Abstract
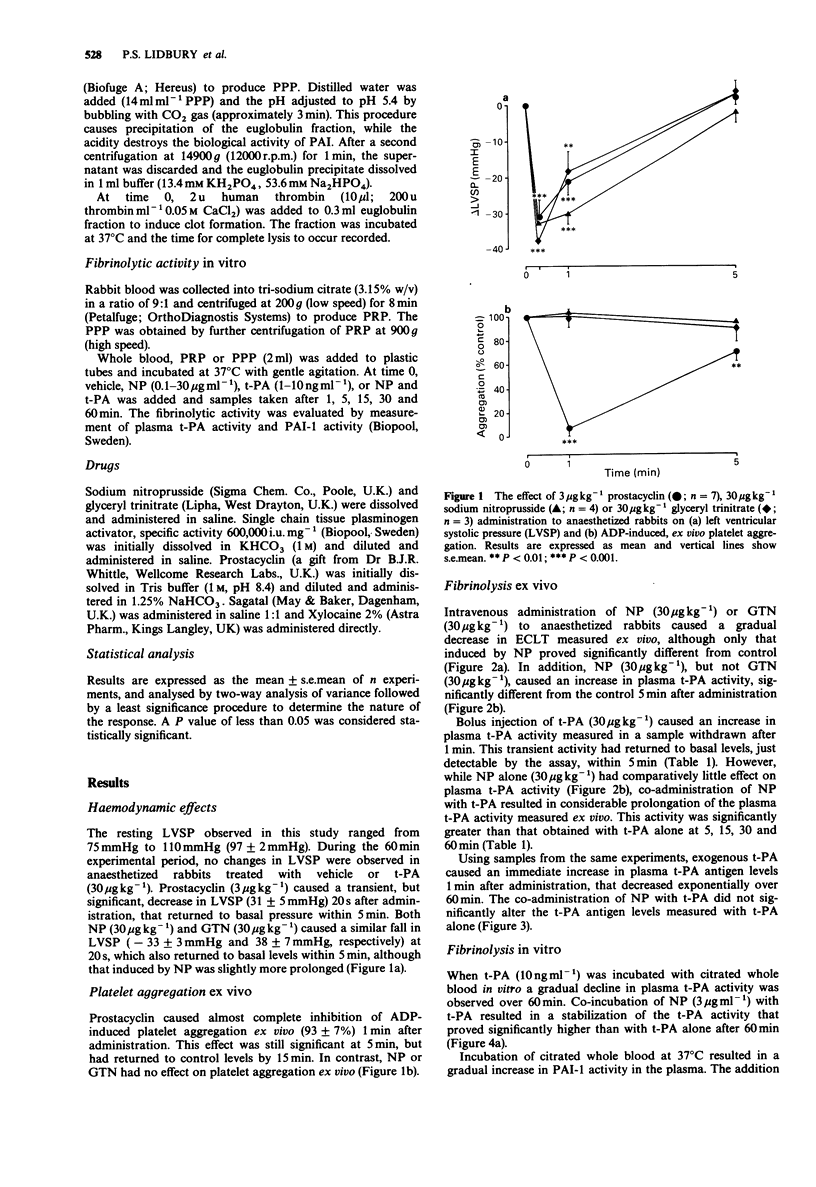
1. We have investigated the effect of sodium nitroprusside (NP) and glyceryl trinitrate (GTN) on fibrinolysis in anaesthetized rabbits ex vivo and in vitro by measurement of euglobulin clot lysis time (ECLT), plasma levels of tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) activity, plasma t-PA antigen levels and plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) activity. 2. In vivo, NP (30 micrograms kg-1), GTN (30 micrograms kg-1) and prostacyclin (3 micrograms kg-1) caused similar transient decreases in left ventricular systolic pressure. However, while prostacyclin induced near-maximal inhibition of ex vivo platelet aggregation, NP or GTN had no effect. 3. Ex vivo, NP caused a significant decrease in ECLT and an increase in plasma t-PA activity. 4. Intravenous co-administration of t-PA (30 micrograms kg-1) with NP caused substantial prolongation of plasma t-PA activity, without affecting t-PA antigen levels. 5. In whole blood in vitro, NP (30 micrograms kg-1) prevented the time-dependent increase in PAI-1 activity and inhibited inactivation of added t-PA (10 ng ml-1). 6. We propose that NP exhibited fibrinolytic activity through increased t-PA activity as a result of inhibition of PAI-1 release from platelets. These results could have important therapeutic consequences when t-PA and nitrate treatments are combined.
