Abstract
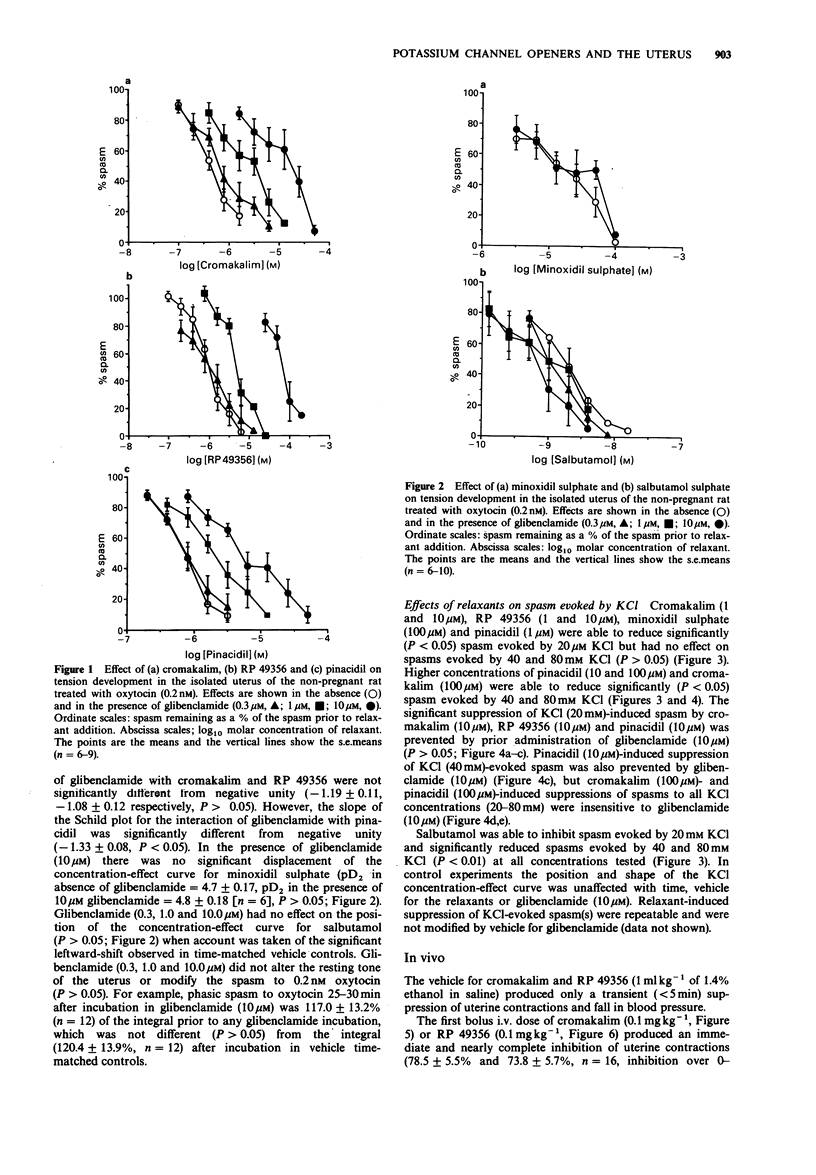
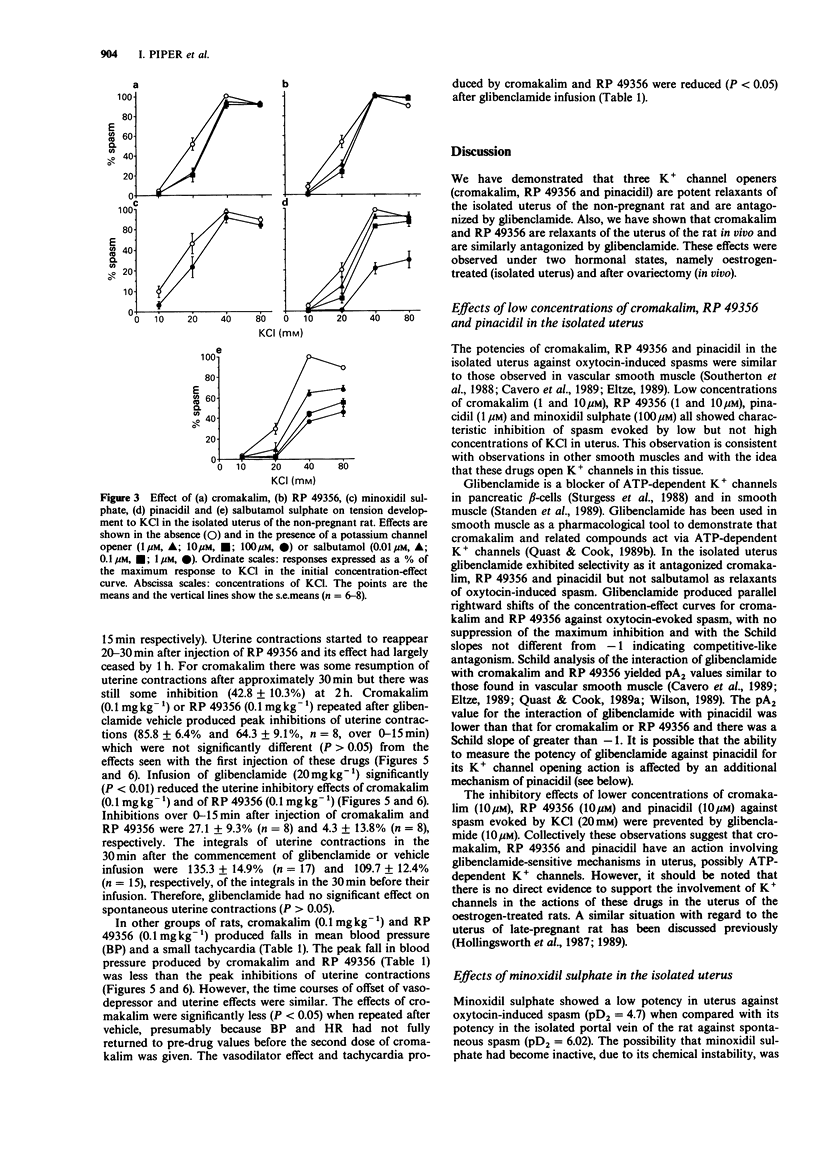
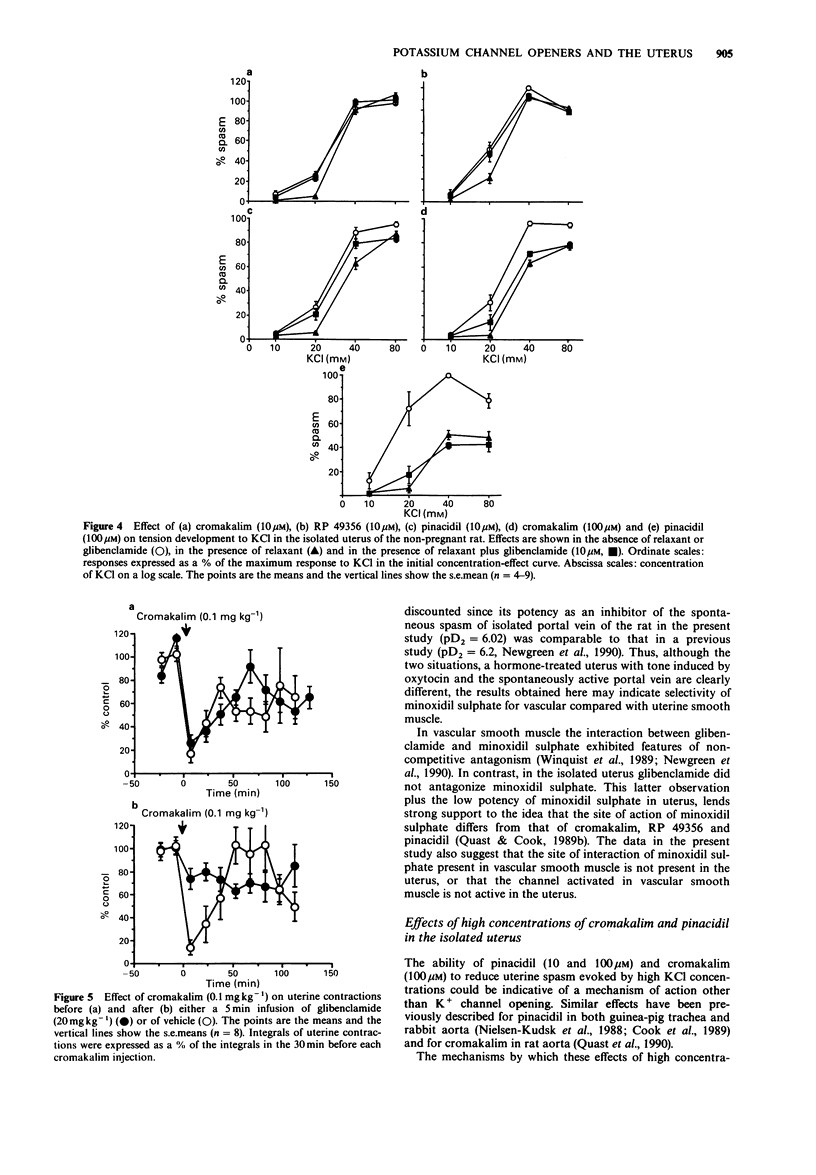
1. The ability of several potassium (K+) channel openers to inhibit spasm of the uterus of the nonpregnant rat and their susceptibility to antagonism by glibenclamide was assessed in vitro and in vivo. 2. In the isolated uterus exposed to oxytocin (0.2 nM), cromakalim, RP 49356 and pinacidil were of similar potency (mean pD2 = 6.4, 6.0 and 6.2 respectively) while minoxidil sulphate was of lower potency (pD2 = 4.7). Glibenclamide antagonized cromakalim and RP 49356 with the interactions consistent with competitive antagonism (mean pA2 of 6.57 and 7.00 respectively). Glibenclamide also antagonized pinacidil (pA2 = 6.22) but the slope of the Schild plot was significantly greater than -1. Neither salbutamol nor minoxidil sulphate was antagonized by glibenclamide (10 microM). 3. Cromakalim (1 and 10 microM), RP 49356 (1 and 10 microM), pinacidil (1 microM) and minoxidil sulphate (100 microM) suppressed spasm evoked by low (less than 40 mM) but not high (greater than or equal to 40 mM) KCl concentrations. Glibenclamide (10 microM) prevented cromakalim (10 microM)-, RP 49356 (10 microM)- and pinacidil (10 microM)-induced suppression of KCl (20 mM)-evoked spasm. Pinacidil (10 and 100 microM), cromakalim (100 microM) and salbutamol (0.01-1 microM) inhibited spasm evoked by all concentrations of KCl (10-80 mM). Suppression of spasm evoked by KCl (10-80 mM) by cromakalim (100 microM) and pinacidil (100 microM) was insensitive to glibenclamide (10 microM). 4. Cromakalim (0.1 mg kg-1) and RP 49356 (0.1 mg kg-1), given by i.v. bolus injection, inhibited uterine contractions, produced a fall in blood pressure and a slight tachycardia in the conscious ovariectomized rat.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
