Abstract
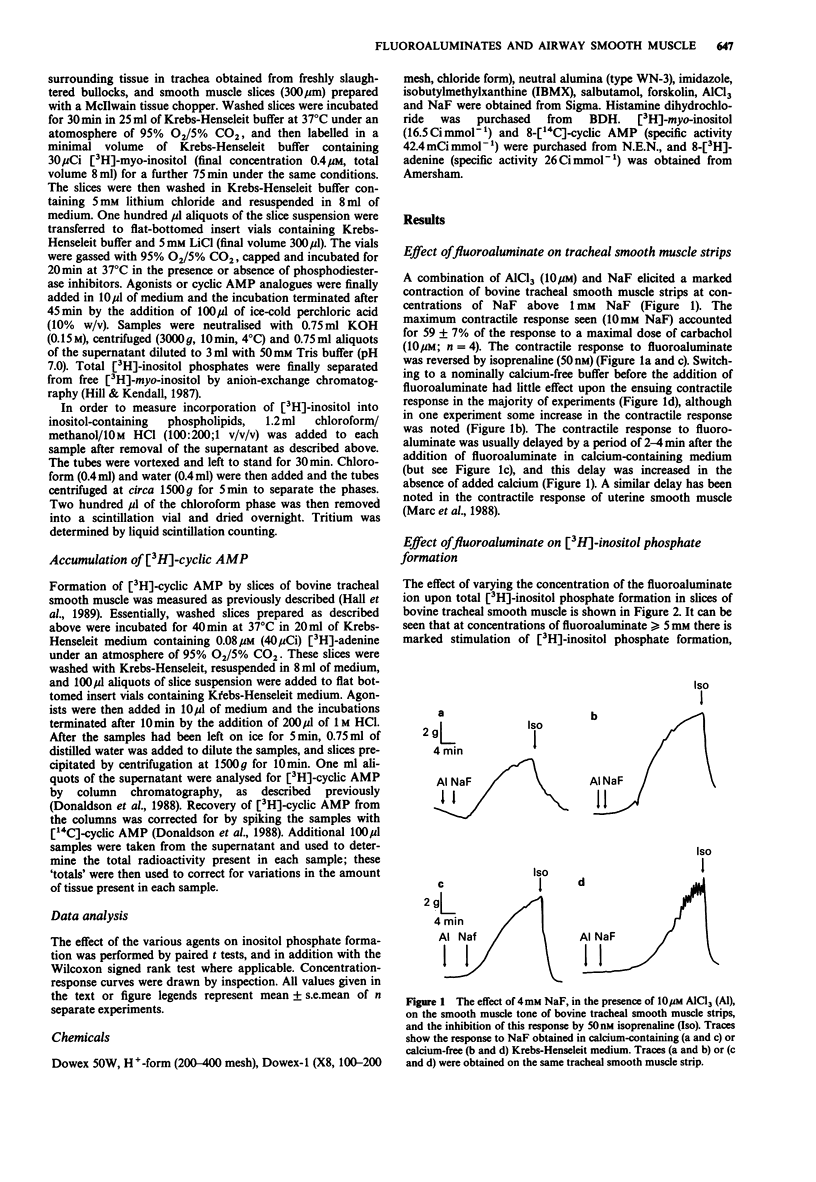
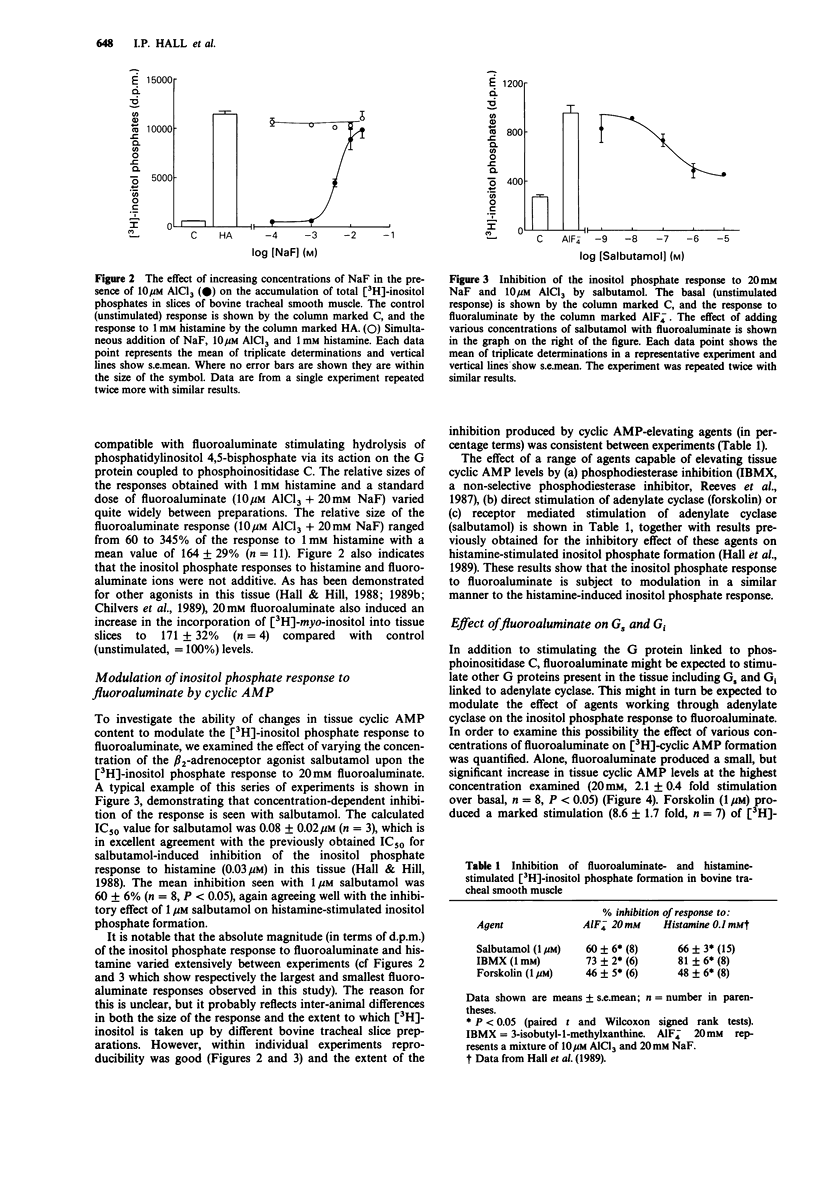
1. The effect of fluoroaluminate complexes (AlCl3 plus NaF) upon smooth muscle tone, [3H]-inositol phosphate accumulation and [3H]-cyclic AMP accumulation has been investigated in slices of bovine tracheal smooth muscle. 2. Fluoroaluminate (10 microM AlCl3 + various concentrations of NaF) elicited concentration-dependent contractions of bovine tracheal smooth muscle strips at concentrations of NaF in the range 1-10 mM. The resultant contractile response was reversed by isoprenaline (50 nM) and was preserved in calcium-free medium. 3. Fluoroaluminate stimulated [3H]-inositol phosphate formation at concentrations of NaF over 1 mM. The response to 20 mM NaF + 10 microM AlCl3 was 164 +/- 29% of the response to 1 mM histamine. Fluoroaluminate also increased the incorporation of [3H]-myo-inositol into membrane phospholipids. 4. Fluoroaluminate produced a small rise in [3H]-cyclic AMP levels (2.1 fold increase over basal with 20 mM NaF). The response to forskolin (1 microM, 8.6 fold over basal) was reduced by fluoroaluminate in a concentration-dependent manner, but still remained significantly (P less than 0.05) elevated over the response to fluoroaluminate alone. 5. The [3H]-inositol phosphate response to fluoroaluminate was inhibited by salbutamol (maximum inhibition 60%, IC50 = 0.08 microM), forskolin (1 microM, 46% inhibition) and isobutylmethylxanthine (1 mM, 73% inhibition). 6. These data suggest that inhibition of agonist-induced inositol phospholipid turnover by cyclic AMP in this tissue can occur at the post-receptor level.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Bocckino S. B., Waynick L. E., Exton J. H. Role of a guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein in the hydrolysis of hepatocyte phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate by calcium-mobilizing hormones and the control of cell calcium. Studies utilizing aluminum fluoride. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14477–14483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilvers E. R., Challiss R. A., Barnes P. J., Nahorski S. R. Mass changes of inositol(1,4,5)trisphosphate in trachealis muscle following agonist stimulation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 30;164(3):587–590. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90269-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claro E., Garcia A., Picatoste F. Carbachol and histamine stimulation of guanine-nucleotide-dependent phosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat brain cortical membranes. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 1;261(1):29–35. doi: 10.1042/bj2610029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Stutchfield J. G-proteins, the inositol lipid signalling pathway, and secretion. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 26;320(1199):247–265. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Bianca V., De Togni P., Grzeskowiak M., Vicentini L. M., Di Virgilio F. Cyclic AMP inhibition of phosphoinositide turnover in human neutrophils. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 May 29;886(3):441–447. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J., Hill S. J., Brown A. M. Kinetic studies on the mechanism by which histamine H1 receptors potentiate cyclic AMP accumulation in guinea pig cerebral cortical slices. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;33(6):626–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall I. P., Donaldson J., Hill S. J. Inhibition of histamine-stimulated inositol phospholipid hydrolysis by agents which increase cyclic AMP levels in bovine tracheal smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;97(2):603–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11992.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall I. P., Hill S. J. Beta-adrenoceptor stimulation inhibits histamine-stimulated inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in bovine tracheal smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1204–1212. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11757.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto T., Hirata M., Ito Y. A role for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in the initiation of agonist-induced contractions of dog tracheal smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Sep;86(1):191–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb09449.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. J., Kendall D. A. Studies on the adenosine-receptor mediating the augmentation of histamine-induced inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in guinea-pig cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul;91(3):661–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotlikoff M. I., Murray R. K., Reynolds E. E. Histamine-induced calcium release and phorbol antagonism in cultured airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 1):C561–C566. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.4.C561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison J. M., Brown J. K. Differential inhibitory effects of forskolin, isoproterenol, and dibutyryl cyclic adenosine monophosphate on phosphoinositide hydrolysis in canine tracheal smooth muscle. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1462–1465. doi: 10.1172/JCI113752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc S., Leiber D., Harbon S. Fluoroaluminates mimic muscarinic- and oxytocin-receptor-mediated generation of inositol phosphates and contraction in the intact guinea-pig myometrium. Role for a pertussis/cholera-toxin-insensitive G protein. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 15;255(2):705–713. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neylon C. B., Summers R. J. Inhibition by cAMP of the phosphoinositide response to alpha 1-adrenoceptor stimulation in rat kidney. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Apr 13;148(3):441–444. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park S., Rasmussen H. Activation of tracheal smooth muscle contraction: synergism between Ca2+ and activators of protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8835–8839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puurunen J., Lohse M. J., Schwabe U. Interactions between intracellular cyclic AMP and agonist-induced inositol phospholipid breakdown in isolated gastric mucosal cells of the rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;336(5):471–477. doi: 10.1007/BF00169301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Aluminum: a requirement for activation of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by fluoride. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4888–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Nishizuka Y. Counteraction of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase activation by adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate in platelets. J Biochem. 1982 Jan;91(1):403–406. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takuwa Y., Takuwa N., Rasmussen H. Carbachol induces a rapid and sustained hydrolysis of polyphosphoinositide in bovine tracheal smooth muscle measurements of the mass of polyphosphoinositides, 1,2-diacylglycerol, and phosphatidic acid. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14670–14675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takuwa Y., Takuwa N., Rasmussen H. Measurement of cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration in bovine tracheal smooth muscle using aequorin. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 1):C817–C827. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.6.C817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., McConnell R. T., Lapetina E. G. The rapid formation of inositol phosphates in human platelets by thrombin is inhibited by prostacyclin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13199–13203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


