Abstract
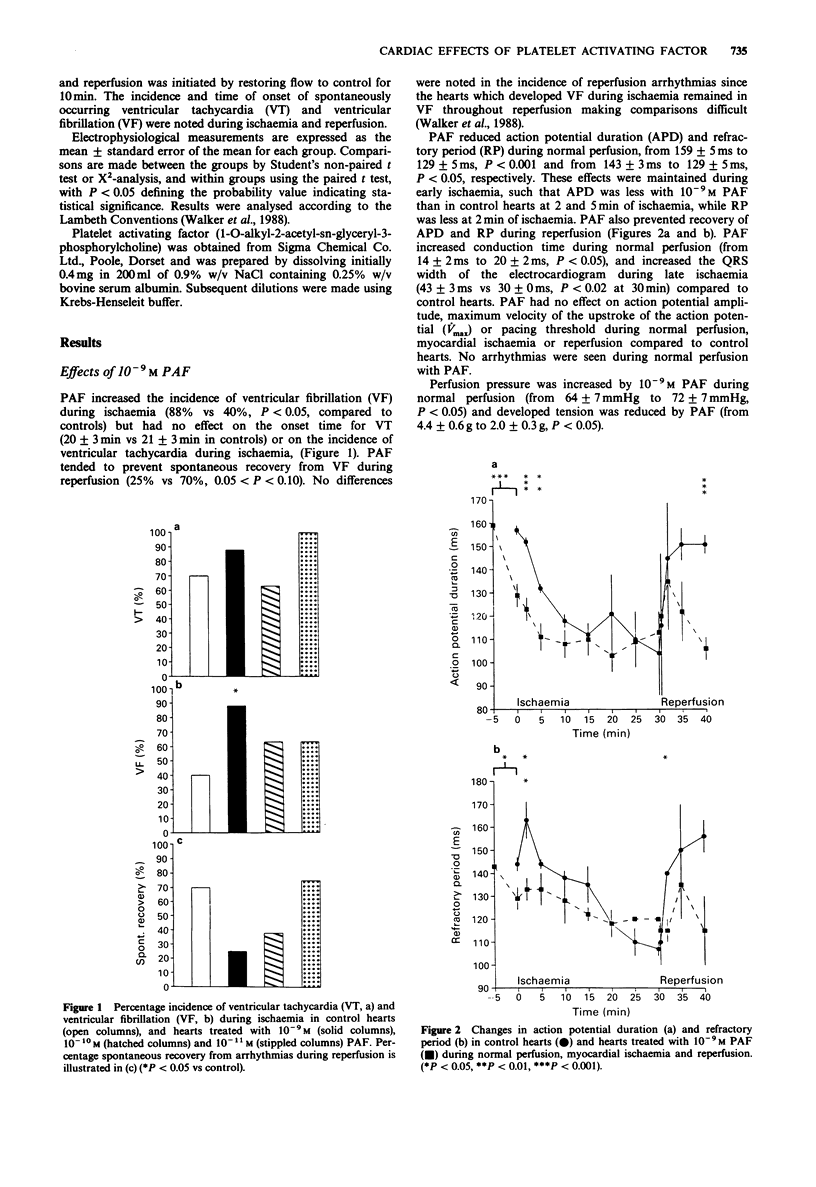
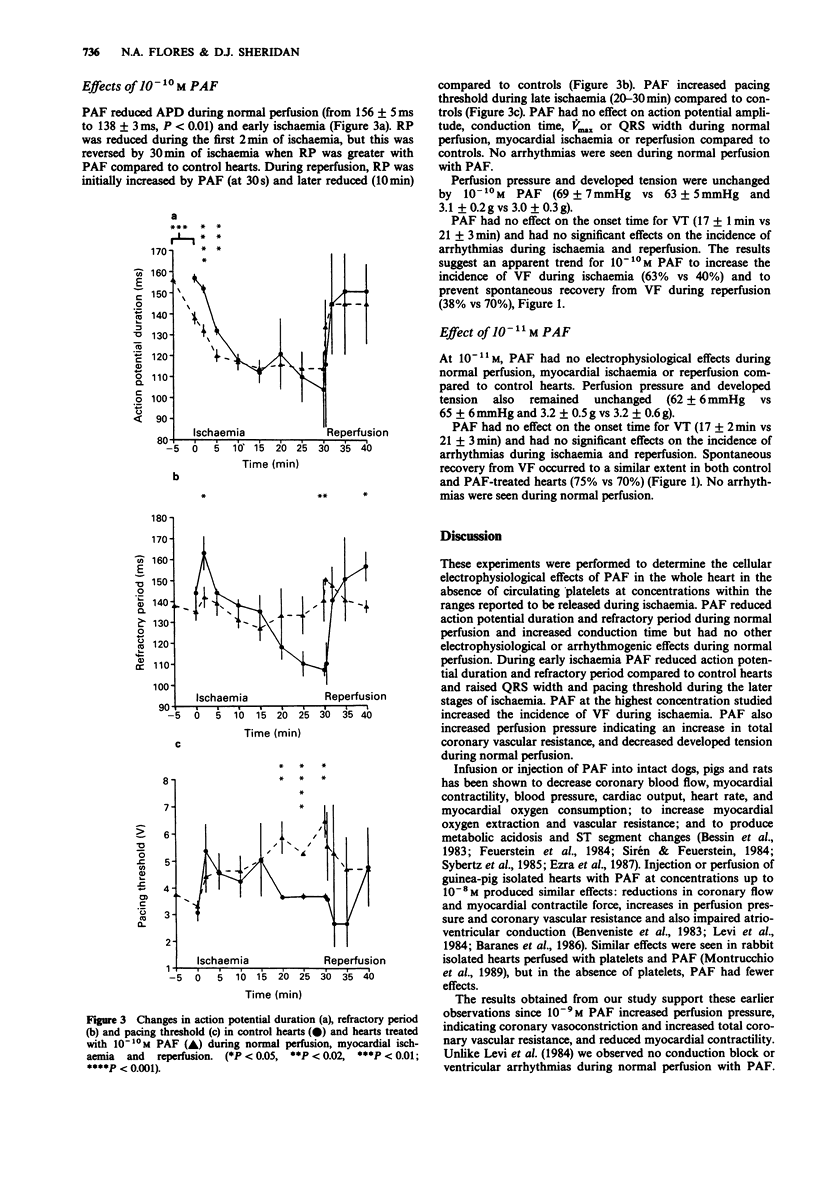
1. Platelet activating factor (PAF) is often used to study the effects of platelet activation. While direct myocardial electrophysiological effects of PAF have been described in superfused myocardial tissue, little is known about its actions on the whole heart. 2. The cellular electrophysiological and arrhythmogenic effects of PAF (10(-11)M, 10(-10)M and 10(-9)M) were studied during normal perfusion, global myocardial ischaemia and reperfusion in Langendorff-perfused guinea-pig hearts at 32 degrees C. 3. PAF (10(-9)M) increased the incidence of ventricular fibrillation during ischaemia and reduced action potential duration (APD) during normal perfusion and early myocardial ischaemia (10(-9)M and 10(-10)M). PAF also reduced refractory period (RP) during normal perfusion (10(-9)M) and early ischaemia (10(-9)M and 10(-10)M). PAF prevented recovery of APD (10(-9)M) and RP (10(-9)M and 10(-10)M) during reperfusion. PAF at a concentration of 10(-11)M had no electrophysiological effects. 4. PAF (10(-9)M) increased the QRS width of the electrocardiogram during late ischaemia while 10(-10)M PAF raised pacing threshold during late ischaemia. 5. Perfusion pressure was increased, and developed tension decreased by 10(-9)M PAF. 6. These results demonstrate that PAF has direct myocardial electrophysiological effects in the whole heart which occur during normal perfusion and are capable of augmenting the effects of myocardial ischaemia, but are independent of the presence of platelets.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alloatti G., Montrucchio G., Mariano F., Tetta C., De Paulis R., Morea M., Emanuelli G., Camussi G. Effect of platelet-activating factor (PAF) on human cardiac muscle. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1986;79(1):108–112. doi: 10.1159/000233953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baranes J., Hellegouarch A., Le Hegarat M., Viossat I., Auguet M., Chabrier P. E., Braquet P. The effects of PAF-acether on the cardiovascular system and their inhibition by a new highly specific PAF-acether receptor antagonist BN 52021. Pharmacol Res Commun. 1986 Aug;18(8):717–737. doi: 10.1016/0031-6989(86)90114-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste J., Boullet C., Brink C., Labat C. The actions of Paf-acether (platelet-activating factor) on guinea-pig isolated heart preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Sep;80(1):81–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11052.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessin P., Bonnet J., Apffel D., Soulard C., Desgroux L., Pelas I., Benveniste J. Acute circulatory collapse caused by platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) in dogs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 21;86(3-4):403–413. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90190-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braquet P., Touqui L., Shen T. Y., Vargaftig B. B. Perspectives in platelet-activating factor research. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Jun;39(2):97–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demopoulos C. A., Pinckard R. N., Hanahan D. J. Platelet-activating factor. Evidence for 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glyceryl-3-phosphorylcholine as the active component (a new class of lipid chemical mediators). J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9355–9358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezra D., Laurindo F. R., Czaja J. F., Snyder F., Goldstein R. E., Feuerstein G. Cardiac and coronary consequences of intracoronary platelet activating factor infusion in the domestic pig. Prostaglandins. 