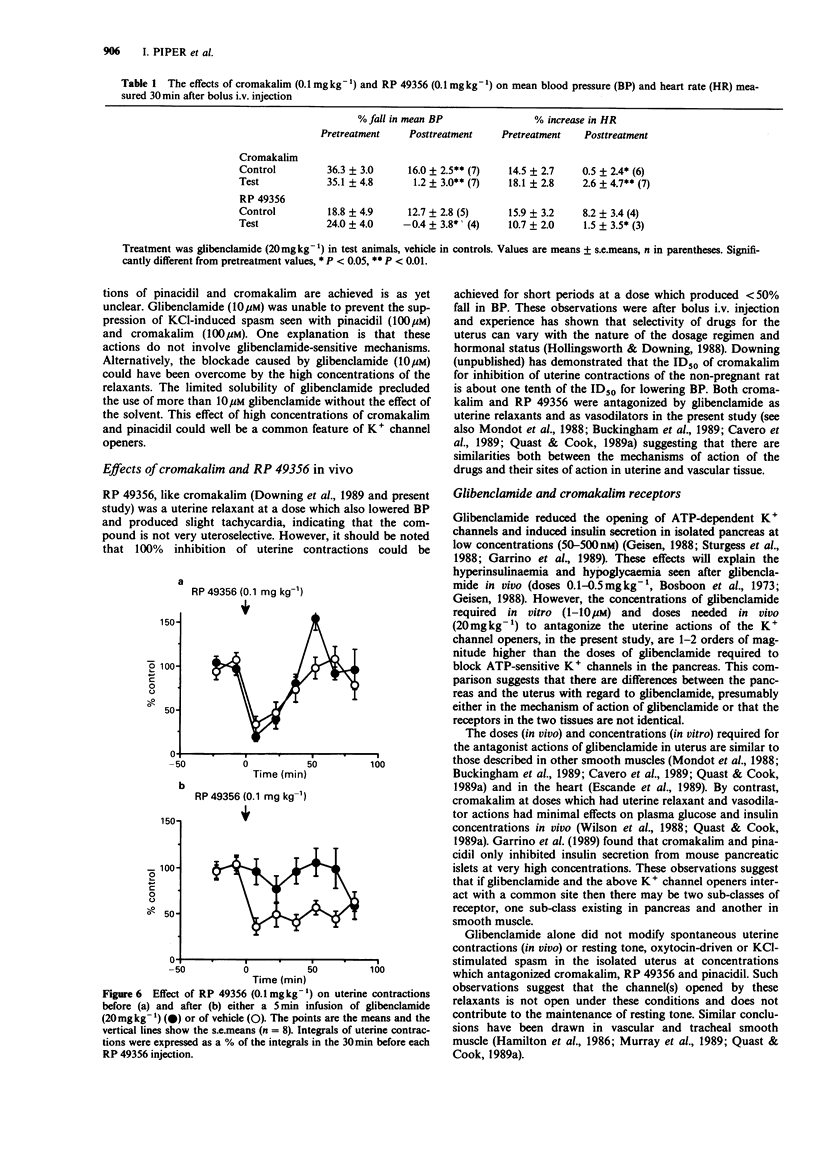
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosboom R. S., Zweens J., Bouman P. R. Effects of feeding and fasting on the insulin secretory response to glucose and sulfonylureas in intact rats and isolated perfused rat pancreas. Diabetologia. 1973 Aug;9(4):243–250. doi: 10.1007/BF01221849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham R. E., Hamilton T. C., Howlett D. R., Mootoo S., Wilson C. Inhibition by glibenclamide of the vasorelaxant action of cromakalim in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):57–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11923.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavero I., Mondot S., Mestre M. Vasorelaxant effects of cromakalim in rats are mediated by glibenclamide-sensitive potassium channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Mar;248(3):1261–1268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook N. S. The pharmacology of potassium channels and their therapeutic potential. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Jan;9(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing S. J., Hollingsworth M. Nifedipine kinetics in the rat and relationship between its serum concentrations and uterine and cardiovascular effects. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;95(1):23–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb16544.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing S. J., Miller M., Hollingsworth M. Tolerance to cromakalim in the rat uterus in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;96(3):732–738. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11875.