from the islets. This inhibition was faster with 100 than with 20 microM phentolamine but its steady-state magnitude was similar with both concentrations. Yohimbine (20-100 microM) also inhibited the efflux rate but was not as potent as phentolamine. 3. In the presence of 6 mM glucose, most ATP-sensitive K+ channels are closed in the beta-cell membrane. Their opening by 100 microM diazoxide caused a marked acceleration of 86Rb efflux from the islets. This acceleration was almost entirely prevented by 20 microM phentolamine. It was barely affected by 20 microM yohimbine and reduced by 50% by 100 microM yohimbine. 4. ATP-sensitive K+ currents were studied in single beta-cells by the whole cell patch-clamp technique. Phentolamine (20-100 microM) caused a progressive but almost complete and irreversible inhibition of the current. The effects of yohimbine were faster but smaller; the inhibition was still incomplete with 100 microM yohimbine. 5. The increase in ATP-sensitive K+ current produced by 100 microM diazoxide was prevented by 100 microM phentolamine but only partially attenuated by 100 microM yohimbine. 6. It is concluded that phentolamine inhibits ATP-sensitive K+ channels in pancreatic beta-cells. This novel effect of phentolamine resembles that of hypoglycaemic sulphonylureas. It may account for previously unexplained effects of the drug.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF
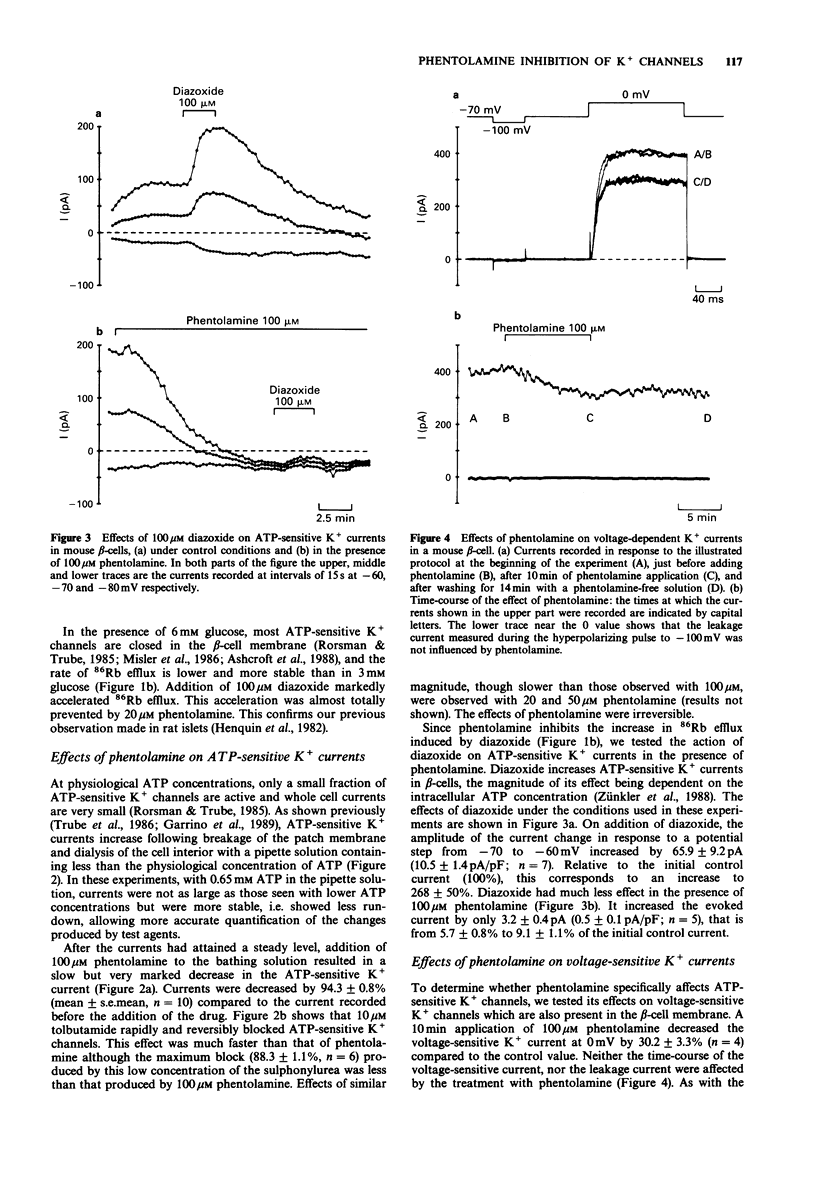


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft F. M., Ashcroft S. J., Harrison D. E. Properties of single potassium channels modulated by glucose in rat pancreatic beta-cells. J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:501–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackard W. G., Aprill C. N., 3rd Mechanisms of action of diazoxide. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Jun;69(6):960–967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr I. M., Marliss E. B., Stauffacher W., Renold A. E. Diazoxide effects on biphasic insulin release: "adrenergic" suppression and enhancement in the perifused rat pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1444–1450. doi: 10.1172/JCI106628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buse M. G., Johnson A. H., Kuperminc D., Buse J. Effect of alpha-adrenergic blockade on insulin secretion in man. Metabolism. 1970 Mar;19(3):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(70)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Effendic S., Luft R. Role of adrenergic receptors in glucose-induced insulin secretion in man. Lancet. 1969 Aug 9;2(7615):301–302. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Illot M. C., Peterson O. H. Interaction of diazoxide, tolbutamide and ATP4- on nucleotide-dependent K+ channels in an insulin-secreting cell line. J Membr Biol. 1987;99(3):215–224. doi: 10.1007/BF01995702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efendić S., Cerasi E., Luft R. Effect of phentolamine and preperfusion with glucose on insulin release from the isolated perfused pancreas from fasted and fed rats. Diabetologia. 1975 Oct;11(5):407–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00429908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrino M. G., Henquin J. C. B cell adrenoceptors and sulphonylurea-induced insulin release in mouse islets. Diabetologia. 1990 Mar;33(3):145–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00404040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrino M. G., Henquin J. C. Highly potent and stereoselective effects of the benzoic acid derivative AZ-DF 265 on pancreatic beta-cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jan;93(1):61–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11405.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrino M. G., Plant T. D., Henquin J. C. Effects of putative activators of K+ channels in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):957–965. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14626.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Charles S., Nenquin M., Mathot F., Tamagawa T. Diazoxide and D600 inhibition of insulin release. Distinct mechanisms explain the specificity for different stimuli. Diabetes. 1982 Sep;31(9):776–783. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.9.776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. D-glucose inhibits potassium efflux from pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1978 Jan 19;271(5642):271–273. doi: 10.1038/271271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Meissner H. P. Opposite effects of tolbutamide and diazoxide on 86Rb+ fluxes and membrane potential in pancreatic B cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Apr 1;31(7):1407–1415. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillaire-Buys D., Gross R., Blayac J. P., Ribes G., Loubatières-Mariani M. M. Effects of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists on insulin secreting cells and pancreatic blood vessels: comparative study. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov 5;117(2):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90610-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist I. Interaction of amines and aminergic blocking agents with blood glucose regulation. II. Alpha-adrenergic blockade. Eur J Pharmacol. 1972 May;18(2):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(72)90246-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Angus J. A. Phentolamine and structurally related compounds selectively antagonize the vascular actions of the K+ channel opener, cromromakalim. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;97(3):941–949. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12035.