Full text
PDF
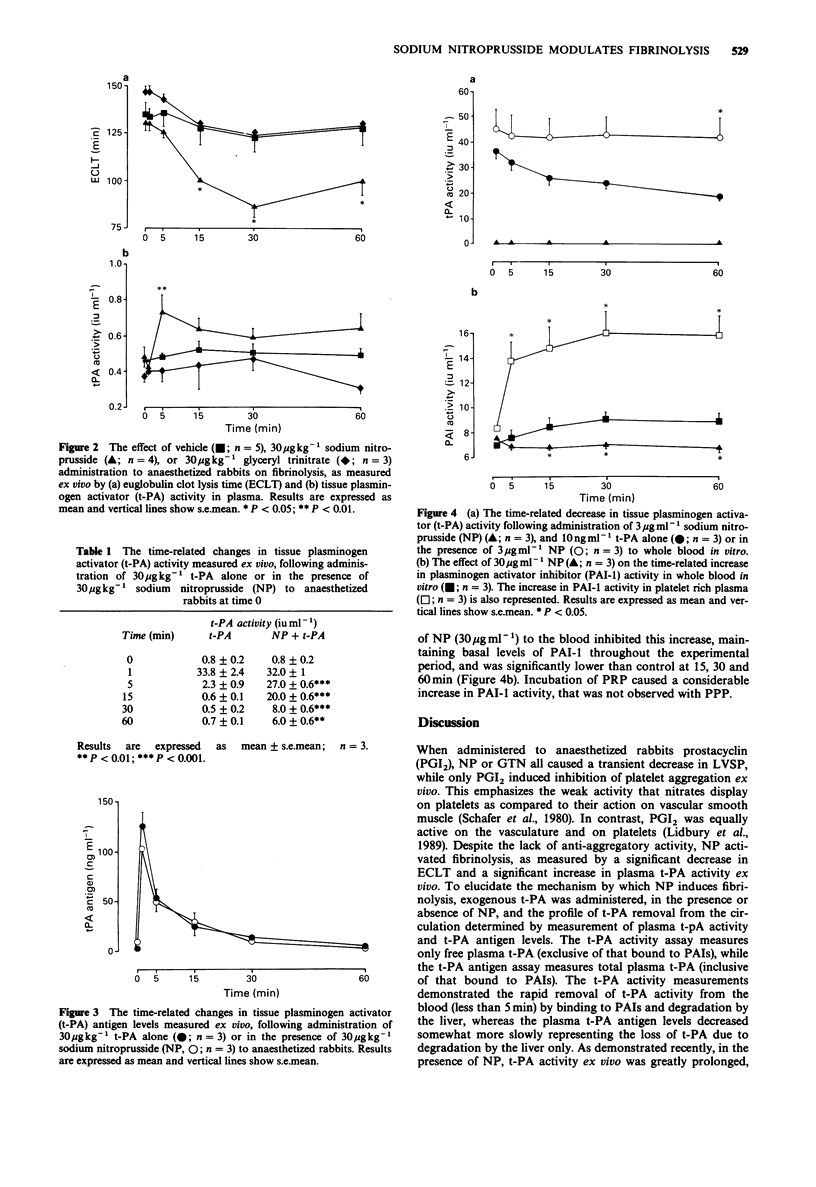

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clarke J. G., Davies G. J., Kerwin R., Hackett D., Larkin S., Dawbarn D., Lee Y., Bloom S. R., Yacoub M., Maseri A. Coronary artery infusion of neuropeptide Y in patients with angina pectoris. Lancet. 1987 May 9;1(8541):1057–1059. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90483-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson L. A., Ginsberg M. H., Loskutoff D. J. Detection and partial characterization of an inhibitor of plasminogen activator in human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1465–1472. doi: 10.1172/JCI111559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feelisch M., Noack E. A. Correlation between nitric oxide formation during degradation of organic nitrates and activation of guanylate cyclase. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul 2;139(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90493-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold H. K., Johns J. A., Leinbach R. C., Yasuda T., Grossbard E., Zusman R., Collen D. A randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled trial of recombinant human tissue-type plasminogen activator in patients with unstable angina pectoris. Circulation. 1987 Jun;75(6):1192–1199. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.75.6.1192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman R. R., Bunting S., Miller O. V. Modulation of human platelet adenylate cyclase by prostacyclin (PGX). Prostaglandins. 1977 Mar;13(3):377–388. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korbut R., Byrska-Danek A., Gryglewski R. J. Fibrinolytic activity of 6-keto-prostaglandin E1. Thromb Haemost. 1983 Dec 30;50(4):893–893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korbut R., Lidbury P. S., Vane J. R. Prolongation of fibrinolytic activity of tissue plasminogen activator by nitrovasodilators. Lancet. 1990 Mar 17;335(8690):669–669. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90462-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korbut R., Lidbury P., Thomas G. R., Vane J. R. Fibrinolytic activity of endothelin-3. Thromb Res. 1989 Sep 15;55(6):797–799. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90311-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruithof E. K., Tran-Thang C., Bachmann F. Studies on the release of a plasminogen activator inhibitor by human platelets. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Apr 30;55(2):201–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidbury P. S., Antunes E., de Nucci G., Vane J. R. Interactions of iloprost and sodium nitroprusside on vascular smooth muscle and platelet aggregation. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98(4):1275–1280. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12674.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellion B. T., Ignarro L. J., Ohlstein E. H., Pontecorvo E. G., Hyman A. L., Kadowitz P. J. Evidence for the inhibitory role of guanosine 3', 5'-monophosphate in ADP-induced human platelet aggregation in the presence of nitric oxide and related vasodilators. Blood. 1981 May;57(5):946–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S. Eighth Gaddum Memorial Lecture. University of London Institute of Education, December 1980. Biological importance of prostacyclin. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 May;76(1):3–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. K., Hussaini I., Bhardwaj R. Prostanoids stimulate fibrinolysis in the rat. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1988 Nov-Dec;296:155–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J., Crawford G. P., Ogston D., Douglas A. S. Studies on an inhibitor of plasminogen activators in human platelets. Br J Haematol. 1974 Apr;26(4):661–668. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb00509.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Comparative pharmacology of endothelium-derived relaxing factor, nitric oxide and prostacyclin in platelets. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep;92(1):181–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11310.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer A. I., Alexander R. W., Handin R. I. Inhibition of platelet function by organic nitrate vasodilators. Blood. 1980 Apr;55(4):649–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateson J. E., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Effects of prostacyclin (PGX) on cyclic AMP concentrations in human platelets. Prostaglandins. 1977 Mar;13(3):389–397. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(77)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON KAULLA K. N., SCHULTZ R. L. Methods for the evaluation of human fibrinolysis; studies with two combined technics. Am J Clin Pathol. 1958 Feb;29(2):104–112. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/29.2.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