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eltze M. Glibenclamide is a competitive antagonist of cromakalim, pinacidil and RP 49356 in guinea-pig pulmonary artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 20;165(2-3):231–239. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90717-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escande D., Thuringer D., Le Guern S., Courteix J., Laville M., Cavero I. Potassium channel openers act through an activation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in guinea-pig cardiac myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Sep;414(6):669–675. doi: 10.1007/BF00582134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrino M. G., Plant T. D., Henquin J. C. Effects of putative activators of K+ channels in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):957–965. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14626.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisen K. Special pharmacology of the new sulfonylurea glimepiride. Arzneimittelforschung. 1988 Aug;38(8):1120–1130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger S. E., Hollingsworth M., Weston A. H. A comparison of several calcium antagonists on uterine, vascular and cardiac muscles from the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 May;85(1):255–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. C., Weir S. W., Weston A. H. Comparison of the effects of BRL 34915 and verapamil on electrical and mechanical activity in rat portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):103–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09476.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. C., Weston A. H. Cromakalim, nicorandil and pinacidil: novel drugs which open potassium channels in smooth muscle. Gen Pharmacol. 1989;20(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(89)90052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingsworth M., Amédée T., Edwards D., Mironneau J., Savineau J. P., Small R. C., Weston A. H. The relaxant action of BRL 34915 in rat uterus. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Aug;91(4):803–813. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11279.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. A., Boyle J. P., Small R. C. Cromakalim-induced relaxation of guinea-pig isolated trachealis: antagonism by glibenclamide and by phentolamine. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):865–874. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newgreen D. T., Bray K. M., McHarg A. D., Weston A. H., Duty S., Brown B. S., Kay P. B., Edwards G., Longmore J., Southerton J. S. The action of diazoxide and minoxidil sulphate on rat blood vessels: a comparison with cromakalim. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):605–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen-Kudsk J. E., Mellemkjaer S., Siggaard C., Nielsen C. B. Effects of pinacidil on guinea-pig airway smooth muscle contracted by asthma mediators. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov 22;157(2-3):221–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90386-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper I., Hollingsworth M. Cromakalim, RP49356, pinacidil and minoxidil sulphate in the rat uterus and their antagonism by glibenclamide. Smooth Muscle Research Group. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98 (Suppl):807P–807P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast U., Cook N. S. In vitro and in vivo comparison of two K+ channel openers, diazoxide and cromakalim, and their inhibition by glibenclamide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jul;250(1):261–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quast U., Cook