Abstract
1. The effects of temperature on the time course of desensitization induced by acetylcholine and histamine, and on the recovery from desensitization were studied in the longitudinal muscle of the guinea-pig ileum. 2. Self- and cross-desensitization produced by acetylcholine (10(-5) M) occurred rapidly in the first 10 min of exposure to the agonist, with the same time course and the same degree of desensitization over the temperature range of 11 degrees C to 31 degrees C. 3. Self-desensitization produced by histamine (10(-5) M) also occurred rapidly in the first 10 min of exposure to the agonist, and showed great temperature-dependence, especially at 11 degrees C and 21 degrees C, but scarcely occurred at 6 degrees C. 4. Cross-desensitization produced by histamine developed gradually with time and showed a moderate temperature-dependence between 11 degrees C and 31 degrees C, but scarcely occurred at 6 degrees C. 5. The recovery processes from desensitization showed marked temperature-dependence. Recovery was halted completely at 11 degrees C. 6. These studies suggest that acetylcholine-induced desensitization may be attributed to a single non-specific mechanism. Histamine-induced desensitization may be due to at least two mechanisms: it occurs in both a specific and non-specific manner. Each of these desensitizations can be characterized by its unique temperature-dependence.
Full text
PDF
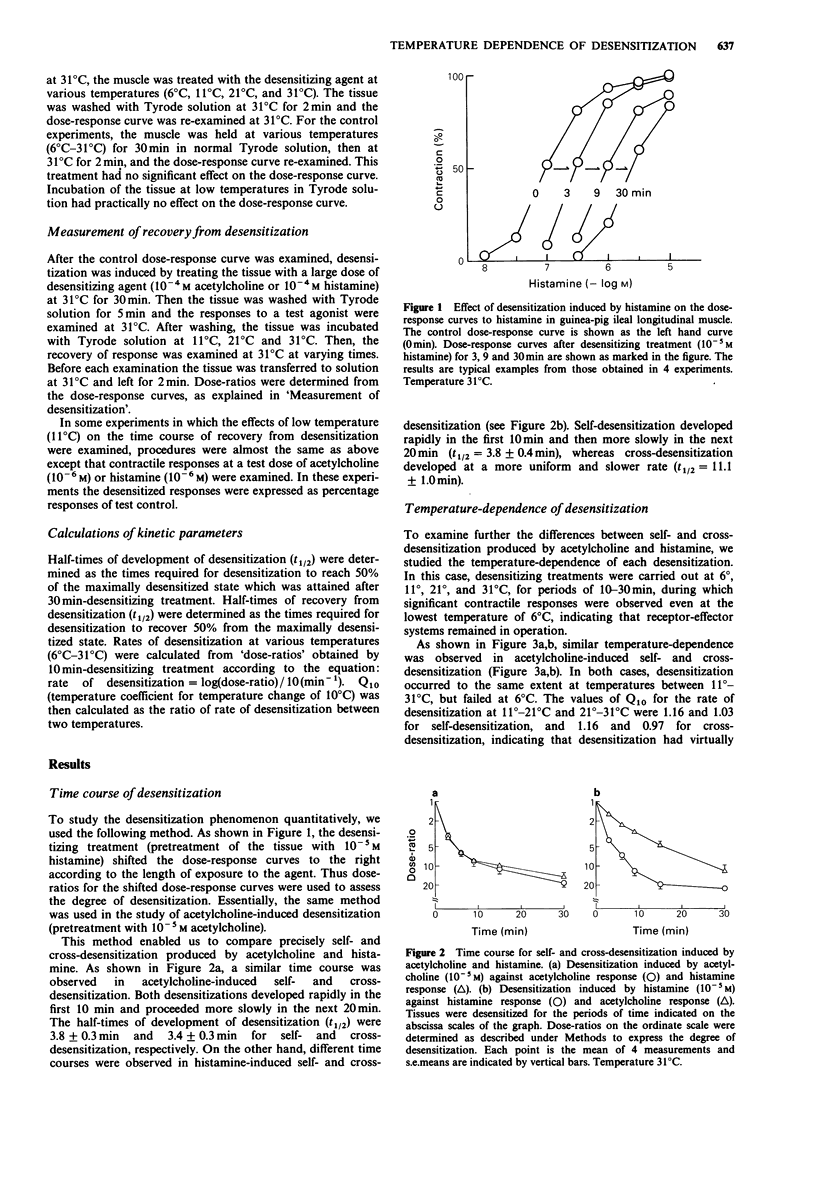
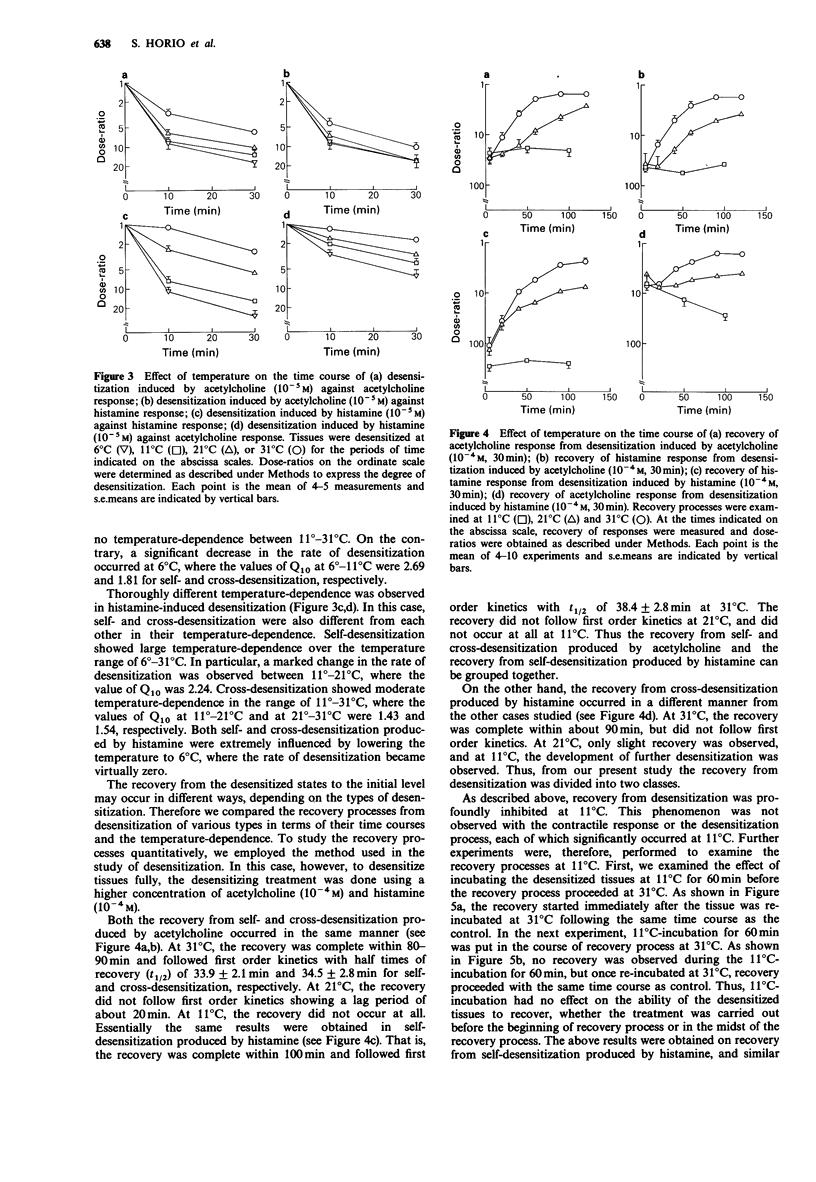


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aboulafia J., Capocci H., Paiva A. C., Paiva T. B. Sodium-dependence of the non-specific desensitization of the guinea-pig ileum induced by acetylcholine and histamine. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Feb;90(2):347–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb08964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielkiewicz B., Cook D. A. The mechanism of the histamine-induced desensitization of guinea-pig ileum. Gen Pharmacol. 1984;15(1):51–54. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(84)90080-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALE M. M. An inhibitory effect of acetycholine on the response of the guineapig ileum to histamine. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1958 Mar;13(1):17–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1958.tb00183.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Fakahany E., Richelson E. Temperature dependence of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor activation, desensitization, and resensitization. J Neurochem. 1980 May;34(5):1288–1295. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb09973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frye L. D., Edidin M. The rapid intermixing of cell surface antigens after formation of mouse-human heterokaryons. J Cell Sci. 1970 Sep;7(2):319–335. doi: 10.1242/jcs.7.2.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosselin R. E., Gosselin R. S. Tachyphylaxis of guinea-pig ileum to histamine and furtrethonium. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Feb;184(2):494–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden T. K., Petch L. A., Traynelis S. F., Waldo G. L. Agonist-induced alteration in the membrane form of muscarinic cholinergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13060–13066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi H., Takeyasu K., Uchida S., Yoshida H. Receptor-activated and energy-dependent decrease of muscarinic cholinergic receptors in guinea-pig vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Nov 5;75(4):305–311. