Abstract
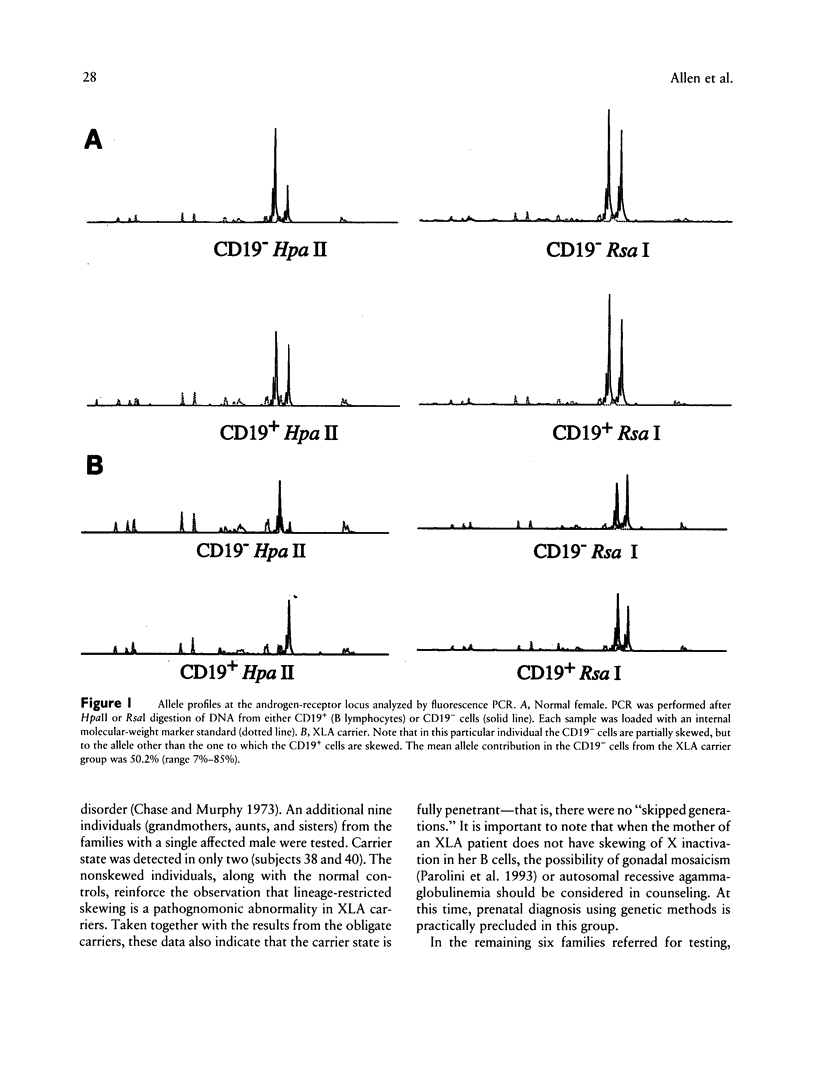
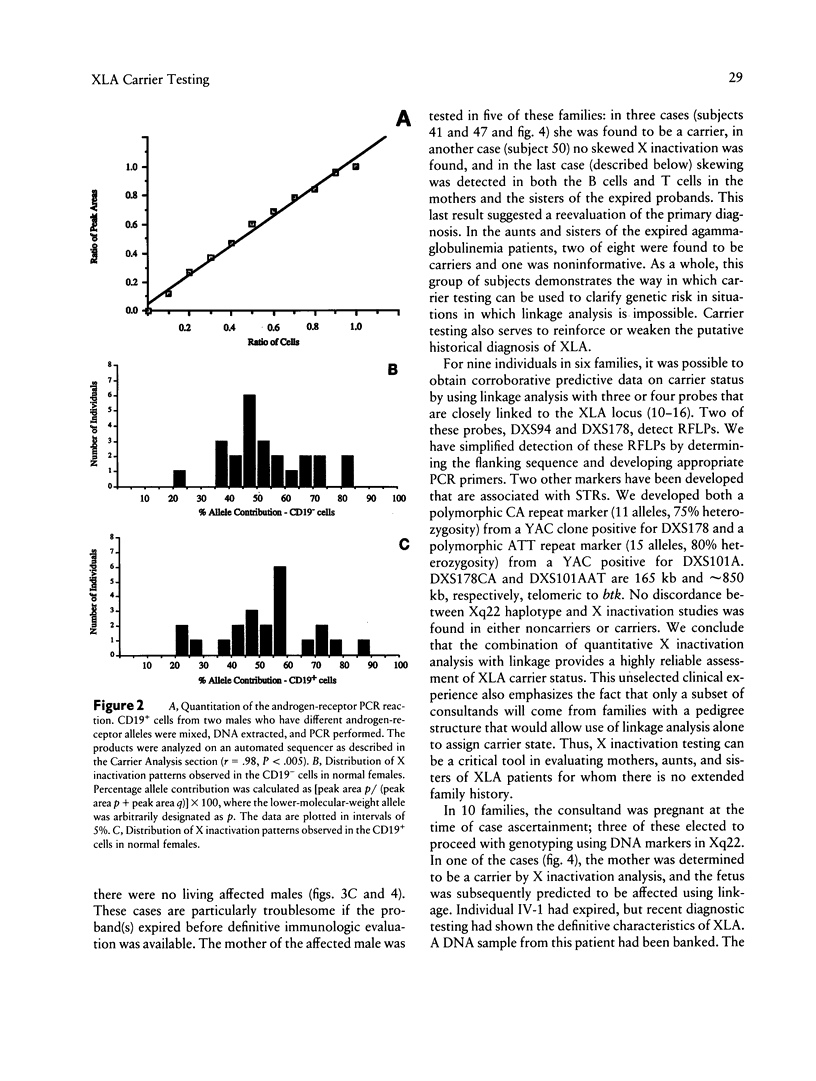
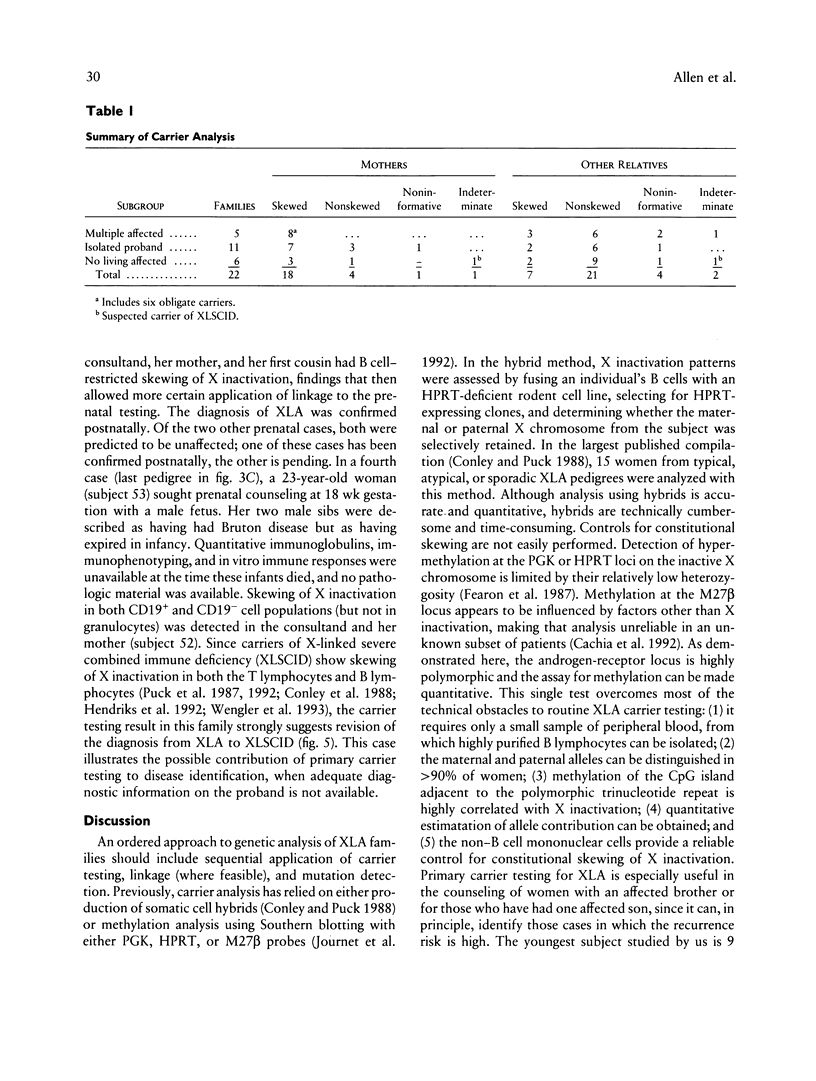
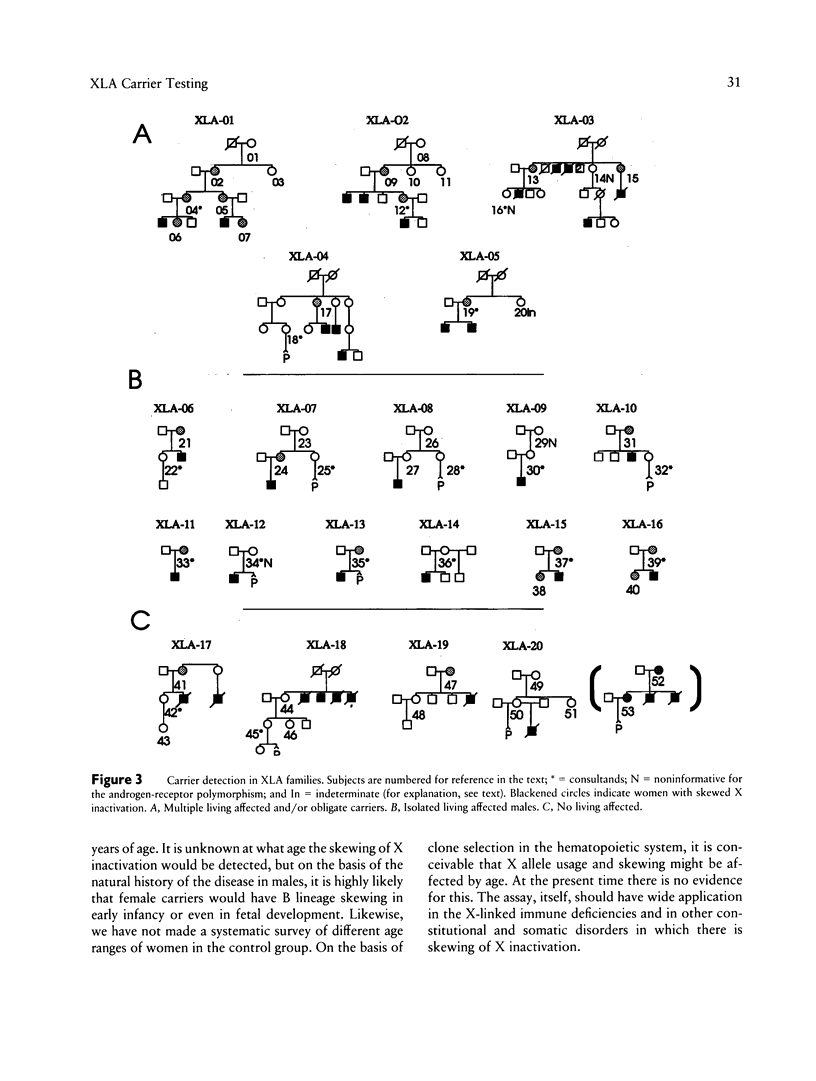
Bruton X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) is a phenotypically recessive genetic disorder of B lymphocyte development. Female carriers of XLA, although asymptomatic, have a characteristic B cell lineage-specific skewing of the pattern of X inactivation. Skewing apparently results from defective growth and maturation of B cell precursors bearing a mutant active X chromosome. In this study, carrier status was tested in 58 women from 22 families referred with a history of agammaglobulinemia. Primary carrier analysis to examine patterns of X inactivation in CD19+ peripheral blood cells (B lymphocytes) was conducted using quantitative PCR at the androgen-receptor locus. Obligate carriers of XLA demonstrated > 95% skewing of X inactivation in peripheral blood CD19+ cells but not in CD19- cells. Carrier status for mothers of isolated affected males could be assessed in 10 of 11 families: 7 women showed skewing, and 3 did not. Five carriers were found in six families in which there were no living affected males. Among all those tested, one individual's carrier status was considered to be indeterminate and five women were noninformative for the carrier test. Results obtained by the carrier test were congruent with linkage analysis (where applicable) using the RFLPs DXS178 and DXS94 and two newly developed polymorphic microsatellite markers, DXS178CA and DXS101AAT. Refinements in techniques for primary carrier testing and genetic mapping of XLA now make possible an ordered approach to diagnosis, prenatal diagnosis, and genetic counseling.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. C., Armitage R. J., Conley M. E., Rosenblatt H., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Bedell M. A., Edelhoff S., Disteche C. M., Simoneaux D. K. CD40 ligand gene defects responsible for X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):990–993. doi: 10.1126/science.7679801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. C., Belmont J. W. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the DXS178 locus. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Jun;1(3):216–216. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.3.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. C., Spriggs M. K., Belmont J. W. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism in the human CD40 ligand gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jun;2(6):828–828. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.6.828-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. C., Zoghbi H. Y., Moseley A. B., Rosenblatt H. M., Belmont J. W. Methylation of HpaII and HhaI sites near the polymorphic CAG repeat in the human androgen-receptor gene correlates with X chromosome inactivation. