Abstract
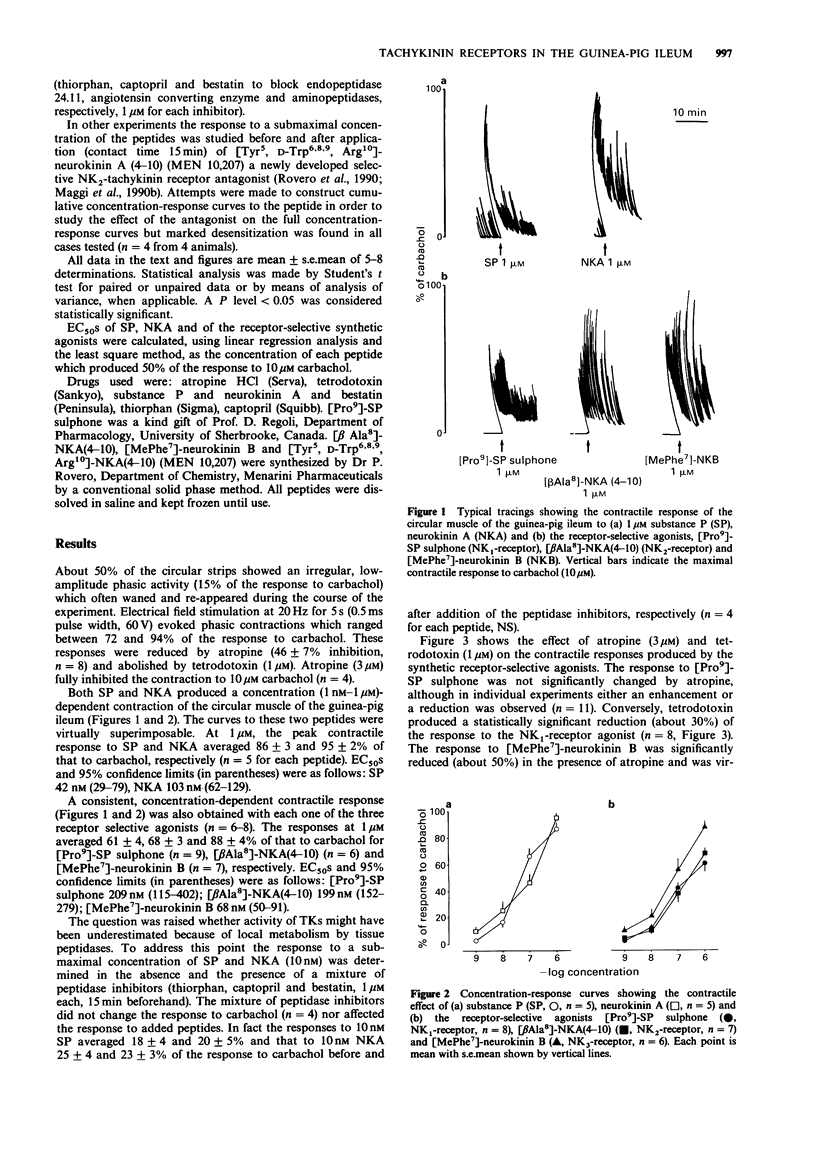
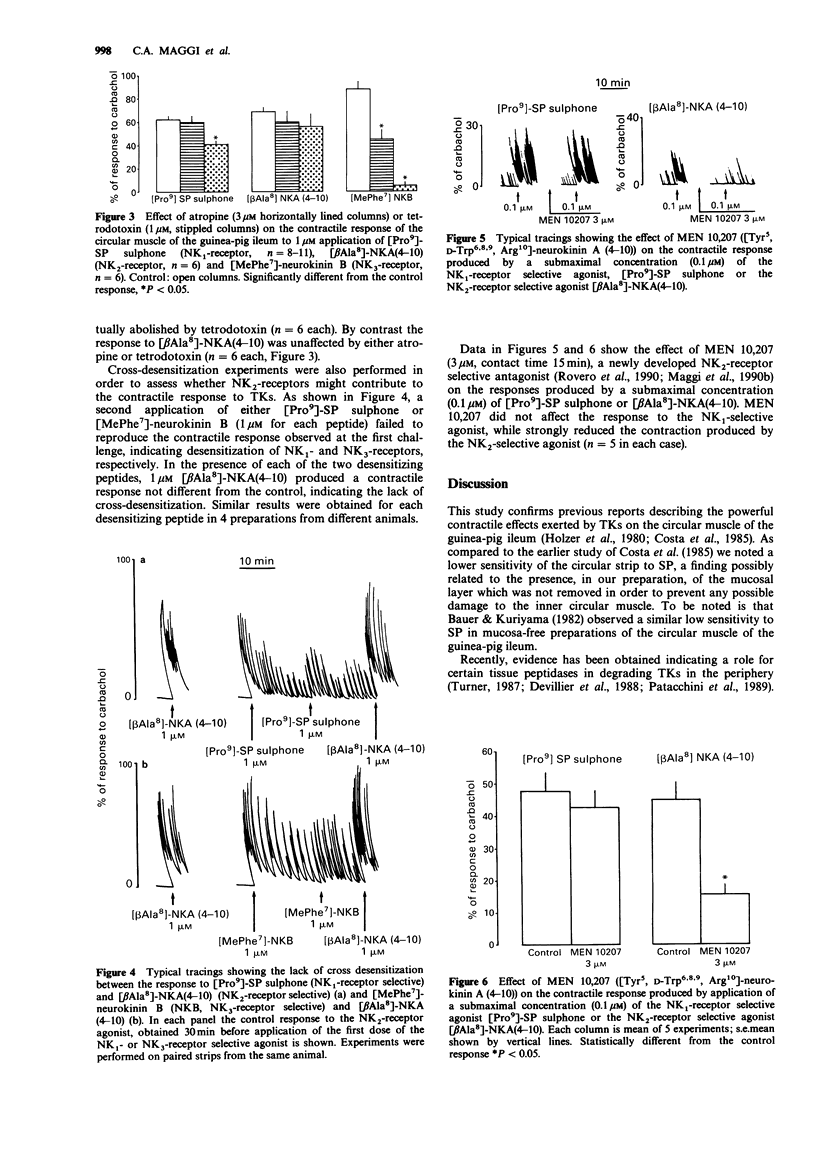
1. We have studied the mechanical response of circular strips of the guinea-pig ileum to tachykinins and characterized the receptors involved by means of receptor-selective agonists. 2. The strips responded to both substance P (SP) and neurokinin A (NKA), as well as to [Pro9]-SP sulphone (selective NK1-receptor agonist), [beta Ala8]-NKA(4-10) (selective NK2-receptor agonist) and [MePhe7]-neurokinin B (selective NK3-receptor agonist). The ED50s of the various peptides (calculated as the concentration of agonist which produced 50% of the response to 10 microM carbachol) were similar, in the range of 40-200 nM, i.e. no clearcut rank order of potency was evident. 3. The response to a submaximal (10 nM) concentration of SP or NKA was unaffected in the presence of peptidase inhibitors (thiorphan, captopril and bestatin, 1 microM each). 4. The response to the NK1-agonist was totally atropine-resistant, but was reduced (about 30% inhibition) by tetrodotoxin. The response to the NK3-receptor agonist was halved by atropine and abolished by tetrodotoxin. The response to the NK2-agonist was unaffected by either atropine or tetrodotoxin. 5. The response to the selective NK2-agonist was unchanged after desensitization of NK1- or NK3-receptors. 6. The response to the NK2-selective agonist was strongly inhibited by [Tyr5, D-Trp6,8,9, Arg10]-NKA(4-10) (MEN 10,207) a selective NK2-receptor antagonist which did not modify the response to the NK1-selective agonist. 7. Our findings indicate that all the three known types of tachykinin receptors mediate the contractile response of the circular muscle of the guinea-pig ileum to peptides of this family.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barthó L., Holzer P., Leander S., Lembeck F. Evidence for an involvement of substance P, but not cholecystokinin-like peptides, in hexamethonium-resistant intestinal peristalsis. Neuroscience. 1989;28(1):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90245-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthó L., Holzer P. Search for a physiological role of substance P in gastrointestinal motility. Neuroscience. 1985 Sep;16(1):1–32. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer V., Kuriyama H. The nature of non-cholinergic, non-adrenergic transmission in longitudinal and circular muscles of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1982 Nov;332:375–391. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burcher E., Buck S. H., Lovenberg W., O'Donohue T. L. Characterization and autoradiographic localization of multiple tachykinin binding sites in gastrointestinal tract and bladder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Mar;236(3):819–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Furness J. B., Llewellyn-Smith I. J., Cuello A. C. Projections of substance P-containing neurons within the guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience. 1981;6(3):411–424. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Furness J. B., Pullin C. O., Bornstein J. Substance P enteric neurons mediate non-cholinergic transmission to the circular muscle of the guinea-pig intestine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;328(4):446–453. doi: 10.1007/BF00692914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devillier P., Advenier C., Drapeau G., Marsac J., Regoli D. Comparison of the effects of epithelium removal and of an enkephalinase inhibitor on the neurokinin-induced contractions of guinea-pig isolated trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;94(3):675–684. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11575.