Abstract
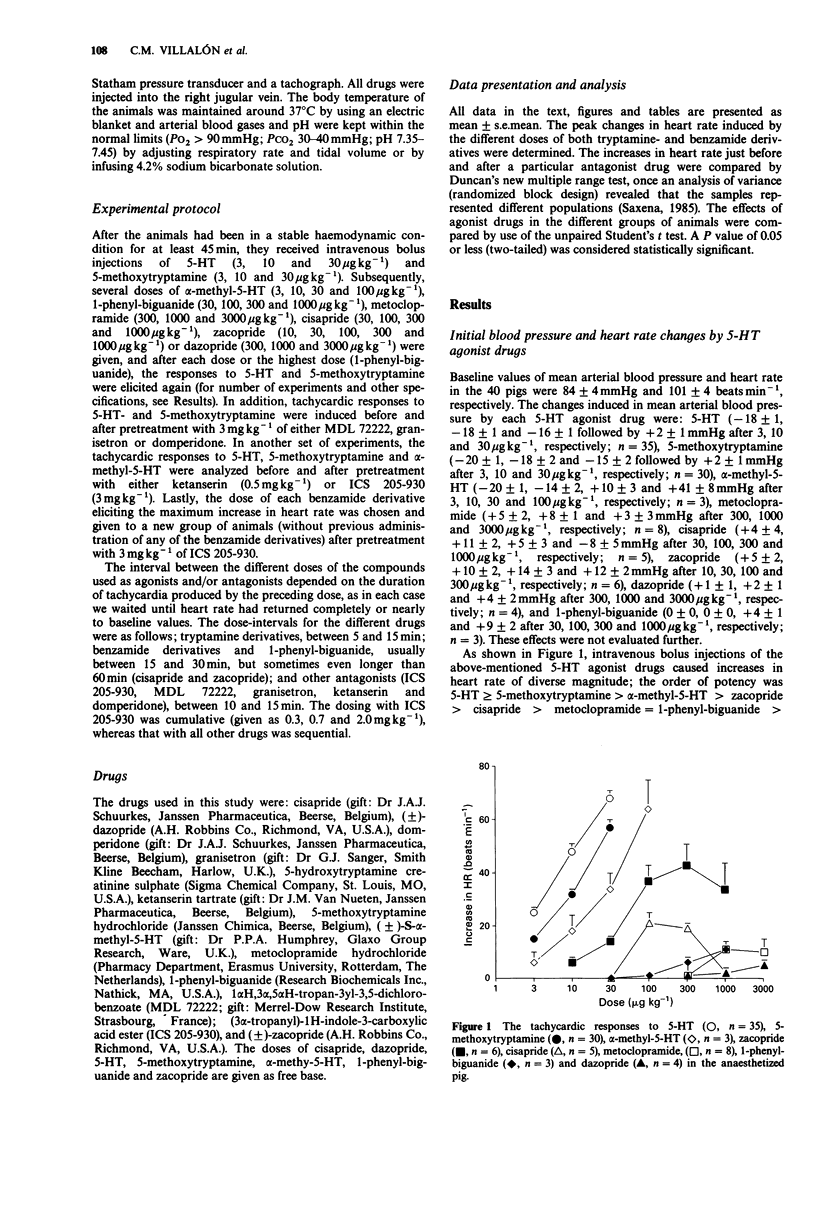
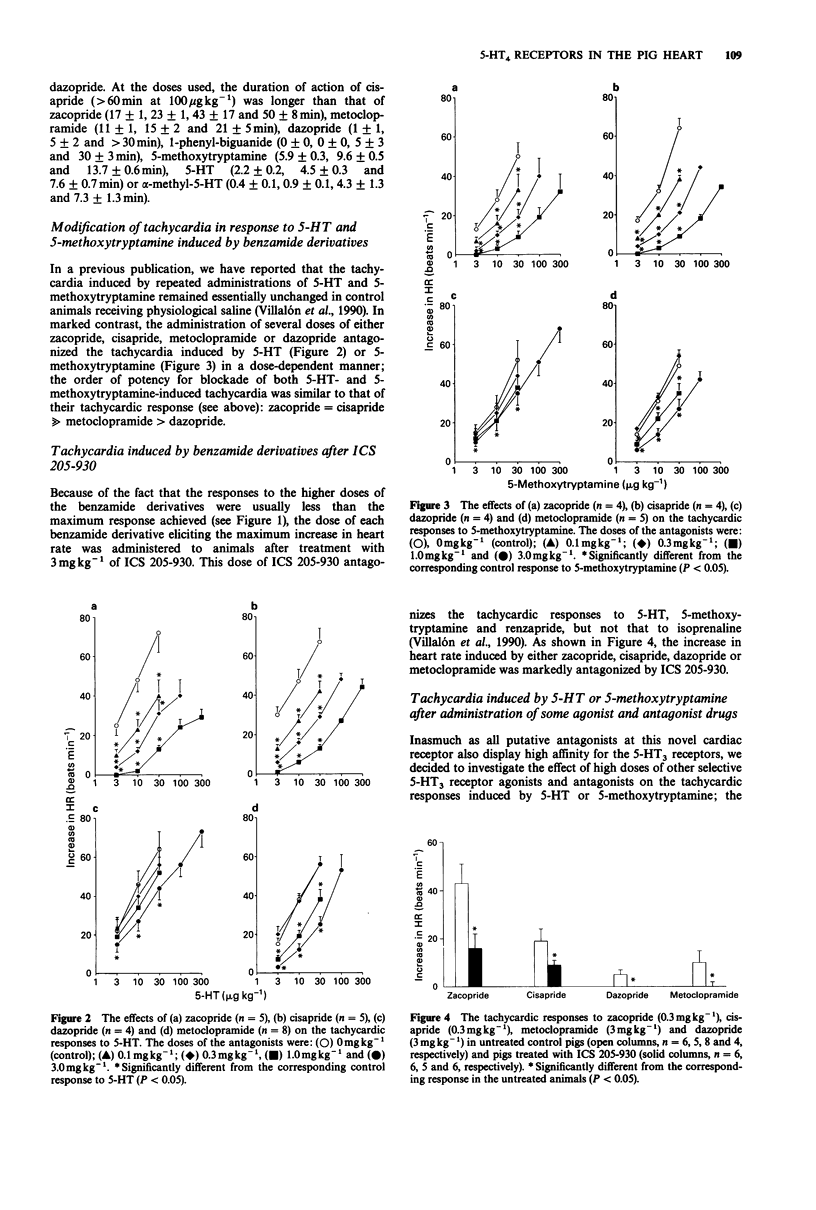
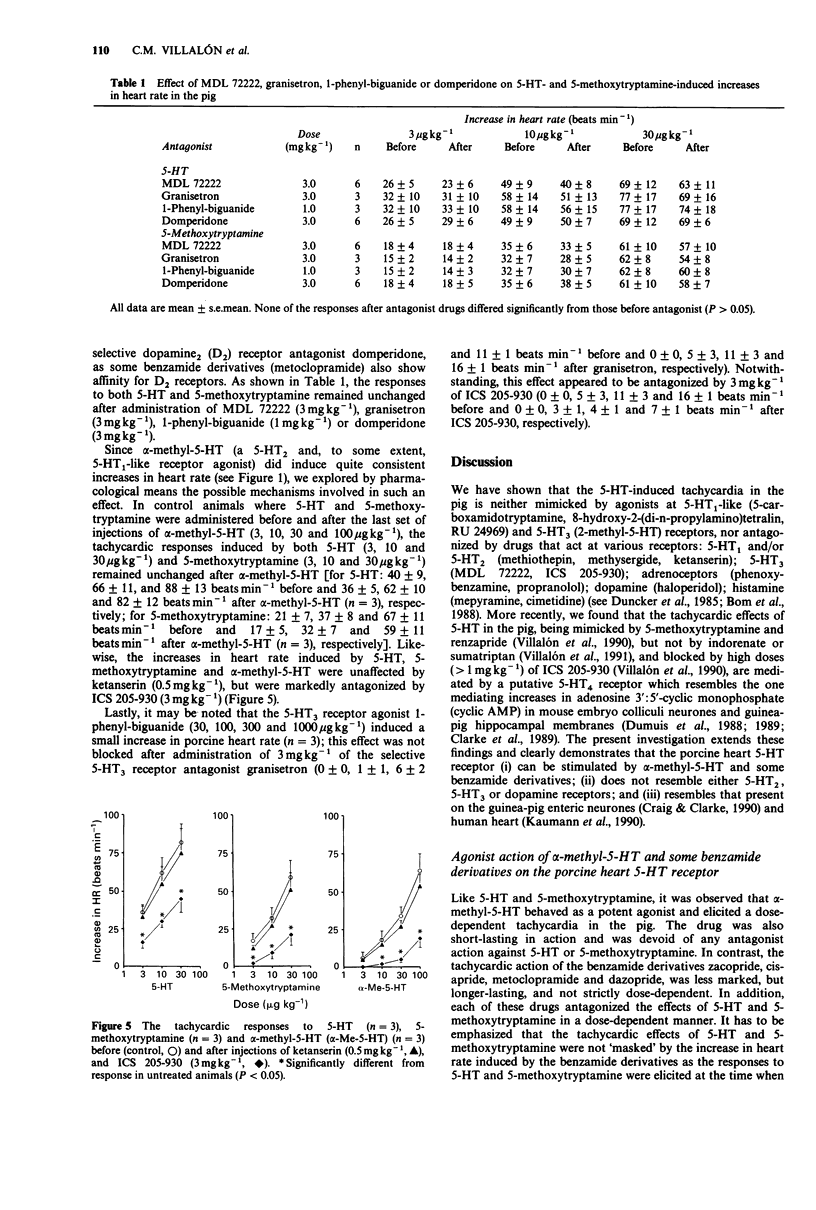
1. It has recently been shown that the tachycardic response to 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) in the anaesthetized pig, being mimicked by 5-methoxytryptamine and renzapride and blocked by high doses of ICS 205-930, is mediated by the putative 5-HT4 receptor. In the present investigation we have further characterized this receptor. 2. Intravenous bolus injections of the tryptamine derivatives, 5-HT (3, 10 and 30 micrograms kg-1), 5-methoxytryptamine (3, 10 and 30 micrograms kg-1) and alpha-methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine (alpha-methyl-5-HT; 3, 10, 30 and 100 micrograms kg-1), resulted in dose-dependent increases in heart rate of, respectively, 25 +/- 2, 48 +/- 3 and 68 +/- 3 beats min-1 (5-HT; n = 35); 15 +/- 1, 32 +/- 2 and 57 +/- 3 beats min-1 (5-methoxytryptamine; n = 30); 6 +/- 4, 18 +/- 6, 34 +/- 6 and 64 +/- 11 beats min-1 (alpha-methyl-5-HT; n = 3).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blandina P., Goldfarb J., Green J. P. Activation of a 5-HT3 receptor releases dopamine from rat striatal slice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct 18;155(3):349–350. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90528-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bom A. H., Duncker D. J., Saxena P. R., Verdouw P. D. 5-Hydroxytryptamine-induced tachycardia in the pig: possible involvement of a new type of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;93(3):663–671. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb10324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke D. E., Craig D. A., Fozard J. R. The 5-HT4 receptor: naughty, but nice. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Oct;10(10):385–386. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90177-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor H. E., Feniuk W., Humphrey P. P., Perren M. J. 5-Carboxamidotryptamine is a selective agonist at 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors mediating vasodilatation and tachycardia in anaesthetized cats. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Feb;87(2):417–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10832.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig D. A., Clarke D. E. Pharmacological characterization of a neuronal receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine in guinea pig ileum with properties similar to the 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Mar;252(3):1378–1386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumuis A., Bouhelal R., Sebben M., Bockaert J. A 5-HT receptor in the central nervous system, positively coupled with adenylate cyclase, is antagonized by ICS 205 930. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jan 27;146(1):187–188. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90503-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumuis A., Sebben M., Bockaert J. The gastrointestinal prokinetic benzamide derivatives are agonists at the non-classical 5-HT receptor (5-HT4) positively coupled to adenylate cyclase in neurons. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;340(4):403–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00167041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fozard J. R. MDL 72222: a potent and highly selective antagonist at neuronal 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 May;326(1):36–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00518776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer D. Functional correlates of serotonin 5-HT1 recognition sites. J Recept Res. 1988;8(1-4):59–81. doi: 10.3109/10799898809048978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaumann A. J., Sanders L., Brown A. M., Murray K. J., Brown M. J. A 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor in human atrium. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):879–885. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14108.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohli J. D., Glock D., Goldberg L. I. Selective DA2 versus DA1 antagonist activity of domperidone in the periphery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Apr 22;89(1-2):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90618-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Leff P., Cambridge D., Barrett V. J. Comparative analysis of two types of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor mediating vasorelaxation: differential classification using tryptamines. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;336(4):365–373. doi: 10.1007/BF00164867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson B. P., Engel G., Donatsch P., Stadler P. A. Identification of serotonin M-receptor subtypes and their specific blockade by a new class of drugs. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):126–131. doi: 10.1038/316126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger G. J. Increased gut cholinergic activity and antagonism of 5-hydroxytryptamine M-receptors by BRL 24924: potential clinical importance of BRL 24924. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 May;91(1):77–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb08985.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger G. J., Nelson D. R. Selective and functional 5-hydroxytryptamine3 receptor antagonism by BRL 43694 (granisetron). Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan 10;159(2):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90695-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena P. R., Lawang A. A comparison of cardiovascular and smooth muscle effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-carboxamidotryptamine, a selective agonist of 5-HT1 receptors. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1985 Oct;277(2):235–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena P. R., Mylecharane E. J., Heiligers J. Analysis of the heart rate effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the cat; mediation of tachycardia by 5-HT1-like receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1985 Aug;330(2):121–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00499904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena P. R., Villalón C. M. Cardiovascular effects of serotonin agonists and antagonists. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1990;15 (Suppl 7):S17–S34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuurkes J. A., Van Nueten J. M., Van Daele P. G., Reyntjens A. J., Janssen P. A. Motor-stimulating properties of cisapride on isolated gastrointestinal preparations of the guinea pig. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Sep;234(3):775–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tricklebank M. D. Interactions between dopamine and 5-HT3 receptors suggest new treatments for psychosis and drug addiction. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Apr;10(4):127–129. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Nueten J. M., Janssen P. A., Van Beek J., Xhonneux R., Verbeuren T. J., Vanhoutte P. M. Vascular effects of ketanserin (R 41 468), a novel antagonist of 5-HT2 serotonergic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Jul;218(1):217–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villalón C. M., den Boer M. O., Heiligers J. P., Saxena P. R. Mediation of 5-hydroxytryptamine-induced tachycardia in the pig by the putative 5-HT4 receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):665–667. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14073.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