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Dec;51(6):1229–1239. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aruffo A., Farrington M., Hollenbaugh D., Li X., Milatovich A., Nonoyama S., Bajorath J., Grosmaire L. S., Stenkamp R., Neubauer M. The CD40 ligand, gp39, is defective in activated T cells from patients with X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90668-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUTON O. C. Agammaglobulinemia. Pediatrics. 1952 Jun;9(6):722–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cachia P. G., Culligan D. J., Thomas E. D., Whittaker J., Jacobs A., Padua R. A. Methylation of the DXS255 hypervariable locus 5' CCGG site may be affected by factors other than X-chromosome activation status. Genomics. 1992 Sep;14(1):70–74. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80285-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campana D., Farrant J., Inamdar N., Webster A. D., Janossy G. Phenotypic features and proliferative activity of B cell progenitors in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 15;145(6):1675–1680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase G. A., Murphy E. A. Risk of recurrence and carrier frequency for X-linked lethal recessives. Hum Hered. 1973;23(1):19–26. doi: 10.1159/000152548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Brown P., Pickard A. R., Buckley R. H., Miller D. S., Raskind W. H., Singer J. W., Fialkow P. J. Expression of the gene defect in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 28;315(9):564–567. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608283150907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Lavoie A., Briggs C., Brown P., Guerra C., Puck J. M. Nonrandom X chromosome inactivation in B cells from carriers of X chromosome-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3090–3094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E. Molecular approaches to analysis of X-linked immunodeficiencies. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:215–238. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Puck J. M. Carrier detection in typical and atypical X-linked agammaglobulinemia. J Pediatr. 1988 May;112(5):688–694. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80683-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Sweinberg S. K. Females with a disorder phenotypically identical to X-linked agammaglobulinemia. J Clin Immunol. 1992 Mar;12(2):139–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00918144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiSanto J. P., Bonnefoy J. Y., Gauchat J. F., Fischer A., de Saint Basile G. CD40 ligand mutations in x-linked immunodeficiency with hyper-IgM. Nature. 