N. S. Moving together: K+ channel openers and ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Nov;10(11):431–435. doi: 10.1016/S0165-6147(89)80003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southerton J. S., Weston A. H., Bray K. M., Newgreen D. T., Taylor S. G. The potassium channel opening action of pinacidil; studies using biochemical, ion flux and microelectrode techniques. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;338(3):310–318. doi: 10.1007/BF00173406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Quayle J. M., Davies N. W., Brayden J. E., Huang Y., Nelson M. T. Hyperpolarizing vasodilators activate ATP-sensitive K+ channels in arterial smooth muscle. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):177–180. doi: 10.1126/science.2501869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess N. C., Kozlowski R. Z., Carrington C. A., Hales C. N., Ashford M. L. Effects of sulphonylureas and diazoxide on insulin secretion and nucleotide-sensitive channels in an insulin-secreting cell line. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;95(1):83–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb16551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. Inhibition by sulphonylureas of vasorelaxation induced by K+ channel activators in vitro. J Auton Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;9(1):71–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1989.tb00198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winquist R. J., Heaney L. A., Wallace A. A., Baskin E. P., Stein R. B., Garcia M. L., Kaczorowski G. J. Glyburide blocks the relaxation response to BRL 34915 (cromakalim), minoxidil sulfate and diazoxide in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jan;248(1):149–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