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90558-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hishinuma S., Uchida M. K. Short-term desensitization of guinea-pig taenia caecum induced by carbachol occurs at intracellular Ca stores and that by histamine at H1-receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;94(3):882–889. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11600.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homburger V., Lucas M., Cantau B., Barabe J., Penit J., Bockaert J. Further evidence that desensitization of beta-adrenergic-sensitive adenylate cyclase proceeds in two steps. Modification of the coupling and loss of beta-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10436–10444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James-Kracke M. R., Roufogalis B. D. Alteration of smooth muscle contractility after muscarinic agonist-induced K+ loss. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr;72(4):609–619. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb09141.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joiner P. D. Studies on the loss of acetylcholine sensitivity in ileal muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Sep;186(3):552–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenakin T. P., Cook D. A. The effect of desensitization on the antagonism of the histamine response by phenoxybenzamine. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 May;17(3):309–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magazanik L. G., Vyskocit F. The effect of temperature on desensitization kinetics at the post-synaptic membrane of the frog muscle fibre. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):285–300. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern R., Bluth R. Studies on the loss of sensitivity in smooth muscle. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1976;35(11):K69–K75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D., ROTHSCHILD A. M. THE CHANGES IN RESPONSE AND IN IONIC CONTENT OF SMOOTH MUSCLE PRODUCED BY ACETYLCHOLINE ACTON AND BY CALCIUM DEFICIENCY. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1965 Apr;24:437–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1965.tb01731.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANG H. P. STIMULANT ACTIONS OF VOLATILE ANAESTHETICS ON SMOOTH MUSCLE. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Apr;22:356–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb02040.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel H., Jim K., Bolger G. T., Gengo P., Triggle D. J. Specific and non-specific desensitization of guinea-pig ileal smooth muscle. J Auton Pharmacol. 1984 Jun;4(2):109–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1984.tb00088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel H., Triggle D. J. Inhibition by concanavalin A, dansylcadaverine and bacitracin of muscarinic receptor-mediated desensitization in guinea-pig Ileal smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jun;225(3):534–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahara I., Edelman G. M. Restriction of the mobility of lymphocyte immunoglobulin receptors by concanavalin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):608–612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