1993 Feb 11;361(6412):541–543. doi: 10.1038/361541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A., Hammond H. A., Jin L., Caskey C. T., Chakraborty R. Genetic variation at five trimeric and tetrameric tandem repeat loci in four human population groups. Genomics. 1992 Feb;12(2):241–253. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90371-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Winkelstein J. A., Civin C. I., Pardoll D. M., Vogelstein B. Carrier detection in X-linked agammaglobulinemia by analysis of X-chromosome inactivation. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 19;316(8):427–431. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702193160802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J. Primordial cell pool size and lineage relationships of five human cell types. Ann Hum Genet. 1973 Jul;37(1):39–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1973.tb01813.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuleihan R., Ramesh N., Loh R., Jabara H., Rosen R. S., Chatila T., Fu S. M., Stamenkovic I., Geha R. S. Defective expression of the CD40 ligand in X chromosome-linked immunoglobulin deficiency with normal or elevated IgM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2170–2173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guioli S., Arveiler B., Bardoni B., Notarangelo L. D., Panina P., Duse M., Ugazio A., Oberlé I., de Saint Basile G., Mandel J. L. Close linkage of probe p212 (DXS178) to X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Hum Genet. 1989 Dec;84(1):19–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00210664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks R. W., Kraakman M. E., Schuurman R. K. X chromosome inactivation patterns in haematopoietic cells of female carriers of X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency determined by methylation analysis at the hypervariable DXS255 locus. Clin Genet. 1992 Sep;42(3):114–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1992.tb03221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi M., Antonarakis S. E., Kasch L., Oldenburg J., Economou-Petersen E., Olek K., Arai M., Inaba H., Kazazian H. H., Jr Molecular characterization of mild-to-moderate hemophilia A: detection of the mutation in 25 of 29 patients by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8307–8311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi M., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Kasch L., Warren T. C., McGinniss M. J., Phillips J. A., 3rd, Kasper C., Janco R., Antonarakis S. E. Molecular characterization of severe hemophilia A suggests that about half the mutations are not within the coding regions and splice junctions of the factor VIII gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7405–7409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Journet O., Durandy A., Doussau M., Le Deist F., Couvreur J., Griscelli C., Fischer A., de Saint-Basile G. Carrier detection and prenatal diagnosis of X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Jul 15;43(5):885–887. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korthäuer U., Graf D., Mages H. W., Brière F., Padayachee M., Malcolm S., Ugazio A. G., Notarangelo L. D., Levinsky R. J., Kroczek R. A. Defective expression of T-cell CD40 ligand causes X-linked immunodeficiency with hyper-IgM. Nature. 1993 Feb 11;361(6412):539–541. doi: 10.1038/361539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan S. P., Kunkel L., Bruns G., Wedgwood R. J., Latt S., Rosen F. S. Mapping of the X-linked agammaglobulinemia locus by use of restriction fragment-length polymorphism. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):649–652. doi: 10.1172/JCI112351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan S. P., Terwilliger J., Parmley R., Raghu G., Sandkuyl L. A., Ott J., Ochs H., Wedgwood R., Rosen F. Identification of a closely linked DNA marker, DXS178, to further refine the X-linked agammaglobulinemia locus. Genomics. 1990 Feb;6(2):238–242. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90562-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovering R., Middleton-Price H. R., O'Reilly M. A., Genet S. A., Parkar M., Sweatman A. K., Bradley L. D., Alterman L. A., Malcolm S., Morgan G. Genetic linkage analysis identifies new proximal and distal flanking markers for the X-linked agammaglobulinemia gene locus, refining its localization in Xq22. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Feb;2(2):139–141. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.2.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm S., de Saint Basile G., Arveiler B., Lau Y. L., Szabo P., Fischer A., Griscelli C., Debre M., Mandel J. L., Callard R. E. Close linkage of random DNA fragments from Xq 21.3-22 to X-linked agammaglobulinaemia (XLA). Hum Genet. 1987 Oct;77(2):172–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00272387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbit M. N. X chromosome inactivation mosaicism in the mouse. Dev Biol. 1971 Oct;26(2):252–263. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi M., Yi H., Rosenblatt H. M., Filipovich A. H., Adelstein S., Modi W. S., McBride O. W., Leonard W. J. Interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain mutation results in X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency in humans. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90167-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Suzuki Y., Sekiya T., Hayashi K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):874–879. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parolini O., Hejtmancik J. F., Allen R. C., Belmont J. W., Lassiter G. L., Henry M. J., Barker D. F., Conley M. E. Linkage analysis and physical mapping near the gene for X-linked agammaglobulinemia at Xq22. Genomics. 