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dion S., D'Orléans-Juste P., Drapeau G., Rhaleb N. E., Rouissi N., Tousignant C., Regoli D. Characterization of neurokinin receptors in various isolated organs by the use of selective agonists. Life Sci. 1987 Nov 16;41(20):2269–2278. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90538-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnerer J., Holzer P., Lembeck F. Release of dynorphin, somatostatin and substance P from the vascularly perfused small intestine of the guinea-pig during peristalsis. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Dec;83(4):919–925. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16532.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G., D'Orléans-Juste P., Dion S., Rhaleb N. E., Rouissi N. E., Regoli D. Selective agonists for substance P and neurokinin receptors. Neuropeptides. 1987 Jul;10(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(87)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Daniel E. E. Substance P: a potent inhibitor of the canine small intestine in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jan;250(1 Pt 1):G21–G27. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.250.1.G21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., McDonald T. J., Alford L., Kostolanska F. Tachykinin activation of muscarinic inhibition in canine small intestine is SPP in nature. Life Sci. 1986 Sep 29;39(13):1123–1128. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90342-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco R., Costa M., Furness J. B. Evidence for the release of endogenous substance P from intestinal nerves. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Apr;306(3):195–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00507103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guard S., Watson S. P. Evidence for neurokinin-3 receptor-mediated tachykinin release in the guinea-pig ileum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Dec 15;144(3):409–412. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90398-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer P. Ascending enteric reflex: multiple neurotransmitter systems and interactions. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 1):G540–G545. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.3.G540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer P., Lembeck F., Donnerer J. Caerulein, substance P, serotonin and cholinomimetics induce rhythmic contractions of the intestinal circular muscle. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;312(2):131–137. doi: 10.1007/BF00569721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby H. I., Lopez I., Wright D., Vaught J. L. Differentiation of multiple neurokinin receptors in the guinea pig ileum. Life Sci. 1986 Nov 24;39(21):1995–2003. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90323-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbinger H., Stauss P., Erlhof I., Holzer P. Antagonist discrimination between subtypes of tachykinin receptors in the guinea-pig ileum. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Oct;334(2):181–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00505819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer R., Gilon C., Chorev M., Selinger Z. Characterization of a neurokinin B receptor site in rat brain using a highly selective radioligand. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10257–10263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer R., Gilon C., Chorev M., Selinger Z. Desensitization with a selective agonist discriminates between multiple tachykinin receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 May;245(2):639–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. M., Iversen L. L., Hanley M. R., Sandberg B. E. The possible existence of multiple receptors for substance P. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Mar;318(4):281–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00501166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llewellyn-Smith I. J., Furness J. B., Costa M. Ultrastructural analysis of substance P-immunoreactive nerve fibers in myenteric ganglia of guinea pig small intestine. J Neurosci. 1989 Jan;9(1):167–174. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-01-00167.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llewellyn-Smith I. J., Furness J. B., Gibbins I. L., Costa M. Quantitative ultrastructural analysis of enkephalin-, substance P-, and VIP-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the circular muscle of the guinea pig small intestine. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Jun 1;272(1):139–148. doi: 10.1002/cne.902720110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Giuliani S., Rovero P., Dion S., Regoli D., Giachetti A., Meli A. Competitive antagonists discriminate between NK2 tachykinin receptor subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):589–592. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15851.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Santicioli P., Giuliani S., Turini D., Barbanti G., Beneforti P., Misuri D., Meli A. Human isolated small intestine: motor responses of the longitudinal muscle to field stimulation and exogenous neuropeptides. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Apr;339(4):415–423. doi: 10.1007/BF00736056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Santicioli P., Giuliani S., Turini D., Barbanti G., Giachetti A., Meli A. Human isolated ileum: motor responses of the circular muscle to electrical field stimulation and exogenous neuropeptides. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;341(3):256–261. doi: 10.1007/BF00169740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patacchini R., Maggi C. A., Rovero P., Regoli D., Drapeau G., Meli A. Effect of thiorphan on tachykinin-induced potentiation of nerve-mediated contractions of the rat isolated vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Aug;250(2):678–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovero P., Pestellini V., Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Regoli D., Giachetti A. A highly selective NK-2 tachykinin receptor antagonist containing D-tryptophan. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan 3;175(1):113–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovero P., Pestellini V., Rhaleb N. E., Dion S., Rouissi N., Tousignant C., Télémaque S., Drapeau G., Regoli D. Structure-activity studies of neurokinin A. Neuropeptides. 1989 May-Jun;13(4):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(89)90080-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. K., Furness J. B. Reflex changes in circular muscle activity elicited by stroking the mucosa: an electrophysiological analysis in the isolated guinea-pig ileum. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1988 Dec;25(2-3):205–218. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(88)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Too H. P., Cordova J. L., Maggio J. E. A novel radioimmunoassay for neuromedin K. I. Absence of neuromedin K-like immunoreactivity in guinea pig ileum and urinary bladder. II. Heterogeneity of tachykinins in guinea pig tissues. Regul Pept. 1989 Sep-Oct;26(2):93–105. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(89)90001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


