Abstract
1. The present study investigated the effects of intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) administration of the GABAB-receptor agonist baclofen on food and water intake in satiated pigs previously trained to make operant responses for food and water, which were available ad libitum. 2. Baclofen (25-100 nmol) i.c.v. produced a dose-related increase in food intake. Baclofen (50 nmol) increased feeding during the first 15 min after administration (P less than 0.01), while the 100 nmol dose increased feeding during the first 30 min (P less than 0.01). None of these doses of baclofen had any affect on the daily (24 h) food intake. 3. The effect of baclofen (50 nmol) on feeding was prevented by pretreating the animals with the GABAB antagonist phaclofen (500 nmol, i.c.v.). 4. Baclofen (25-100 nmol) i.c.v. had no significant effects on water intake. 5. Intravenous administration of baclofen (100 nmol) had no effect on food intake, thus eliminating the possibility that i.c.v. baclofen might have stimulated feeding by a peripheral mode of action. 6. These results show that baclofen increases food intake in satiated pigs, and that this effect is mediated by the drug acting at central GABAB-receptors.
Full text
PDF
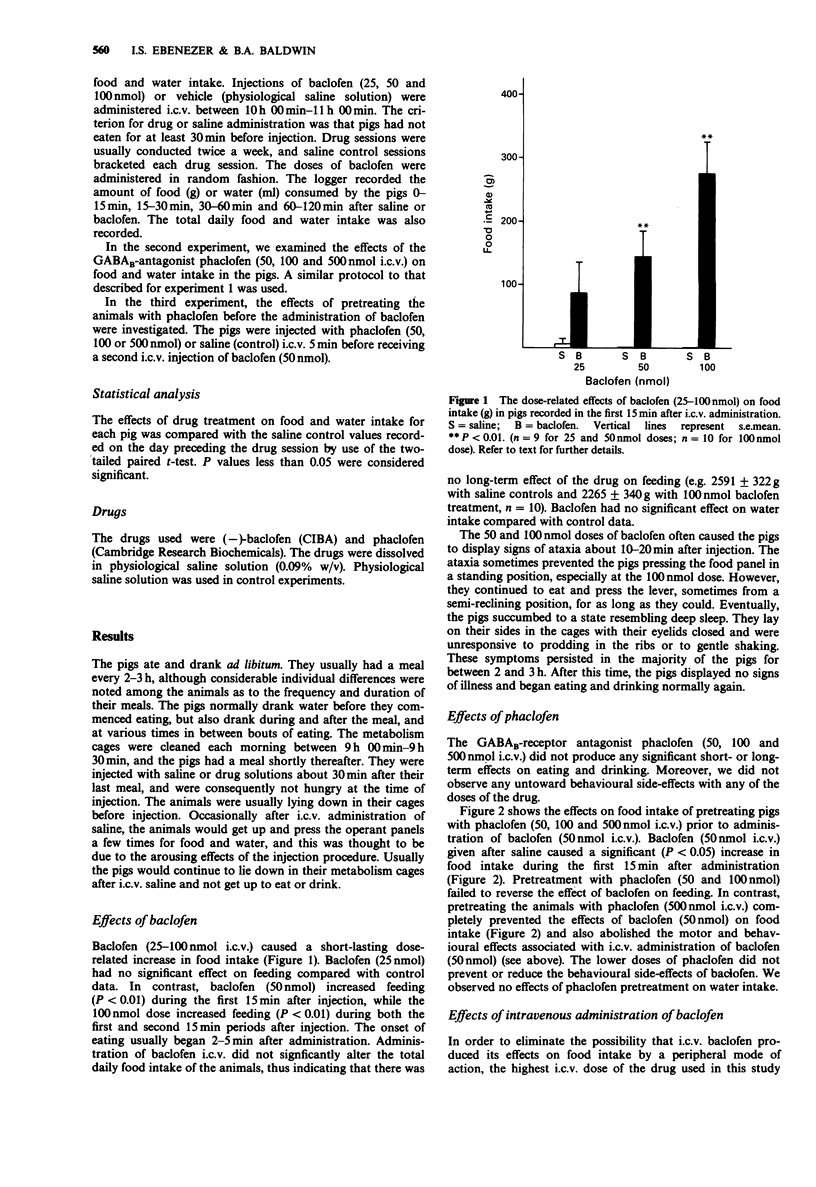
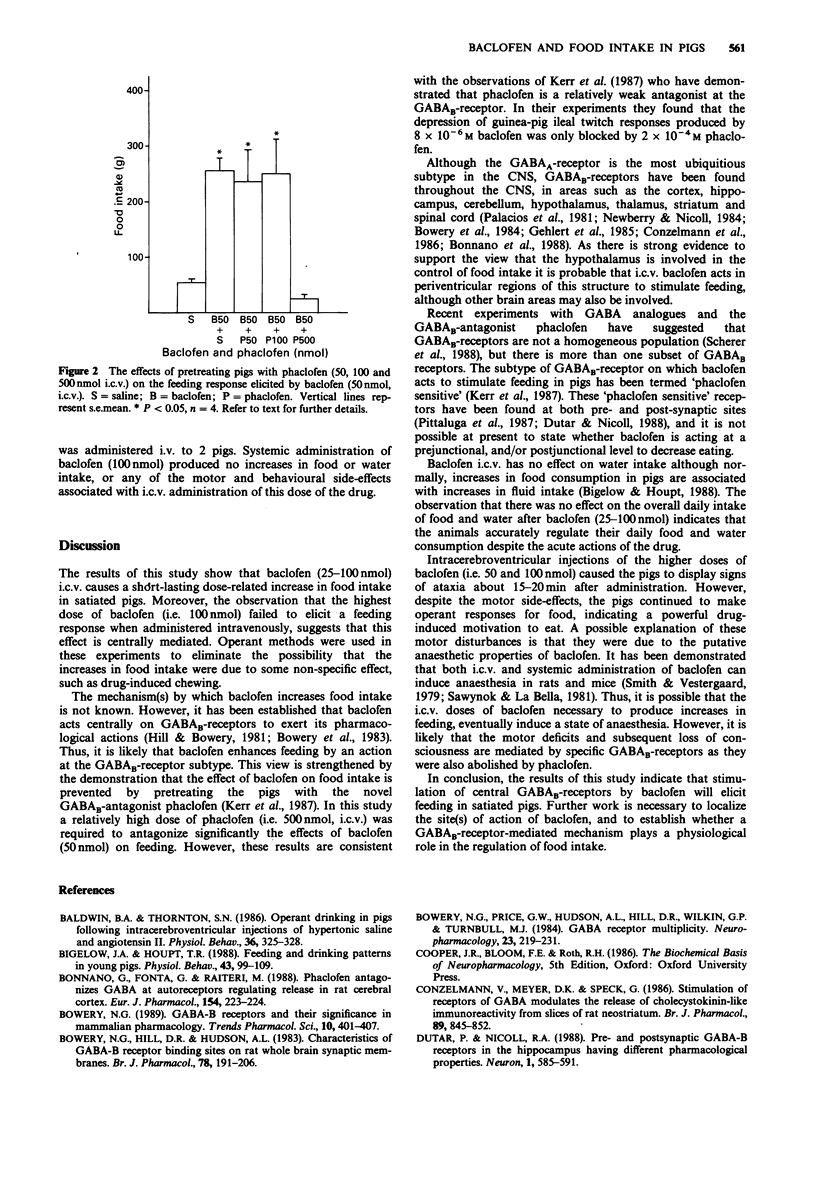

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin B. A., Thornton S. N. Operant drinking in pigs following intracerebroventricular injections of hypertonic solutions and angiotensin II. Physiol Behav. 1986;36(2):325–328. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(86)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigelow J. A., Houpt T. R. Feeding and drinking patterns in young pigs. Physiol Behav. 1988;43(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(88)90104-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonanno G., Fontana G., Raiteri M. Phaclofen antagonizes GABA at autoreceptors regulating release in rat cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep 13;154(2):223–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Hill D. R., Hudson A. L. Characteristics of GABAB receptor binding sites on rat whole brain synaptic membranes. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan;78(1):191–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb09380.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Price G. W., Hudson A. L., Hill D. R., Wilkin G. P., Turnbull M. J. GABA receptor multiplicity. Visualization of different receptor types in the mammalian CNS. Neuropharmacology. 