Abstract
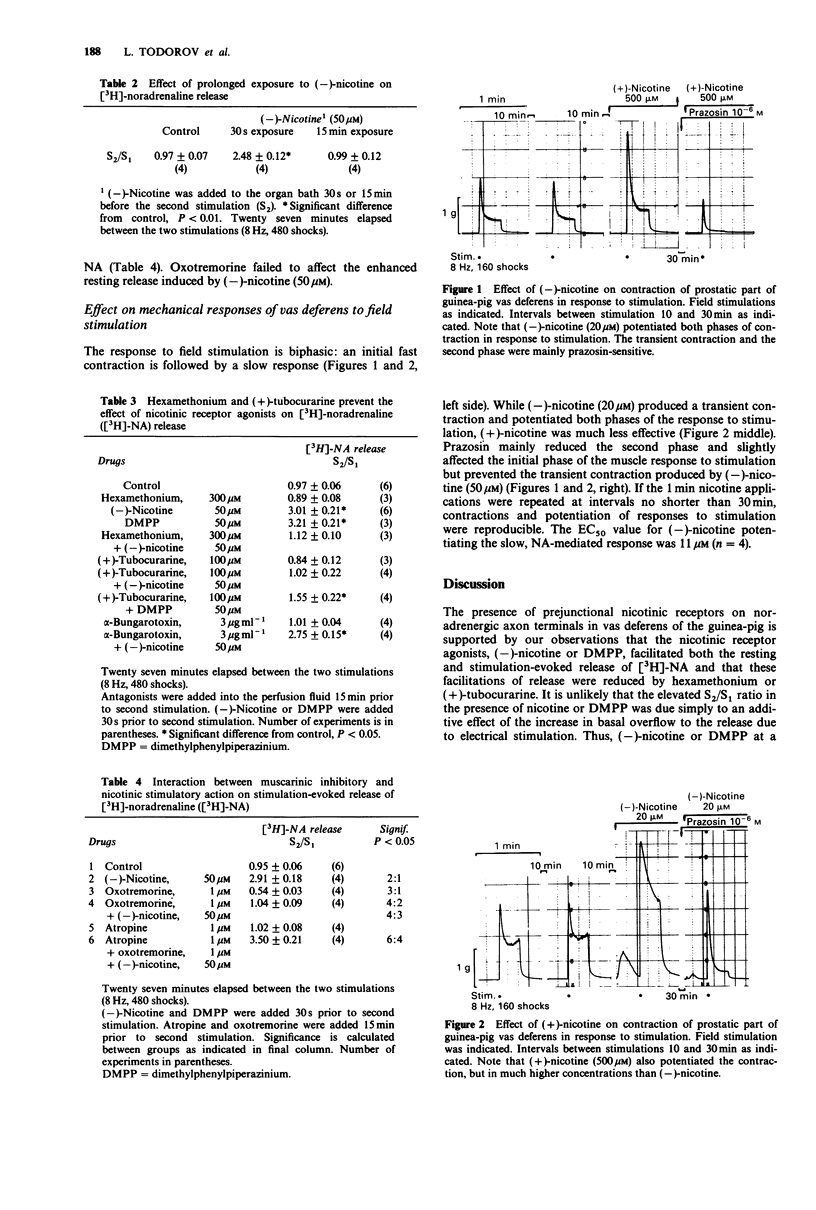
In guinea-pig prostatic vas deferens loaded with [3H]-noradrenaline ([3H]-NA), nicotinic receptor agonists, nicotine and dimethylphenylpiperazinium (DMPP) enhanced the resting and facilitated the stimulation-evoked release of [3H]-NA in a concentration-dependent fashion. The effect of nicotine on both contraction of vas deferens and release of NA in response to field stimulation was stereospecific in favour of the naturally occurring (-)-enantiomer. Prolonged (15 min) exposure to (-)-nicotine resulted in a cessation of the facilitatory effect on NA release and on responses of the vas deferens to field stimulation. 2 The rank order of agonist potency in facilitating NA release was DMPP = (-)-nicotine greater than (+)-nicotine. Cytisine had no agonistic activity. The dissociation constants (KD) of antagonists were 9.3 +/- 0.6 and 31.4 +/- 2.4 microM for (+)-tubocurarine and hexamethonium, respectively, when (-)-nicotine was used as agonist. alpha-Bungarotoxin had no antagonistic activity. These findings suggest that nicotinic receptors located on noradrenergic axon terminals are different from those located postsynaptically in striated muscle or ganglia but seem similar to those present on cholinergic axon terminals at the neuromuscular junction. 3. Cotinine, the breakdown product of nicotine failed to have any agonistic activity indicating that nicotine itself is responsible for the effects observed on axon terminals. 4 Stimulation of presynaptic muscarinic receptors by oxotremorine prevented the nicotine-induced facilitation of [3H]-NA release, indicating the presence of both inhibitory muscarinic and facilitatory nicotinic receptors on noradrenergic axon terminals.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENTLEY G. A., SABINE J. R. THE EFFECTS OF GANGLION-BLOCKING AND POSTGANGLIONIC SYMPATHOLYTIC DRUGS ON PREPARATIONS OF THE GUINEA-PIG VAS DEFERENS. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Aug;21:190–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01515.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRMINGHAM A. T., WILSON A. B. PREGANGLIONIC AND POSTGANGLIONIC STIMULATION OF THE GUINEA-PIG ISOLATED VAS DEFERENS PREPARATION. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Dec;21:569–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb02024.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Belleroche J., Bradford H. F. Biochemical evidence for the presence of presynaptic receptors on dopaminergic nerve terminals. Brain Res. 1978 Feb 17;142(1):53–68. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuder H., Siebenborn R., Muscholl E. Nicotine receptors do not modulate the 3H-noradrenaline release from the isolated rat heart evoked by sympathetic nerve stimulation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Mar;318(4):301–307. doi: 10.1007/BF00501169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushi Y., Wakui M. Involvement of cholinergic nerves in excitatory junction potentials through prejunctional nicotinic receptors in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Auton Pharmacol. 1987 Dec;7(4):309–315. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1987.tb00159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorguieff M. F., Le Floc'h M. L., Westfall T. C., Glowinski J., Besson M. J. Nicotinic effect of acetylcholine on the release of newly synthesized (3H)dopamine in rat striatal slices and cat caudate nucleus. Brain Res. 1976 Apr 16;106(1):117–131. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D., Deneris E., Luyten W., Kochhar A., Patrick J., Heinemann S. Members of a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor gene family are expressed in different regions of the mammalian central nervous system. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):965–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90705-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob P., 3rd, Benowitz N. L., Shulgin A. T. Recent studies of nicotine metabolism in humans. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1988 May;30(1):249–253. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(88)90453-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll J., Somogyi G. T., Illés P., Vizi E. S. Acetylcholine release from isolated vas deferens of the rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1972;274(2):198–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00501855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindmar R., Löffelholz K., Muscholl E. A muscarinic mechanism inhibiting the release of noradrenaline from peripheral adrenergic nerve fibres by nicotinic agents. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Feb;32(2):280–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00972.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loring R. H., Zigmond R. E. Characterization of neuronal nicotinic receptors by snake venom neurotoxins. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Feb;11(2):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90168-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. M., ZAIMIS E. The methonium. Pharmacol Rev. 1952 Sep;4(3):219–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapier C., Lunt G. G., Wonnacott S. Stereoselective nicotine-induced release of dopamine from striatal synaptosomes: concentration dependence and repetitive stimulation. J Neurochem. 1988 Apr;50(4):1123–1130. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb10582.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. M. A cholinergic component in the innervation of the longitudinal smooth muscle of the guinea pig vas deferens. The fine structural localization of acetylcholinesterase. J Cell Biol. 1969 May;41(2):462–476. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.2.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. A., Jarvis M., Iyer R., Feyerabend C. Relation of nicotine yield of cigarettes to blood nicotine concentrations in smokers. Br Med J. 1980 Apr 5;280(6219):972–976. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6219.972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L. Pre- and post-junctional receptor-mediated cholinergic interactions with adrenergic transmission in guinea-pig vas deferens. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1975;288(2-3):305–310. doi: 10.1007/BF00500535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarlov S. R., Langer S. Z. The fate of 3 H-norepinephrine released from isolated atria and vas deferens: effect of field stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Nov;179(2):186–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S., Burnstock G. Origin of ATP release in the rat vas deferens: concomitant measurement of [3H]noradrenaline and [14C]ATP. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec 6;158(1-2):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90254-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S., Harsing L. G., Jr, Zimanvi I., Gaal G. Release and turnover of noradrenaline in isolated median eminence: lack of negative feedback modulation. Neuroscience. 1985 Dec;16(4):907–916. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90105-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S., Somogyi G. T., Nagashima H., Duncalf D., Chaudhry I. A., Kobayashi O., Goldiner P. L., Foldes F. F. Tubocurarine and pancuronium inhibit evoked release of acetylcholine from the mouse hemidiaphragm preparation. Br J Anaesth. 1987 Feb;59(2):226–231. doi: 10.1093/bja/59.2.226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vizi E. S., Somogyi G. T. Prejunctional modulation of acetylcholine release from the skeletal neuromuscular junction: link between positive (nicotinic)- and negative (muscarinic)-feedback modulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):65–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11924.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westfall T. C., Brasted M. The mechanism of action of nicotine on adrenergic neurons in the perfused guinea-pig heart. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Sep;182(3):409–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westfall T. C. Effect of nicotine and other drugs on the release of 3H-norepinephrine and 3H-dopamine from rat brain slices. Neuropharmacology. 1974 Aug;13(8):693–700. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(74)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wonnacott S. Brain nicotine binding sites. Hum Toxicol. 1987 Sep;6(5):343–353. doi: 10.1177/096032718700600502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


