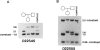Abstract
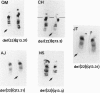
We have studied seven patients who have chromosome 22q13.3 deletions as revealed by high-resolution cytogenetic analysis. Clinical evaluation of the patients revealed a common phenotype that includes generalized developmental delay, normal or accelerated growth, hypotonia, severe delays in expressive speech, and mild facial dysmorphic features. Dosage analysis using a series of genetically mapped probes showed that the proximal breakpoints of the deletions varied over approximately 13.8 cM, between loci D22S92 and D22S94. The most distally mapped locus, arylsulfatase A (ARSA), was deleted in all seven patients. Therefore, the smallest region of overlap (critical region) extends between locus D22S94 and a region distal to ARSA, a distance of > 25.5 cM.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Budarf M. L., McDermid H. E., Sellinger B., Emanuel B. S. Isolation and regional localization of 35 unique anonymous DNA markers for human chromosome 22. Genomics. 1991 Aug;10(4):996–1002. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90190-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll D. A., Budarf M. L., Emanuel B. S. A genetic etiology for DiGeorge syndrome: consistent deletions and microdeletions of 22q11. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 May;50(5):924–933. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll D. A., Spinner N. B., Budarf M. L., McDonald-McGinn D. M., Zackai E. H., Goldberg R. B., Shprintzen R. J., Saal H. M., Zonana J., Jones M. C. Deletions and microdeletions of 22q11.2 in velo-cardio-facial syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Sep 15;44(2):261–268. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320440237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumanski J. P., Carlbom E., Collins V. P., Nordenskjöld M., Emanuel B. S., Budarf M. L., McDermid H. E., Wolff R., O'Connell P., White R. A map of 22 loci on human chromosome 22. Genomics. 1991 Nov;11(3):709–719. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90079-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraccaro M., Lindsten J., Ford C. E., Iselius L. The 11q;22q translocation: a European collaborative analysis of 43 cases. Hum Genet. 1980;56(1):21–51. doi: 10.1007/BF00281567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandelman K. Y., Gibson L., Meyn M. S., Yang-Feng T. L. Molecular definition of the smallest region of deletion overlap in the Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Sep;51(3):571–578. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough A. C., Smith C. A., Howell S. M., Wolf C. R., Bryant S. P., Spurr N. K. Localization of the CYP2D gene locus to human chromosome 22q13.1 by polymerase chain reaction, in situ hybridization, and linkage analysis. Genomics. 1993 Feb;15(2):430–432. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg F., Guzzetta V., Montes de Oca-Luna R., Magenis R. E., Smith A. C., Richter S. F., Kondo I., Dobyns W. B., Patel P. I., Lupski J. R. Molecular analysis of the Smith-Magenis syndrome: a possible contiguous-gene syndrome associated with del(17)(p11.2). Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;49(6):1207–1218. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamabe J., Kuroki Y., Imaizumi K., Sugimoto T., Fukushima Y., Yamaguchi A., Izumikawa Y., Niikawa N. DNA deletion and its parental origin in Angelman syndrome patients. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Oct 1;41(1):64–68. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320410117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman G. E., Greenberg F., Ledbetter D. H. Multiple congenital anomaly/mental retardation (MCA/MR) syndrome with Goldenhar complex due to a terminal del(22q). Am J Med Genet. 1988 Apr;29(4):909–915. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320290423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog R., Holzmann K., Blin N. A TaqI RFLP for the human arylsulfatase A gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6746–6746. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6746-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D., Goldberg R., Wilson D., Lindsay E., Carey A., Goodship J., Burn J., Cross I., Shprintzen R. J., Scambler P. J. Confirmation that the velo-cardio-facial syndrome is associated with haplo-insufficiency of genes at chromosome 22q11. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Feb 1;45(3):308–312. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320450306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirshenbaum G., Chmura M., Rhone D. P. Long arm deletion of chromosome 22. J Med Genet. 