Abstract
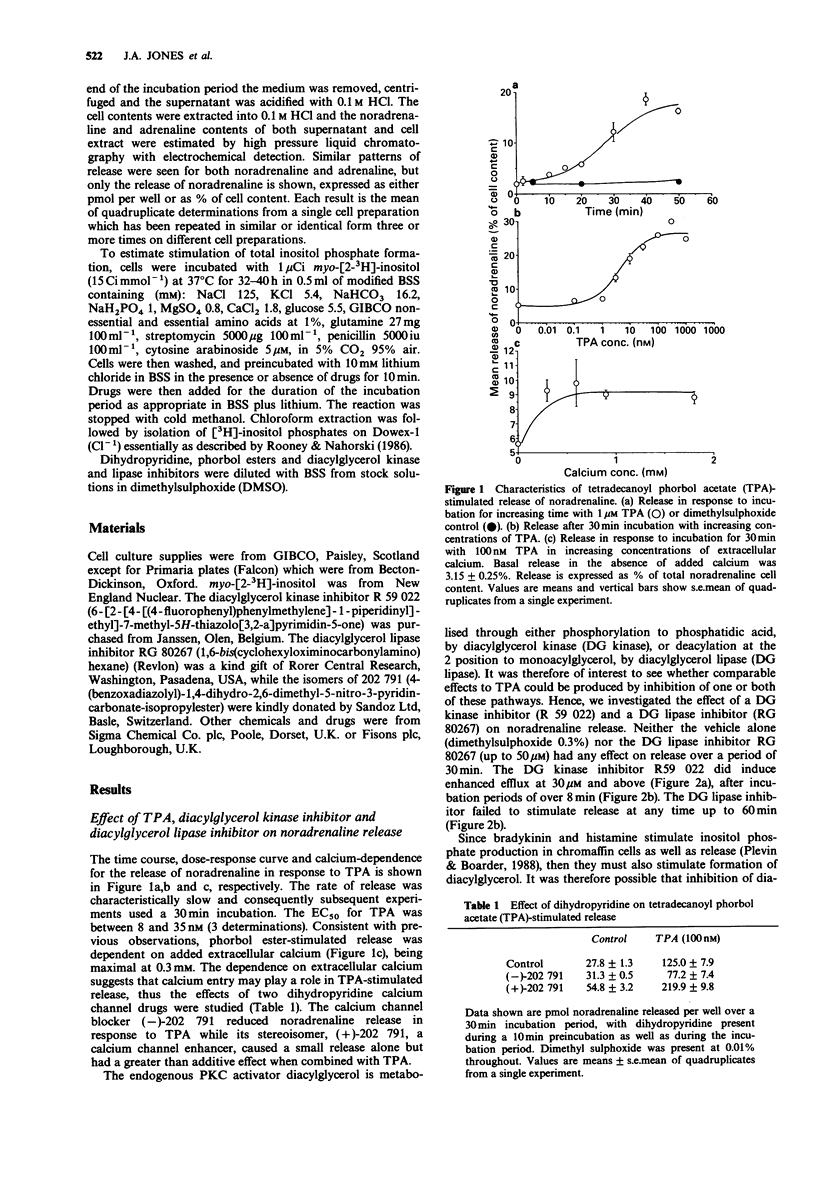
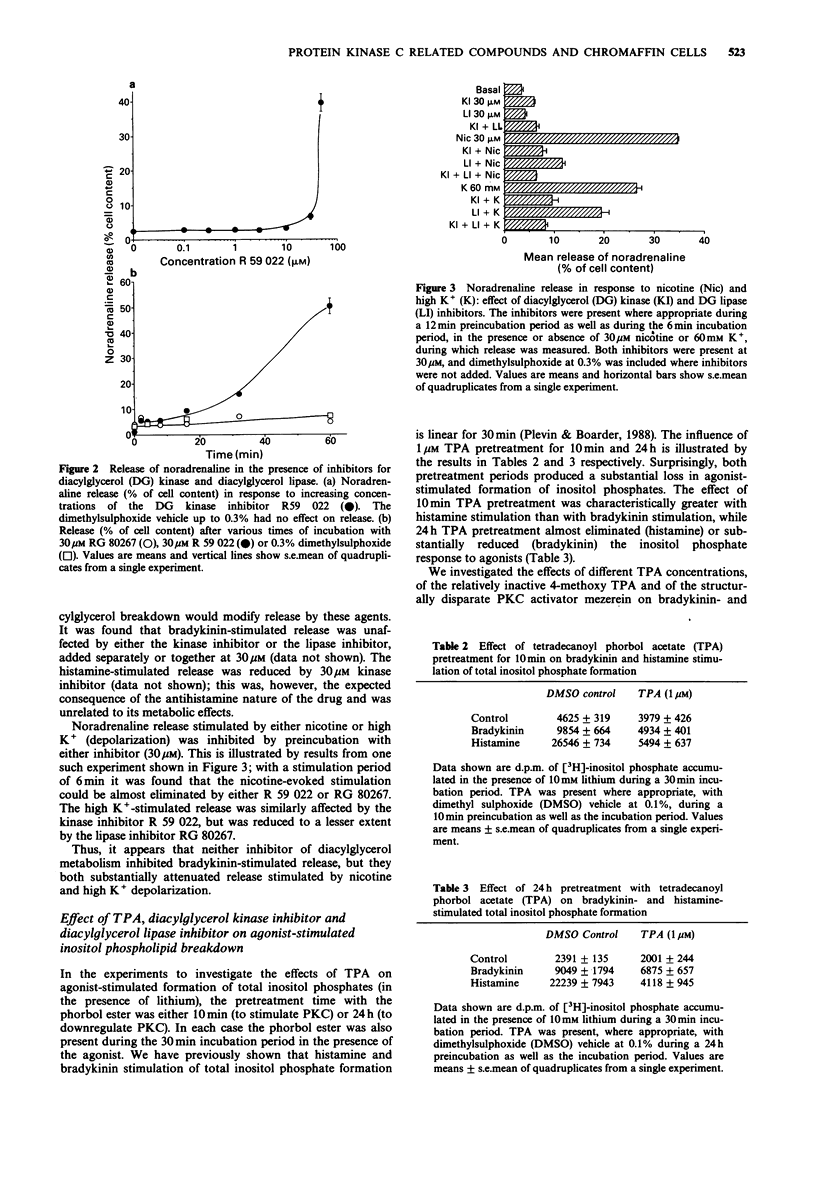
1. We have investigated the modification of catecholamine efflux and inositol phosphate formation in cultured adrenal chromaffin cells by tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate (TPA) and inhibitors of diacylglycerol kinase (R 59,022) and diacylglycerol lipase (RG 80267), the two principal pathways of diacylglycerol metabolism. 2. TPA (1 nM to 1 microM) elicited a slow, calcium-dependent, sustained release of noradrenaline, which was partially blocked by the dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker (-)-202,791 and potentiated by the channel enhancer (+)-202,791. 3. R 59,022 enhanced noradrenaline efflux at 30 and 50 microM, while the lipase inhibitor RG 80267 failed to elicit release. 4. Neither R 59,022 nor RG 80267 affected bradykinin- or histamine-stimulated release, but both drugs substantially attenuated nicotine- and high K(+)-stimulated release. 5. Pretreatment for 10 min with TPA (but not the relatively inactive 4-methoxy TPA) or the non-phorbol protein kinase C stimulator mezerein potently inhibited bradykinin- and histamine-stimulated accumulation of total [3H]-inositol phosphate; inhibition of [3H]-inositol phosphate formation was also seen with 24 h TPA treatment. 6. Neither R 59,022 nor RG 80267, separately or together, affected bradykinin-stimulated [3H]-inositol phosphate formation. 7. Thus while the mechanism exists for inhibition of formation of inositol phosphates by stimulation of protein kinase C, these studies failed to show that this mechanism is activated by agonists acting on phospholipase C linked receptors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert P. R., Wolfson G., Tashjian A. H., Jr Diacylglycerol increases cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration in rat pituitary cells. Relationship to thyrotropin-releasing hormone action. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6577–6581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albino A. P., Le Strange R., Oliff A. I., Furth M. E., Old L. J. Transforming ras genes from human melanoma: a manifestation of tumour heterogeneity? Nature. 1984 Mar 1;308(5954):69–72. doi: 10.1038/308069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner M. A., Holz R. W. Phorbol esters enhance exocytosis from chromaffin cells by two mechanisms. J Neurochem. 1990 Jan;54(1):205–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb13302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boarder M. R., Plevin R., Marriott D. B. Angiotensin II potentiates prostaglandin stimulation of cyclic AMP levels in intact bovine adrenal medulla cells but not adenylate cyclase in permeabilized cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15319–15324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocklehurst K. W., Morita K., Pollard H. B. Characterization of protein kinase C and its role in catecholamine secretion from bovine adrenal-medullary cells. Biochem J. 1985 May 15;228(1):35–42. doi: 10.1042/bj2280035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brocklehurst K. W., Pollard H. B. Enhancement of Ca2+-induced catecholamine release by the phorbol ester TPA in digitonin-permeabilized cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1985 Apr 8;183(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80964-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. P., Morgan R. O., Catt K. J. Dependence of secretory responses to gonadotropin-releasing hormone on diacylglycerol metabolism. Studies with a diacylglycerol lipase inhibitor, RHC 80267. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18614–18620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch M. F., Lapetina E. G. Dual mechanisms of platelet hormone receptor desensitization. Differential importance between agonists of protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):584–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRiemer S. A., Strong J. A., Albert K. A., Greengard P., Kaczmarek L. K. Enhancement of calcium current in Aplysia neurones by phorbol ester and protein kinase C. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):313–316. doi: 10.1038/313313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Virgilio F., Pozzan T., Wollheim C. B., Vicentini L. M., Meldolesi J. Tumor promoter phorbol myristate acetate inhibits Ca2+ influx through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in two secretory cell lines, PC12 and RINm5F. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):32–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond A. H. Bidirectional control of cytosolic free calcium by thyrotropin-releasing hormone in pituitary cells. 1985 Jun 27-Jul 3Nature. 315(6022):752–755. doi: 10.1038/315752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris K. M., Kongsamut S., Miller R. J. Protein kinase C mediated regulation of calcium channels in PC-12 pheochromocytoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 13;134(3):1298–1305. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90391-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Earp H. S., Harden T. K. Long-term phorbol ester treatment down-regulates protein kinase C and sensitizes the phosphoinositide signaling pathway to hormone and growth factor stimulation. Evidence for a role of protein kinase C in agonist-induced desensitization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7610–7619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W. G., Rittenhouse S. E. Inhibition of protein kinase C by staurosporine promotes elevated accumulations of inositol trisphosphates and tetrakisphosphate in human platelets exposed to thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6070–6074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Baker P. F. The phorbol ester TPA increases the affinity of exocytosis for calcium in 'leaky' adrenal medullary cells. FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 22;160(1-2):98–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80944-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama Y., Kitayama S., Dohi T., Tsujimoto A. Evidence that prostaglandins activate calcium channels to enhance basal and stimulation-evoked catecholamine release from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells in culture. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 May 1;37(9):1725–1730. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90435-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livett B. G., Marley P. D. Effects of opioid peptides and morphine on histamine-induced catecholamine secretion from cultured, bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct;89(2):327–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10264.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriott D., Adams M., Boarder M. R. Effect of forskolin and prostaglandin E1 on stimulus secretion coupling in cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1988 Feb;50(2):616–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb02955.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthies H. J., Palfrey H. C., Hirning L. D., Miller R. J. Down regulation of protein kinase C in neuronal cells: effects on neurotransmitter release. J Neurosci. 1987 Apr;7(4):1198–1206. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-04-01198.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy S. A., Hallam T. J., Merritt J. E. Activation of protein kinase C in human neutrophils attenuates agonist-stimulated rises in cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration by inhibiting bivalent-cation influx and intracellular Ca2+ release in addition to stimulating Ca2+ efflux. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 1;264(2):357–364. doi: 10.1042/bj2640357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mege J. L., Tao W., Molski T. F., Gomez-Cambronero J., Huang C. K., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Diacylglycerol kinase inhibitor R59022 and stimulated neutrophil responses. Am J Physiol. 1988 Nov;255(5 Pt 1):C589–C594. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.5.C589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble E. P., Bommer M., Liebisch D., Herz A. H1-histaminergic activation of catecholamine release by chromaffin cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Jan 15;37(2):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90721-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P. J., Marriott D. B., Boarder M. R. Evidence for a dihydropyridine-sensitive and conotoxin-insensitive release of noradrenaline and uptake of calcium in adrenal chromaffin cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):133–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11933.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen P. J., Plevin R., Boarder M. R. Characterization of bradykinin-stimulated release of noradrenaline from cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Mar;248(3):1231–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Ochsner M., Whitebread S., De Gasparo M. Down-regulation of protein kinase C potentiates angiotensin II-stimulated polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in vascular smooth-muscle cells. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 15;262(1):285–291. doi: 10.1042/bj2620285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevin R., Boarder M. R. Stimulation of formation of inositol phosphates in primary cultures of bovine adrenal chromaffin cells by angiotensin II, histamine, bradykinin, and carbachol. J Neurochem. 1988 Aug;51(2):634–641. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevin R., Owen P. J., Marriott D. B., Jones J. A., Boarder M. R. Role of phosphoinositide turnover and cyclic AMP accumulation in prostaglandin-stimulated noradrenaline release from cultured adrenal chromaffin cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Mar;252(3):1296–1303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocotte S. L., Frye R. A., Senter R. A., TerBush D. R., Lee S. A., Holz R. W. Effects of phorbol ester on catecholamine secretion and protein phosphorylation in adrenal medullary cell cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):930–934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse S. E., Sasson J. P. Mass changes in myoinositol trisphosphate in human platelets stimulated by thrombin. Inhibitory effects of phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8657–8660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney T. A., Nahorski S. R. Regional characterization of agonist and depolarization-induced phosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Dec;239(3):873–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland C. A., Amin D. Relative activities of rat and dog platelet phospholipase A2 and diglyceride lipase. Selective inhibition of diglyceride lipase by RHC 80267. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14006–14010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakade A. R., Malhotra R. K., Wakade T. D. Phorbol ester facilitates 45Ca accumulation and catecholamine secretion by nicotine and excess K+ but not by muscarine in rat adrenal medulla. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):698–700. doi: 10.1038/321698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan D. C., Bunn S. J., Livett B. G. Effects of phorbol esters and forskolin on basal and histamine-induced accumulation of inositol phosphates in cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1989 Oct;53(4):1219–1227. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimlichman R., Goldstein D. S., Zimlichman S., Stull R., Keiser H. R. Angiotensin II increases cytosolic calcium and stimulates catecholamine release in cultured bovine adrenomedullary cells. Cell Calcium. 1987 Aug;8(4):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(87)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Chaffoy de Courcelles D. C., Roevens P., Van Belle H. R 59 022, a diacylglycerol kinase inhibitor. Its effect on diacylglycerol and thrombin-induced C kinase activation in the intact platelet. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15762–15770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


