Abstract
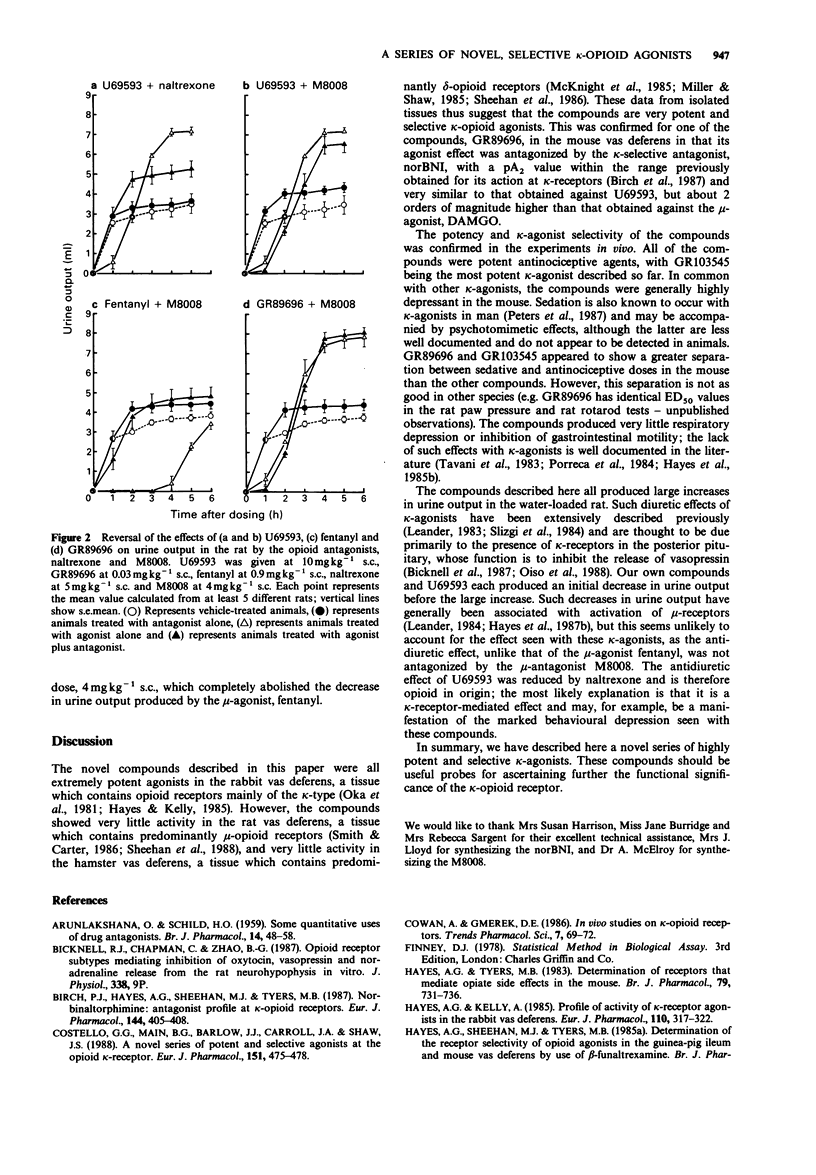
1. This paper describes the opioid receptor pharmacology and in vivo activity of several novel benzene-acetamidopiperidine and benzeneacetamidopiperazine analogues. 2. These compounds all showed potent, naloxone-reversible, full agonist activity in the field-stimulated rabbit vas deferens, indicating that they are kappa-opioid agonists; but showed very little activity in the rat or hamster vas deferens, indicating good selectivity with regard to mu- and delta-opioid receptors. 3. They were all potent antinociceptive agents, the most potent compound, GR 103545, having an ED50 value in the mouse abdominal constriction test of 0.25 micrograms kg-1 s.c. The compounds also produced sedation and diuresis, but had little effect on respiration rate or gastrointestinal motility. 4. It is concluded that the seven novel compounds described are all potent and selective agonists for the kappa-opioid receptor.
Full text
PDF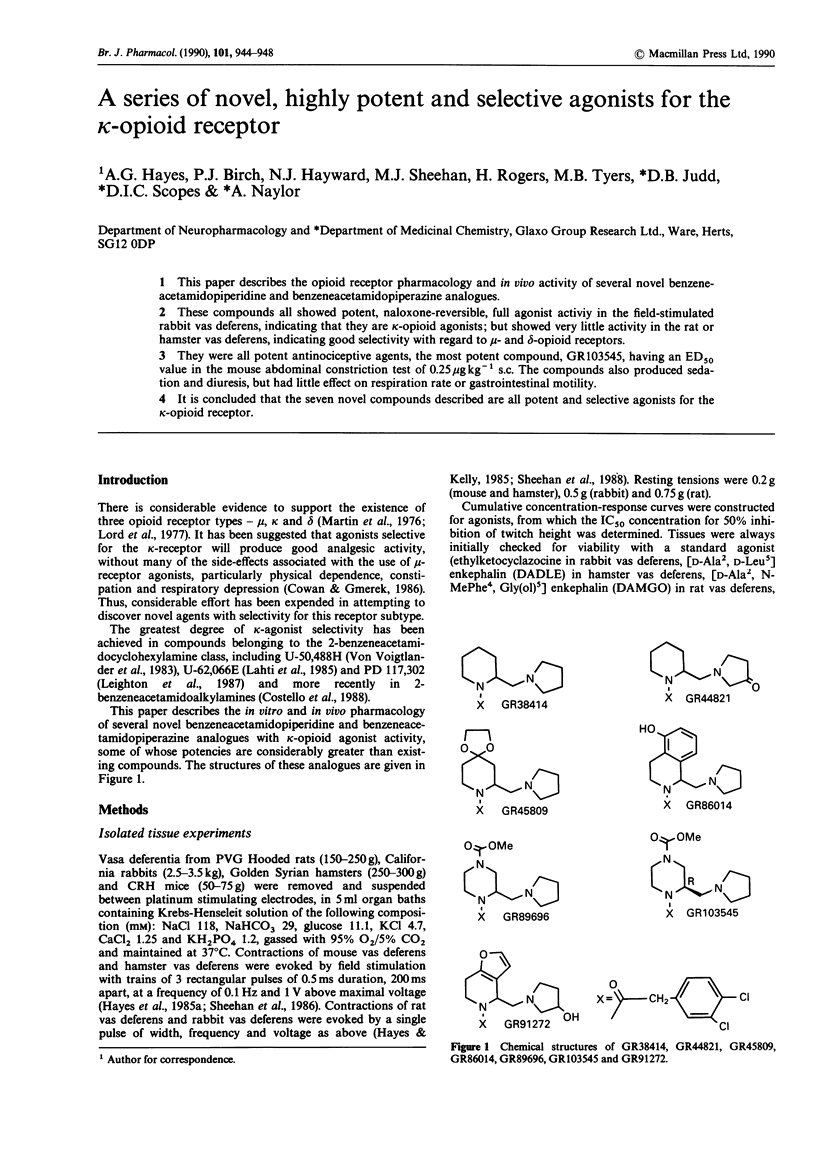



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch P. J., Hayes A. G., Sheehan M. J., Tyers M. B. Norbinaltorphimine: antagonist profile at kappa opioid receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Dec 15;144(3):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90397-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello G. F., Main B. G., Barlow J. J., Carroll J. A., Shaw J. S. A novel series of potent and selective agonists at the opioid kappa-receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 14;151(3):475–478. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90546-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes A. G., Sheehan M. J., Tyers M. B. Differential sensitivity of models of antinociception in the rat, mouse and guinea-pig to mu- and kappa-opioid receptor agonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Aug;91(4):823–832. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11281.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes A. G., Skingle M., Tyers M. B. Effect of beta-funaltrexamine on opioid side-effects produced by morphine and U-50, 488H. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;37(11):841–843. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1985.tb04985.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes A. G., Skingle M., Tyers M. B. Evaluation of the receptor selectivities of opioid drugs by investigating the block of their effect on urine output by beta-funaltrexamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Mar;240(3):984–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes A. G., Tyers M. B. Determination of receptors that mediate opiate side effects in the mouse. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jul;79(3):731–736. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10011.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes A., Kelly A. Profile of activity of kappa receptor agonists in the rabbit vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Apr 16;110(3):317–322. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90558-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahti R. A., Mickelson M. M., McCall J. M., Von Voigtlander P. F. [3H]U-69593 a highly selective ligand for the opioid kappa receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 26;109(2):281–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90431-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leander J. D. A kappa opioid effect: increased urination in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jan;224(1):89–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leander J. D. Effects of full and partial kappa agonists and mu agonists on urine output of normally hydrated rats. Neuropeptides. 