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Insel P. A. Are there multiple imidazoline binding sites? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Sep;10(9):342–344. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misbin R. I., Edgar P. J., Lockwood D. H. Adrenergic regulation of insulin secretion during fasting in normal subjects. Diabetes. 1970 Oct;19(10):688–693. doi: 10.2337/diab.19.10.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misler S., Falke L. C., Gillis K., McDaniel M. L. A metabolite-regulated potassium channel in rat pancreatic B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7119–7123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. A., Boyle J. P., Small R. C. Cromakalim-induced relaxation of guinea-pig isolated trachealis: antagonism by glibenclamide and by phentolamine. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):865–874. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaki T., Nakadate T., Kato R. Alpha 2-adrenoceptors modulating insulin release from isolated pancreatic islets. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Aug;313(2):151–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00498572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostenson C. G., Pigon J., Doxey J. C., Efendic S. Alpha 2-adrenoceptor blockade does not enhance glucose-induced insulin release in normal subjects or patients with noninsulin-dependent diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Nov;67(5):1054–1059. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-5-1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Findlay I. Electrophysiology of the pancreas. Physiol Rev. 1987 Jul;67(3):1054–1116. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.3.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant T. D. Properties and calcium-dependent inactivation of calcium currents in cultured mouse pancreatic B-cells. J Physiol. 1988 Oct;404:731–747. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter J., Andrews S., Blackard W. Biphasic effect of phentolamine on glucose-induced insulin release by pancreatic islets: possible mechanism of action at high concentrations (10(-3) M). Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1978 Dec;22(3):523–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P., Halter J. B., Porte D., Jr A role for alpha-adrenergic receptors in abnormal insulin secretion in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):791–795. doi: 10.1172/JCI108338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P., Porte D., Jr Adrenergic modulation of basal insulin secretion in man. Diabetes. 1973 Jan;22(1):1–8. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Trube G. Calcium and delayed potassium currents in mouse pancreatic beta-cells under voltage-clamp conditions. J Physiol. 1986 May;374:531–550. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Trube G. Glucose dependent K+-channels in pancreatic beta-cells are regulated by intracellular ATP. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Dec;405(4):305–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00595682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satin L. S., Hopkins W. F., Fatherazi S., Cook D. L. Expression of a rapid, low-voltage threshold K current in insulin-secreting cells is dependent on intracellular calcium buffering. J Membr Biol. 1989 Dec;112(3):213–222. doi: 10.1007/BF01870952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz A., Hasselblatt A. An insulin-releasing property of imidazoline derivatives is not limited to compounds that block alpha-adrenoceptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;340(3):321–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00168517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz A., Hasselblatt A. Phentolamine, a deceptive tool to investigate sympathetic nervous control of insulin release. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;337(6):637–643. doi: 10.1007/BF00175789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M., Furman B. L. Augmentation of glucose induced insulin secretion by pertussis vaccine, phentolamine and benextramine: involvement of mechanisms additional to prevention of the inhibitory actions of catecholamines in rats. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1988 May;118(1):89–95. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1180089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Quayle J. M., Davies N. W., Brayden J. E., Huang Y., Nelson M. T. Hyperpolarizing vasodilators activate ATP-sensitive K+ channels in arterial smooth muscle. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):177–180. doi: 10.1126/science.2501869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess N. C., Kozlowski R. Z., Carrington C. A., Hales C. N., Ashford M. L. Effects of sulphonylureas and diazoxide on insulin secretion and nucleotide-sensitive channels in an insulin-secreting cell line. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;95(1):83–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb16551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trube G., Rorsman P., Ohno-Shosaku T. Opposite effects of tolbutamide and diazoxide on the ATP-dependent K+ channel in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Nov;407(5):493–499. doi: 10.1007/BF00657506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zünkler B. J., Lenzen S., Männer K., Panten U., Trube G. Concentration-dependent effects of tolbutamide, meglitinide, glipizide, glibenclamide and diazoxide on ATP-regulated K+ currents in pancreatic B-cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;337(2):225–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00169252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