1993 Feb;15(2):342–349. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck J. M., Nussbaum R. L., Conley M. E. Carrier detection in X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency based on patterns of X chromosome inactivation. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1395–1400. doi: 10.1172/JCI112967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck J. M., Stewart C. C., Nussbaum R. L. Maximum-likelihood analysis of human T-cell X chromosome inactivation patterns: normal women versus carriers of X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Apr;50(4):742–748. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings D. J., Saffran D. C., Tsukada S., Largaespada D. A., Grimaldi J. C., Cohen L., Mohr R. N., Bazan J. F., Howard M., Copeland N. G. Mutation of unique region of Bruton's tyrosine kinase in immunodeficient XID mice. Science. 1993 Jul 16;261(5119):358–361. doi: 10.1126/science.8332901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen F. S., Cooper M. D., Wedgwood R. J. The primary immunodeficiencies (1). N Engl J Med. 1984 Jul 26;311(4):235–242. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198407263110406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. D., Sideras P., Smith C. I., Vorechovský I., Chapman V., Paul W. E. Colocalization of X-linked agammaglobulinemia and X-linked immunodeficiency genes. Science. 1993 Jul 16;261(5119):355–358. doi: 10.1126/science.8332900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada S., Saffran D. C., Rawlings D. J., Parolini O., Allen R. C., Klisak I., Sparkes R. S., Kubagawa H., Mohandas T., Quan S. Deficient expression of a B cell cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase in human X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):279–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90667-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetrie D., Vorechovský I., Sideras P., Holland J., Davies A., Flinter F., Hammarström L., Kinnon C., Levinsky R., Bobrow M. The gene involved in X-linked agammaglobulinaemia is a member of the src family of protein-tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1993 Jan 21;361(6409):226–233. doi: 10.1038/361226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G. S., Allen R. C., Parolini O., Smith H., Conley M. E. Nonrandom X chromosome inactivation in natural killer cells from obligate carriers of X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):700–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weers M., Mensink R. G., Kenter M., Schuurman R. K. Three dinucleotide repeat polymorphisms at the DXS178 locus. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Nov;1(8):653–653. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.8.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


