Abstract
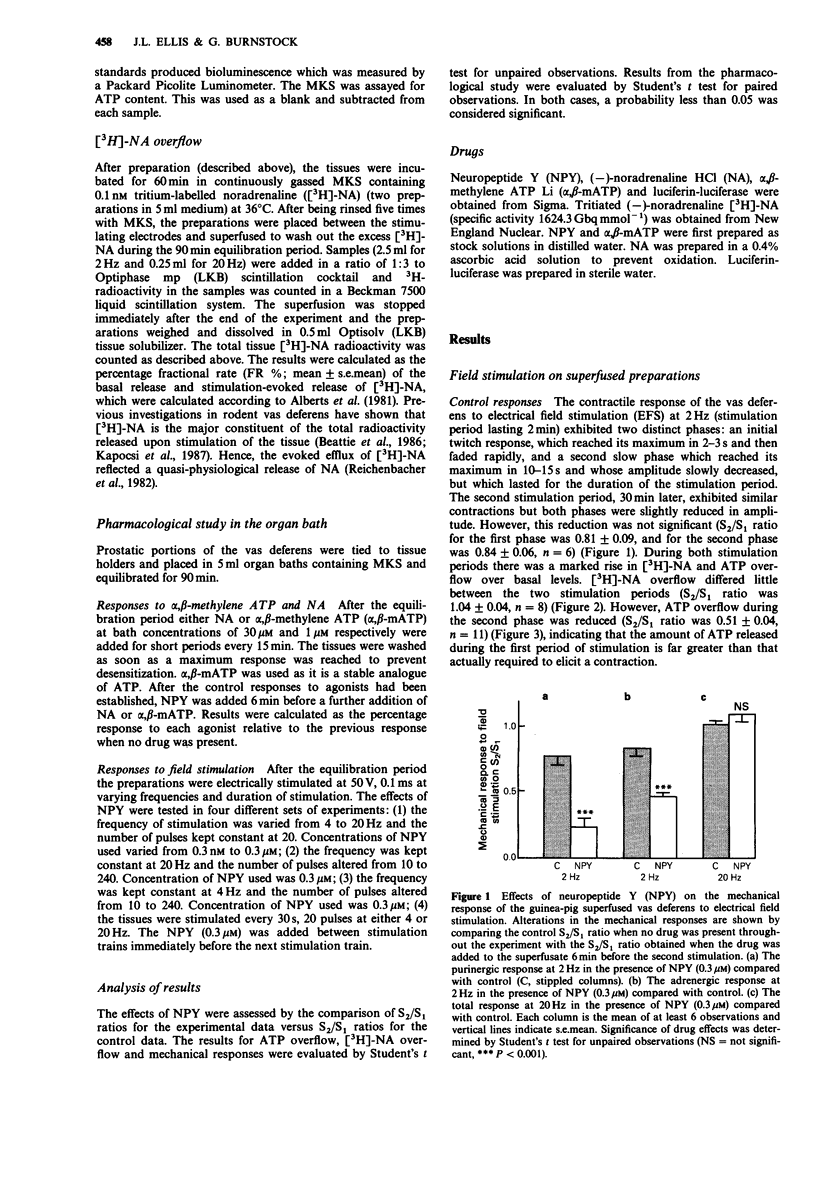
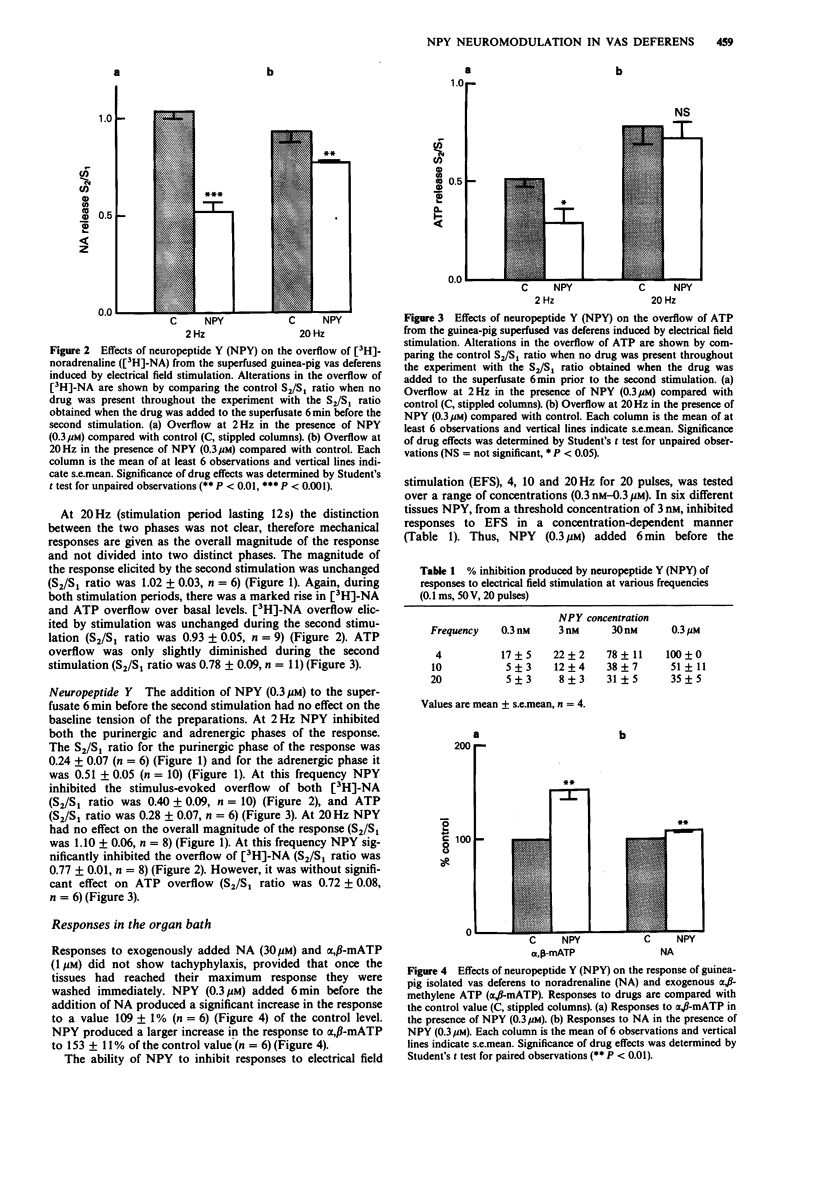
1. We examined the neuromodulatory effects of neuropeptide Y (NPY) on purinergic and adrenergic co-transmission in the guinea-pig vas deferens. 2. In superfused vas deferens preparations, NPY (0.3 microM) inhibited the stimulus-evoked overflow of both ATP and [3H]-noradrenaline ([3H]-NA) at 2 Hz, but only the stimulus-evoked release of [3H]-NA at 20 Hz. 3. Postjunctionally, NPY greatly enhanced responses to alpha,beta-methylene ATP and to a lesser extent to exogenous NA. 4. Preparations stimulated in organ baths showed frequency-dependent contractions to field stimulation. NPY abolished responses to field stimulation at low frequency and a small number of pulses. At high frequency (20 Hz), NPY abolished responses elicited by 10 pulses, inhibited responses by 50% at 20 pulses and had little effect on preparations stimulated for 240 pulses. 5. Our study suggests that NPY neuromodulates co-transmission in the vas deferens by inhibiting the release of ATP and NA and that these effects predominate over the postjunctional enhancement by NPY. These results also show that the physiological effect of NPY will be determined both by the frequency at which the nerves are discharging and the duration of their firing.