1987 Jul;34(1):41–57. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(87)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerstein G., Boyd L. M., Ezra D., Goldstein R. E. Effect of platelet-activating factor on coronary circulation of the domestic pig. Am J Physiol. 1984 Mar;246(3 Pt 2):H466–H471. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1984.246.3.H466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald D. J., Roy L., Catella F., FitzGerald G. A. Platelet activation in unstable coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 1986 Oct 16;315(16):983–989. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198610163151602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi R., Burke J. A., Guo Z. G., Hattori Y., Hoppens C. M., McManus L. M., Hanahan D. J., Pinckard R. N. Acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine (AGEPC). A putative mediator of cardiac anaphylaxis in the guinea pig. Circ Res. 1984 Feb;54(2):117–124. doi: 10.1161/01.res.54.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotner G. Z., Lynch J. M., Betz S. J., Henson P. M. Human neutrophil-derived platelet activating factor. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):676–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McManus L. M., Hanahan D. J., Pinckard R. N. Human platelet stimulation by acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine. J Clin Invest. 1981 Mar;67(3):903–906. doi: 10.1172/JCI110108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta P., Mehta J. Platelet function studies in coronary artery disease. V. Evidence for enhanced platelet microthrombus formation activity in acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 1979 Apr;43(4):757–760. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(79)90075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelson J. K., Simpson P. J., Lucchesi B. R. Myocardial dysfunction and coronary vasoconstriction induced by platelet-activating factor in the post-infarcted rabbit isolated heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1988 Jun;20(6):547–561. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(88)80081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montrucchio G., Alloatti G., Tetta C., De Luca R., Saunders R. N., Emanuelli G., Camussi G. Release of platelet-activating factor from ischemic-reperfused rabbit heart. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 2):H1236–H1246. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.4.H1236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montrucchio G., Camussi G., Tetta C., Emanuelli G., Orzan F., Libero L., Brusca A. Intravascular release of platelet-activating factor during atrial pacing. Lancet. 1986 Aug 2;2(8501):293–293. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penny W. J., Sheridan D. J. Arrhythmias and cellular electrophysiological changes during myocardial "ischaemia" and reperfusion. Cardiovasc Res. 1983 Jun;17(6):363–372. doi: 10.1093/cvr/17.6.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty A. C., Scrutton M. C. Platelet aggregation in whole blood: is the response to adrenaline, 5-hydroxytryptamine and PAF a direct consequence of stimulation by these agonists? Thromb Res. 1989 Apr 15;54(2):151–159. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel A., Braquet P., Mest H. J. The effect of the specific PAF antagonist BN 52021 and the calcium blocker diltiazem on PAF induced arrhythmogenicity. Pharmacol Res Commun. 1987 Oct;19(10):703–712. doi: 10.1016/0031-6989(87)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. A., Genovese A., Levi R. Negative inotropic effect of platelet-activating factor on human myocardium: a pharmacological study. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Dec;243(3):834–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rösen R., Dausch W., Beck E., Klaus W. Platelet induced aggravation of acute ischaemia in an isolated rabbit heart model. Cardiovasc Res. 1987 Apr;21(4):293–298. doi: 10.1093/cvr/21.4.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan D. J., Bell A. J., Penny W. J., Culling W. A microcomputer system for real-time analysis of cardiac action potentials. J Med Eng Technol. 1983 Sep-Oct;7(5):238–242. doi: 10.3109/03091908309032591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirén A. L., Feuerstein G. Effects of PAF and BN 52021 on cardiac function and regional blood flow in conscious rats. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jul;257(1 Pt 2):H25–H32. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.1.H25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisson J. H., Prescott S. M., McIntyre T. M., Zimmerman G. A. Production of platelet-activating factor by stimulated human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Correlation of synthesis with release, functional events, and leukotriene B4 metabolism. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3918–3926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slattery C. W., Beaumont D. O. Sheep platelets as a model for human platelets: evidence for specific PAF (platelet activating factor) receptors. Thromb Res. 1989 Sep 1;55(5):569–576. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90389-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sybertz E. J., Watkins R. W., Baum T., Pula K., Rivelli M. Cardiac, coronary and peripheral vascular effects of acetyl glyceryl ether phosphoryl choline in the anesthetized dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jan;232(1):156–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamargo J., Tejerina T., Delgado C., Barrigon S. Electrophysiological effects of platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) in guinea-pig papillary muscles. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 26;109(2):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90423-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainwright C. L., Parratt J. R., Bigaud M. The effects of PAF antagonists on arrhythmias and platelets during acute myocardial ischaemia and reperfusion. Eur Heart J. 1989 Mar;10(3):235–243. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a059471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. J., Curtis M. J., Hearse D. J., Campbell R. W., Janse M. J., Yellon D. M., Cobbe S. M., Coker S. J., Harness J. B., Harron D. W. The Lambeth Conventions: guidelines for the study of arrhythmias in ischaemia infarction, and reperfusion. Cardiovasc Res. 1988 Jul;22(7):447–455. doi: 10.1093/cvr/22.7.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M., Prescott S. M. Production of platelet-activating factor by human vascular endothelial cells: evidence for a requirement for specific agonists and modulation by prostacyclin. Circulation. 1985 Oct;72(4):718–727. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.72.4.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