1988 Nov;25(11):780–780. doi: 10.1136/jmg.25.11.780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M., White R. L. A highly polymorphic locus in human DNA revealed by cosmid-derived probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6206–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermid H. E., Duncan A. M., Brasch K. R., Holden J. J., Magenis E., Sheehy R., Burn J., Kardon N., Noel B., Schinzel A. Characterization of the supernumerary chromosome in cat eye syndrome. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):646–648. doi: 10.1126/science.3961499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehrabian M., Gitt M. A., Sparkes R. S., Leffler H., Barondes S. H., Lusis A. J. Two members of the S-lac lectin gene family, LGALS1 and LGALS2, reside in close proximity on human chromosome 22q12-q13. Genomics. 1993 Feb;15(2):418–420. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narahara K., Takahashi Y., Murakami M., Tsuji K., Yokoyama Y., Murakami R., Ninomiya S., Seino Y. Terminal 22q deletion associated with a partial deficiency of arylsulphatase A. J Med Genet. 1992 Jun;29(6):432–433. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.6.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelan M. C., Thomas G. R., Saul R. A., Rogers R. C., Taylor H. A., Wenger D. A., McDermid H. E. Cytogenetic, biochemical, and molecular analyses of a 22q13 deletion. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Jul 15;43(5):872–876. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Josephs S. F., Jarrett R., Reitz M. S., Jr, Wong-Staal F. Nucleotide sequence of transforming human c-sis cDNA clones with homology to platelet-derived growth factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5007–5018. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. P., Bottani A., Xie Y. G., Balakrishman J., Binkert F., Mächler M., Prader A., Schinzel A. Molecular, cytogenetic, and clinical investigations of Prader-Willi syndrome patients. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;49(6):1219–1234. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romain D. R., Goldsmith J., Cairney H., Columbano-Green L. M., Smythe R. H., Parfitt R. G. Partial monosomy for chromosome 22 in a patient with del(22)(pter----q13.1::q13.33----qter). J Med Genet. 1990 Sep;27(9):588–589. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.9.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouleau G. A., Haines J. L., Bazanowski A., Colella-Crowley A., Trofatter J. A., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Gusella J. F. A genetic linkage map of the long arm of human chromosome 22. Genomics. 1989 Jan;4(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scambler P. J., Carey A. H., Wyse R. K., Roach S., Dumanski J. P., Nordenskjold M., Williamson R. Microdeletions within 22q11 associated with sporadic and familial DiGeorge syndrome. Genomics. 1991 May;10(1):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90501-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenman G., Sahlin P., Dumanski J. P., Hagiwara K., Ishikawa F., Miyazono K., Collins V. P., Heldin C. H. Regional localization of the human platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor (ECGF1) gene to chromosome 22q13. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1992;59(1):22–23. doi: 10.1159/000133191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. D., Harris P., Galt J., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Cloned DNA probes regionally mapped to human chromosome 21 and their use in determining the origin of nondisjunction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):4125–4132. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.4125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Desnick R. J. Structural organization and complete sequence of the human alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase gene: homology with the alpha-galactosidase A gene provides evidence for evolution from a common ancestral gene. Genomics. 1991 May;10(1):133–142. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90493-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt J. L., Olson I. A., Johnston A. W., Ross H. S., Couzin D. A., Stephen G. S. A familial pericentric inversion of chromosome 22 with a recombinant subject illustrating a 'pure' partial monosomy syndrome. J Med Genet. 1985 Aug;22(4):283–287. doi: 10.1136/jmg.22.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Stoffel M., Espinosa R., 3rd, Xiang K. S., Seino M., Seino S., Le Beau M. M., Bell G. I. Human somatostatin receptor genes: localization to human chromosomes 14, 17, and 22 and identification of simple tandem repeat polymorphisms. Genomics. 1993 Feb;15(2):449–452. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- vanTuinen P., Dobyns W. B., Rich D. C., Summers K. M., Robinson T. J., Nakamura Y., Ledbetter D. H. Molecular detection of microscopic and submicroscopic deletions associated with Miller-Dieker syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):587–596. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]