1984 Feb;23(2B):219–231. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(84)90063-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. GABAB receptors and their significance in mammalian pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Oct;10(10):401–407. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann U., Meyer D. K., Sperk G. Stimulation of receptors of gamma-aminobutyric acid modulates the release of cholecystokinin-like immunoreactivity from slices of rat neostriatum. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Dec;89(4):845–852. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb11190.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutar P., Nicoll R. A. Pre- and postsynaptic GABAB receptors in the hippocampus have different pharmacological properties. Neuron. 1988 Sep;1(7):585–591. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehlert D. R., Yamamura H. I., Wamsley J. K. gamma-Aminobutyric acidB receptors in the rat brain: quantitative autoradiographic localization using [3H](-)-baclofen. Neurosci Lett. 1985 May 14;56(2):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard C. L., Seoane J. R., Matte J. J. Studies of the role of gamma-aminobutyric acid in the hypothalamic control of feed intake in sheep. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;63(10):1297–1301. doi: 10.1139/y85-214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandison L., Guidotti A. Stimulation of food intake by muscimol and beta endorphin. Neuropharmacology. 1977 Jul-Aug;16(7-8):533–536. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(77)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. R., Bowery N. G. 3H-baclofen and 3H-GABA bind to bicuculline-insensitive GABA B sites in rat brain. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):149–152. doi: 10.1038/290149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J., Alheid G. F., Newberg A., Grossman S. P. GABA stimulation and blockade in the hypothalamus and midbrain: effects on feeding and locomotor activity. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1977 Dec;7(6):537–541. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(77)90250-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J., Rothstein J., Grossman S. P. GABA and hypothalamic feeding systems. I. Topographic analysis of the effects of microinjections of muscimol. Physiol Behav. 1979 Dec;23(6):1123–1134. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(79)90306-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr D. I., Ong J., Prager R. H., Gynther B. D., Curtis D. R. Phaclofen: a peripheral and central baclofen antagonist. Brain Res. 1987 Mar 3;405(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90999-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry N. R., Nicoll R. A. A bicuculline-resistant inhibitory post-synaptic potential in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 Mar;348:239–254. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W. Drug interactions at the GABA receptor-ionophore complex. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982;22:245–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.22.040182.001333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios J. M., Wamsley J. K., Kuhar M. J. High affinity GABA receptors-autoradiographic localization. Brain Res. 1981 Oct 19;222(2):285–307. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittaluga A., Asaro D., Pellegrini G., Raiteri M. Studies on [3H]GABA and endogenous GABA release in rat cerebral cortex suggest the presence of autoreceptors of the GABAB type. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Nov 24;144(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J., Labella F. S. Naloxone antagonizes inhibitory and unmasks excitatory effects of baclofen. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;33(9):597–599. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1981.tb13874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer R. W., Ferkany J. W., Enna S. J. Evidence for pharmacologically distinct subsets of GABAB receptors. Brain Res Bull. 1988 Sep;21(3):439–443. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(88)90156-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seoane J. R., Dumont F., Girard C. L., Bédard L., Matte J. J. Effects of intraventricular injections of gamma-aminobutyric acid and related substances on feeding behavior in satiated sheep. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;62(10):1296–1299. doi: 10.1139/y84-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. F., Vestergaard P. The role of monoamines for the central effects of Baclofen on behavior of rats. J Neural Transm. 1979;46(3):215–223. doi: 10.1007/BF01250787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner A. J., Whittle S. R. Biochemical dissection of the gamma-aminobutyrate synapse. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):29–41. doi: 10.1042/bj2090029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