1984 Dec;5(1-3):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(84)90083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton G. E., Johnson M. A., Meecham K. G., Hill R. G., Hughes J. Pharmacological profile of PD 117302, a selective kappa-opioid agonist. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Dec;92(4):915–922. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11398.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R., Eades C. G., Thompson J. A., Huppler R. E., Gilbert P. E. The effects of morphine- and nalorphine- like drugs in the nondependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jun;197(3):517–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight A. T., Corbett A. D., Marcoli M., Kosterlitz H. W. The opioid receptors in the hamster vas deferens are of the delta-type. Neuropharmacology. 1985 Nov;24(11):1011–1017. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(85)90184-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L., Shaw J. S. Characterisation of the delta-opioid receptor on the hamster vas deferens. Neuropeptides. 1985 Dec;6(6):531–536. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(85)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oiso Y., Iwasaki Y., Kondo K., Takatsuki K., Tomita A. Effect of the opioid kappa-receptor agonist U50488H on the secretion of arginine vasopressin. Study on the mechanism of U50488H-induced diuresis. Neuroendocrinology. 1988 Dec;48(6):658–662. doi: 10.1159/000125078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Negishi K., Suda M., Matsumiya T., Inazu T., Ueki M. Rabbit vas deferens: a specific bioassay for opioid kappa-receptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 17;73(2-3):235–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G. R., Ward N. J., Antal E. G., Lai P. Y., deMaar E. W. Diuretic actions in man of a selective kappa opioid agonist: U-62,066E. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Jan;240(1):128–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porreca F., Mosberg H. I., Hurst R., Hruby V. J., Burks T. F. Roles of mu, delta and kappa opioid receptors in spinal and supraspinal mediation of gastrointestinal transit effects and hot-plate analgesia in the mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Aug;230(2):341–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan M. J., Hayes A. G., Tyers M. B. Lack of evidence for epsilon-opioid receptors in the rat vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep 23;154(3):237–245. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90197-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan M. J., Hayes A. G., Tyers M. B. Pharmacology of delta-opioid receptors in the hamster vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct 14;130(1-2):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90183-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slizgi G. R., Taylor C. J., Ludens J. H. Effects of the highly selective kappa opioid, U-50, 488, on renal function in the anesthetized dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Sep;230(3):641–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. F., Carter A. Delta receptors in the rat vas deferens. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1986 Dec;284(2):181–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavani A., Gambino M. C., Petrillo P. The opioid kappa-selective compound U-50,488H does not inhibit intestinal propulsion in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1984 May;36(5):343–344. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1984.tb04391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonvoigtlander P. F., Lahti R. A., Ludens J. H. U-50,488: a selective and structurally novel non-Mu (kappa) opioid agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jan;224(1):7–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


