Abstract
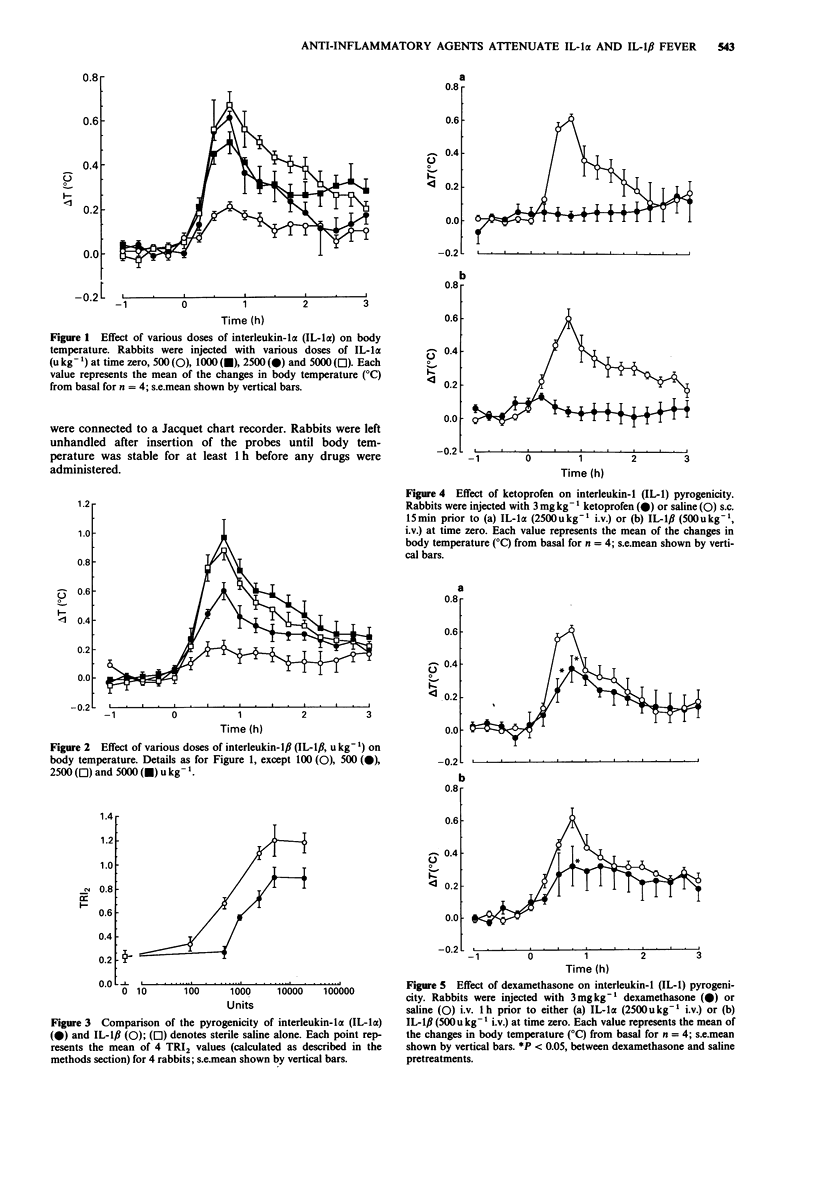
1. The pyrogenic effects of intravenously administered human recombinant interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1 alpha) and IL-1 beta were studied in the rabbit. 2. Both cytokines produced dose-related increases in body temperature. At all doses studied (100-5000 u kg-1) both cytokines elicited a monophasic increase in body temperature, beginning 15 min and reaching a maximum 45 min after administration. 3. A comparison of thermal response index (TRI2, the magnitude of febrile responses over 2 h obtained by integrating the change in temperature in degrees C against time in hours) values indicated that IL-1 beta (500 u kg-1, TRI2 = 0.69 +/- 0.04, n = 4) was approximately 5 fold more potent than IL-1 alpha (2500 u kg-1, TRI2 = 0.73 +/- 0.07, n = 4, all values are means +/- s.e.means) in elevating body temperature. delta Tmax values for the above doses of IL-1 beta and IL-1 alpha were 0.60 +/- 0.06 and 0.61 +/- 0.03 respectively. When IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta were heated for 30 min at 60 degrees C prior to administration no biological activity was observed. 4. A cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor, ketoprofen (3 mg kg-1) administered 15 min before either cytokine completely abolished the fever induced by both IL-1 alpha (2500 u kg-1) and IL-1 beta (500 u kg-1). 5. Intravenous administration of the steroidal anti-inflammatory agent dexamethasone (3 mg kg-1) 1 h before either cytokine attenuated the fever induced by IL-1 alpha (2500 u kg-1) and IL-1 beta (500 u kg-1).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abul H., Davidson J., Milton A. S., Rotondo D. Dexamethasone pre-treatment is antipyretic toward polyinosinic: polycytidylic acid, lipopolysaccharide and interleukin 1/endogenous pyrogen. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Mar;335(3):305–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00172802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auron P. E., Rosenwasser L. J., Matsushima K., Copeland T., Dinarello C. A., Oppenheim J. J., Webb A. C. Human and murine interleukin 1 possess sequence and structural similarities. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1985;2(3):169–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coceani F., Lees J., Dinarello C. A. Occurrence of interleukin-1 in cerebrospinal fluid of the conscious cat. Brain Res. 1988 Apr 19;446(2):245–250. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90883-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dascombe M. J. The pharmacology of fever. Prog Neurobiol. 1985;25(4):327–373. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(85)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Ikejima T., Warner S. J., Orencole S. F., Lonnemann G., Cannon J. G., Libby P. Interleukin 1 induces interleukin 1. I. Induction of circulating interleukin 1 in rabbits in vivo and in human mononuclear cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1902–1910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J., Blackwell G. J. Anti-inflammatory steroids induce biosynthesis of a phospholipase A2 inhibitor which prevents prostaglandin generation. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):456–459. doi: 10.1038/278456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furutani Y., Notake M., Yamayoshi M., Yamagishi J., Nomura H., Ohue M., Furuta R., Fukui T., Yamada M., Nakamura S. Cloning and characterization of the cDNAs for human and rabbit interleukin-1 precursor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 26;13(16):5869–5882. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.16.5869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher G., Taylor N., Willdridge J. Separate but complementary roles for the two forms of interleukin 1 in the growth of transformed human B lymphoblasts. Scand J Immunol. 1987 Sep;26(3):295–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1987.tb02263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian P. L., Kaffka K. L., Stern A. S., Woehle D., Benjamin W. R., Dechiara T. M., Gubler U., Farrar J. J., Mizel S. B., Lomedico P. T. Interleukin 1 alpha and interleukin 1 beta bind to the same receptor on T cells. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4509–4514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Chensue S. W., Phan S. H. Prostaglandins as endogenous mediators of interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):186–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P. T., Gubler U., Hellmann C. P., Dukovich M., Giri J. G., Pan Y. C., Collier K., Semionow R., Chua A. O., Mizel S. B. Cloning and expression of murine interleukin-1 cDNA in Escherichia coli. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):458–462. doi: 10.1038/312458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maliszewski C. R., Baker P. E., Schoenborn M. A., Davis B. S., Cosman D., Gillis S., Cerretti D. P. Cloning, sequence and expression of bovine interleukin 1 alpha and interleukin 1 beta complementary DNAs. Mol Immunol. 1988 May;25(5):429–437. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(88)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March C. J., Mosley B., Larsen A., Cerretti D. P., Braedt G., Price V., Gillis S., Henney C. S., Kronheim S. R., Grabstein K. Cloning, sequence and expression of two distinct human interleukin-1 complementary DNAs. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):641–647. doi: 10.1038/315641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton A. S., Wendlandt S. A possible role for prostaglandin E1 as a modulator for temperature regulation in the central nervous system of the cat. J Physiol. 1970 Apr;207(2):76P–77P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton A. S., Wendlandt S. Effects on body temperature of prostaglandins of the A, E and F series on injection into the third ventricle of unanaesthetized cats and rabbits. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(2):325–336. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B., Dayer J. M., Krane S. M., Mergenhagen S. E. Stimulation of rheumatoid synovial cell collagenase and prostaglandin production by partially purified lymphocyte-activating factor (interleukin 1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2474–2477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton R. C., Covington M. The activation of human fibroblast prostaglandin E production by interleukin 1. Cell Immunol. 1987 Dec;110(2):338–349. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(87)90127-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothwell N. J. CRF is involved in the pyrogenic and thermogenic effects of interleukin 1 beta in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 1):E111–E115. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.256.1.E111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotondo D., Abul H. T., Milton A. S., Davidson J. Pyrogenic immunomodulators increase the level of prostaglandin E2 in the blood simultaneously with the onset of fever. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep 13;154(2):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotondo D., Abul H. T., Milton A. S., Davidson J. The pyrogenic actions of the interferon-inducer, polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid are antagonised by ketoprofen. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun 4;137(2-3):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90231-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims J. E., March C. J., Cosman D., Widmer M. B., MacDonald H. R., McMahan C. J., Grubin C. E., Wignall J. M., Jackson J. L., Call S. M. cDNA expression cloning of the IL-1 receptor, a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):585–589. doi: 10.1126/science.2969618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt J. T., Bernheim H. A. Differences in endogenous pyrogen fevers induced by iv and icv routes in rabbits. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1985 Aug;59(2):342–347. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1985.59.2.342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao D. M., Levine L. Stimulation of arachidonic acid metabolism: differences in potencies of recombinant human interleukin-1 alpha and interleukin-1 beta on two cell types. Prostaglandins. 1986 Nov;32(5):709–718. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(86)90193-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


