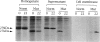Abstract
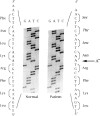
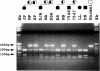
To date, three different structural gene mutations have been identified in patients with carbonic anhydrase II deficiency (osteopetrosis with renal tubular acidosis and cerebral calcification). These include a missense mutation (H107Y) in two families, a splice junction mutation in intron 5 in one of these families, and a splice junction mutation in intron 2 for which many Arabic patients are homozygous. We report here a novel mutation for which carbonic anhydrase II-deficient patients from seven unrelated Hispanic families were found to be homozygous. The proband was a 2 1/2-year-old Hispanic girl of Puerto Rican ancestry who was unique clinically, in that she had no evidence of renal tubular acidosis, even though she did have osteopetrosis, developmental delay, and cerebral calcification. She proved to be homozygous for a single-base deletion in the coding region of exon 7 that produces a frameshift that changes the next 12 amino acids before leading to chain termination and that also introduces a new MaeIII restriction site. The 27-kD truncated enzyme produced when the mutant cDNA was expressed in COS cells was enzymatically inactive, present mainly in insoluble aggregates, and detectable immunologically at only 5% the level of the 29-kD normal carbonic anhydrase II expressed from the wild-type cDNA. Metabolic labeling revealed that this 27-kD mutant protein has an accelerated rate of degradation. Six subsequent Hispanic patients of Caribbean ancestry, all of whom had osteopetrosis and renal tubular acidosis but who varied widely in clinical severity, were found to be homozygous for the same mutation.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hu P. Y., Roth D. E., Skaggs L. A., Venta P. J., Tashian R. E., Guibaud P., Sly W. S. A splice junction mutation in intron 2 of the carbonic anhydrase II gene of osteopetrosis patients from Arabic countries. Hum Mutat. 1992;1(4):288–292. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380010404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Sollner-Webb B. High level transient expression of a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene by DEAE-dextran mediated DNA transfection coupled with a dimethyl sulfoxide or glycerol shock treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5707–5717. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Magnusson G. High efficiency polyoma DNA transfection of chloroquine treated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1295–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki J., Takaki S., Araki K., Tashiro F., Tominaga A., Takatsu K., Yamamura K. Expression vector system based on the chicken beta-actin promoter directs efficient production of interleukin-5. Gene. 1989 Jul 15;79(2):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90209-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. E., Venta P. J., Tashian R. E., Sly W. S. Molecular basis of human carbonic anhydrase II deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz G. J., Brion L. P., Corey H. E., Dorfman H. D. Case report 668. Carbonic anhydrase II deficiency syndrome (osteopetrosis associated with renal tubular acidosis and cerebral calcification). Skeletal Radiol. 1991;20(6):447–452. doi: 10.1007/BF00191090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sly W. S., Whyte M. P., Sundaram V., Tashian R. E., Hewett-Emmett D., Guibaud P., Vainsel M., Baluarte H. J., Gruskin A., Al-Mosawi M. Carbonic anhydrase II deficiency in 12 families with the autosomal recessive syndrome of osteopetrosis with renal tubular acidosis and cerebral calcification. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jul 18;313(3):139–145. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198507183130302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaram V., Rumbolo P., Grubb J., Strisciuglio P., Sly W. S. Carbonic anhydrase II deficiency: diagnosis and carrier detection using differential enzyme inhibition and inactivation. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Feb;38(2):125–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venta P. J., Welty R. J., Johnson T. M., Sly W. S., Tashian R. E. Carbonic anhydrase II deficiency syndrome in a Belgian family is caused by a point mutation at an invariant histidine residue (107 His----Tyr): complete structure of the normal human CA II gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Nov;49(5):1082–1090. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waheed A., Zhu X. L., Sly W. S. Membrane-associated carbonic anhydrase from rat lung. Purification, characterization, tissue distribution, and comparison with carbonic anhydrase IVs of other mammals. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3308–3311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Oshima A., Shimmoto M., Fukuhara Y., Sakuraba H., Yanagisawa N., Suzuki Y. Human beta-galactosidase gene mutations in GM1-gangliosidosis: a common mutation among Japanese adult/chronic cases. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Aug;49(2):435–442. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X. L., Sly W. S. Carbonic anhydrase IV from human lung. Purification, characterization, and comparison with membrane carbonic anhydrase from human kidney. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8795–8801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]