Full text
PDF
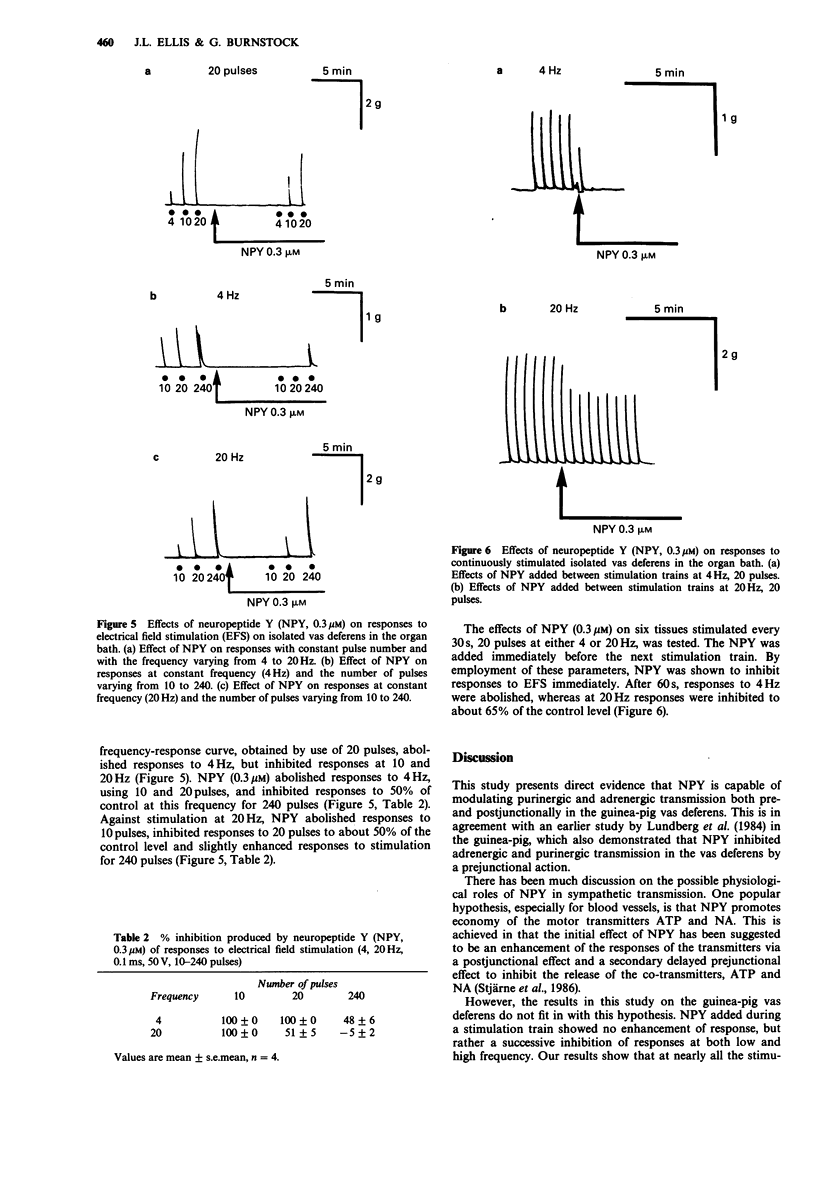


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts P., Bartfai T., Stjärne L. Site(s) and ionic basis of alpha-autoinhibition and facilitation of "3H'noradrenaline secretion in guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:297–334. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beattie D. T., Cunnane T. C., Muir T. C. Effects of calcium channel antagonists on action potential conduction and transmitter release in the guinea-pig vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Sep;89(1):235–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb11140.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Copeland J. R., Emson P. C., McCulloch J., Uddman R. Nerve fibers containing neuropeptide Y in the cerebrovascular bed: immunocytochemistry, radioimmunoassay, and vasomotor effects. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1987 Feb;7(1):45–57. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1987.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried G., Lagercrantz H., Hökfelt T. Improved isolation of small noradrenergic vesicles from rat seminal ducts following castration. A density gradient centrifugation and morphological study. Neuroscience. 1978;3(12):1271–1291. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90147-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried G., Terenius L., Brodin E., Efendic S., Dockray G., Fahrenkrug J., Goldstein M., Hökfelt T. Neuropeptide Y, enkephalin and noradrenaline coexist in sympathetic neurons innervating the bovine spleen. Biochemical and immunohistochemical evidence. Cell Tissue Res. 1986;243(3):495–508. doi: 10.1007/BF00218056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried G., Terenius L., Hökfelt T., Goldstein M. Evidence for differential localization of noradrenaline and neuropeptide Y in neuronal storage vesicles isolated from rat vas deferens. J Neurosci. 1985 Feb;5(2):450–458. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-02-00450.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapocsi J., Somogyi G. T., Ludvig N., Serfozo P., Harsing L. G., Jr, Woods R. J., Vizi E. S. Neurochemical evidence for two types of presynaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Neurochem Res. 1987 Feb;12(2):141–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00979530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasakov L., Ellis J., Kirkpatrick K., Milner P., Burnstock G. Direct evidence for concomitant release of noradrenaline, adenosine 5'-triphosphate and neuropeptide Y from sympathetic nerve supplying the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1988 Feb;22(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(88)90156-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagercrantz H. On the composition and function of large dense cored vesicles in sympathetic nerves. Neuroscience. 1976;1(2):81–92. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Hua X. Y., Franco-Cereceda A. Effects of neuropeptide Y (NPY) on mechanical activity and neurotransmission in the heart, vas deferens and urinary bladder of the guinea-pig. Acta Physiol Scand. 1984 Aug;121(4):325–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1984.tb07463.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Rudehill A., Sollevi A., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Hamberger B. Frequency- and reserpine-dependent chemical coding of sympathetic transmission: differential release of noradrenaline and neuropeptide Y from pig spleen. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Jan 2;63(1):96–100. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Stjarne L. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) depresses the secretion of 3H-noradrenaline and the contractile response evoked by field stimulation, in rat vas deferens. Acta Physiol Scand. 1984 Mar;120(3):477–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1984.tb07410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K. Pancreatic polypeptide family (APP, BPP, NPY and PYY) in relation to sympathetic vasoconstriction resistant to alpha-adrenoceptor blockade. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):393–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernow J., Saria A., Lundberg J. M. Mechanisms underlying pre- and postjunctional effects of neuropeptide Y in sympathetic vascular control. Acta Physiol Scand. 1986 Feb;126(2):239–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1986.tb07811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichenbacher D., Reimann W., Starke K. alpha-Adrenoceptor-mediated inhibition of noradrenaline release in rabbit brain cortex slices. Receptor properties and role of the biophase concentration of noradrenaline. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Apr;319(1):71–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00491481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon P., Burnstock G. Inhibition of excitatory junction potentials in guinea-pig vas deferens by alpha, beta-methylene-ATP: further evidence for ATP and noradrenaline as cotransmitters. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Apr 13;100(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90318-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon P., Westfall D. P. Pharmacological evidence that adenosine triphosphate and noradrenaline are co-transmitters in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1984 Feb;347:561–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P. E., Williams S. G. Use of the liquid scintillation spectrometer for determining adenosine triphosphate by the luciferase enzyme. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jun;29(3):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90323-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L., Astrand P. Relative pre- and postjunctional roles of noradrenaline and adenosine 5'-triphosphate as neurotransmitters of the sympathetic nerves of guinea-pig and mouse vas deferens. Neuroscience. 1985 Mar;14(3):929–946. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L., Lundberg J. M., Astrand P. Neuropeptide Y--a cotransmitter with noradrenaline and adenosine 5'-triphosphate in the sympathetic nerves of the mouse vas deferens? A biochemical, physiological and electropharmacological study. Neuroscience. 1986 May;18(1):151–166. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L., Lundberg J. M. On the possible roles of noradrenaline, adenosine 5'-triphosphate and neuropeptide Y as sympathetic cotransmitters in the mouse vas deferens. Prog Brain Res. 1986;68:263–278. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Carlquist M., Mutt V. Neuropeptide Y--a novel brain peptide with structural similarities to peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):659–660. doi: 10.1038/296659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Dusting H. K., Rand M. J. Pre- and postjunctional effects of neuropeptide Y on the rabbit isolated ear artery. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1988 May;15(5):411–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1988.tb01094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


