Abstract
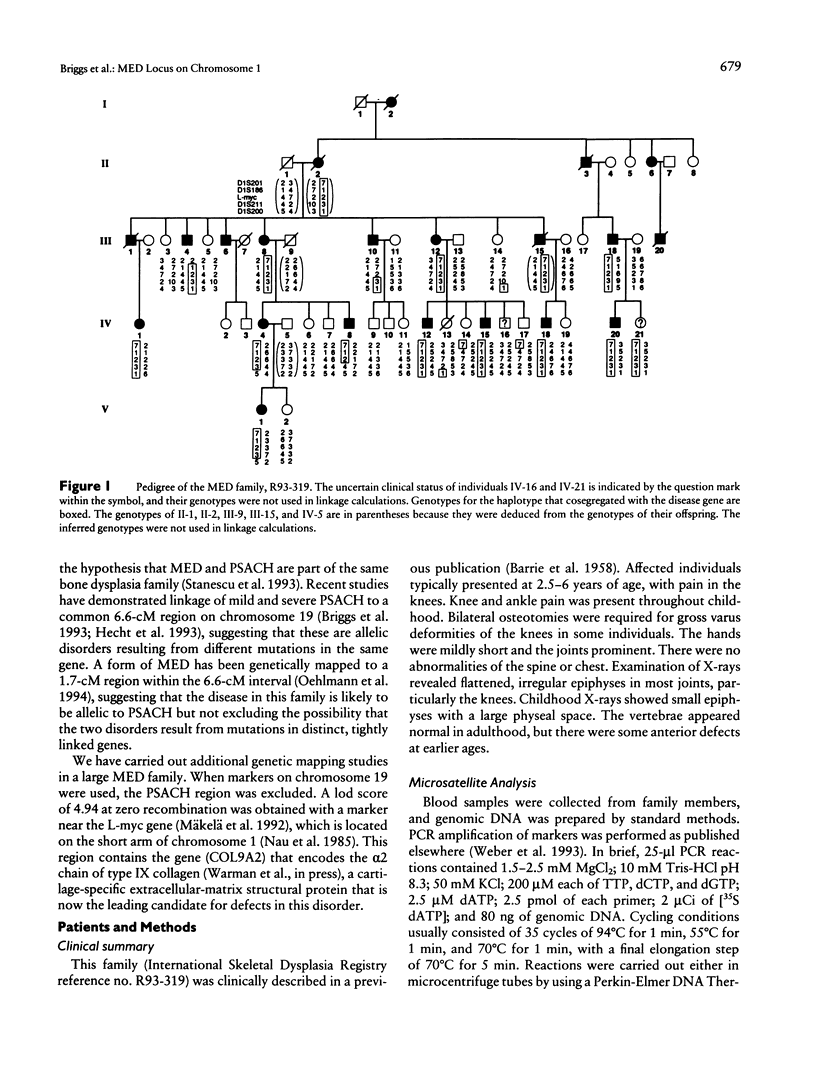
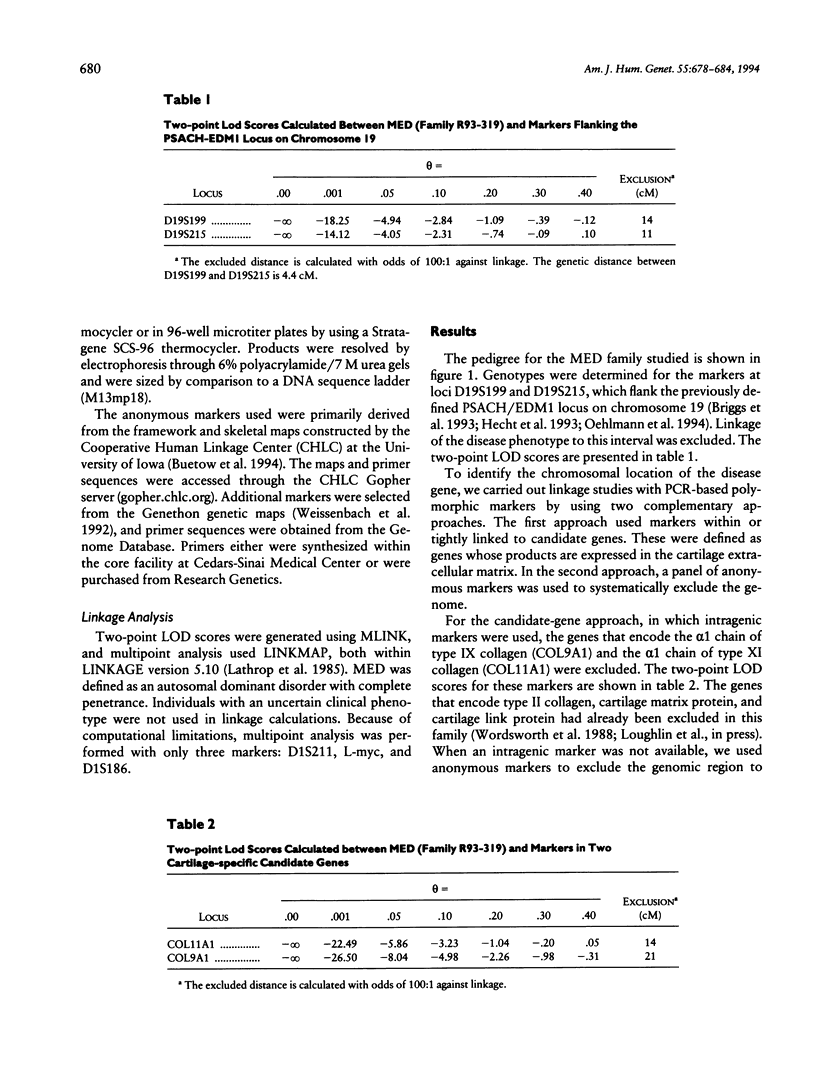
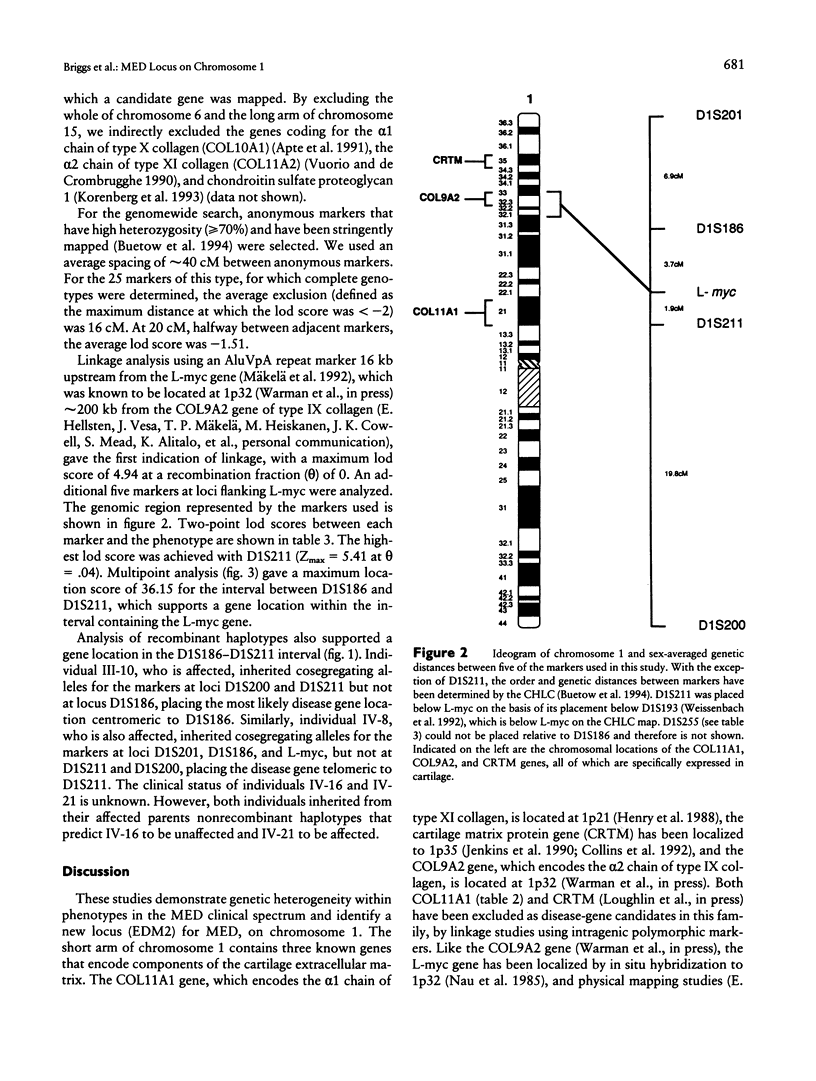
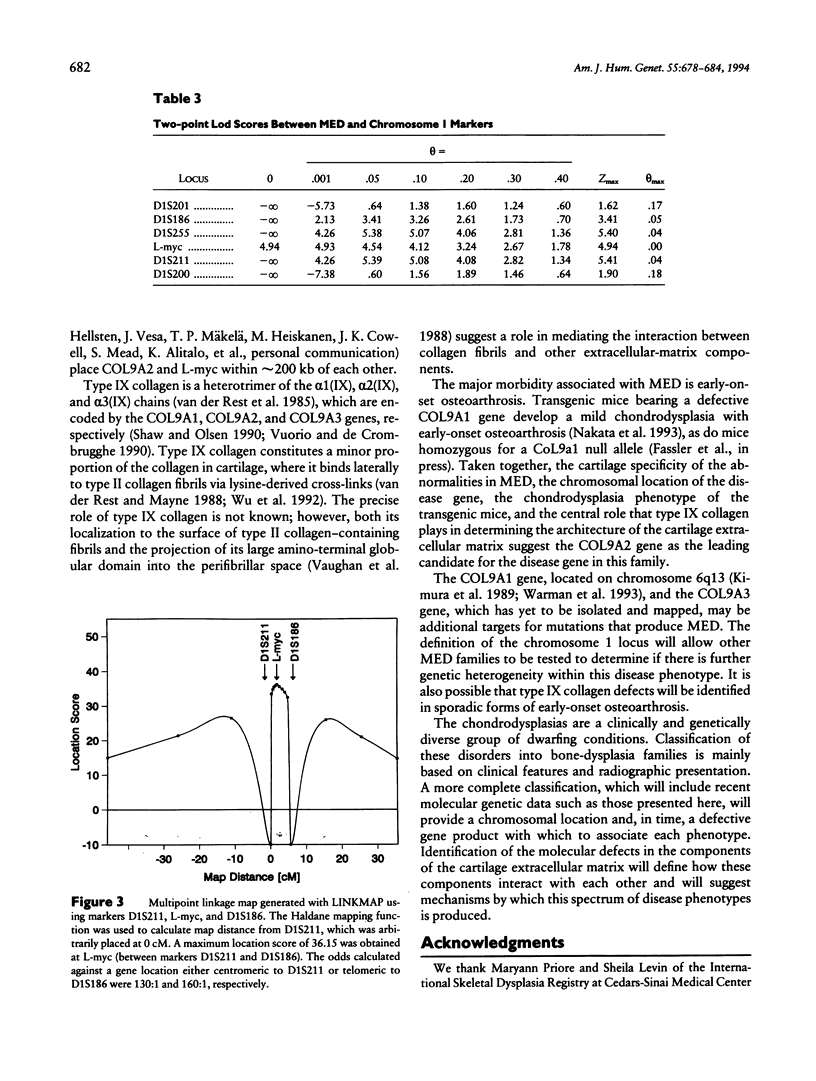
Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia (MED) is a dominantly inherited chondrodysplasia characterized by mild short stature and early-onset osteoarthrosis. Some forms of MED clinically resemble another chondrodysplasia phenotype, the mild form of pseudoachondroplasia (PSACH). On the basis of their clinical similarities as well as similar ultrastructural and biochemical features in cartilage from some patients, it has been proposed that MED and PSACH belong to a single bone-dysplasia family. Recently, both mild and severe PSACH as well as a form of MED have been linked to the same interval on chromosome 19, suggesting that they may be allelic disorders. Linkage studies with the chromosome 19 markers were carried out in a large family with MED and excluded the previously identified interval. Using this family, we have identified an MED locus on the short arm of chromosome 1, in a region containing the gene (COL9A2) that encodes the α2 chain of type IX collagen, a structural component of the cartilage extracellular matrix.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apte S., Mattei M. G., Olsen B. R. Cloning of human alpha 1(X) collagen DNA and localization of the COL10A1 gene to the q21-q22 region of human chromosome 6. FEBS Lett. 1991 May 6;282(2):393–396. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80521-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRIE H., CARTER C., SUTCLIFFE J. Multiple epiphysial dysplasia. Br Med J. 1958 Jul 19;2(5089):133–137. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5089.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. D., Rasmussen I. M., Weber J. L., Yuen J., Reinker K., Garber A. P., Rimoin D. L., Cohn D. H. Genetic linkage of mild pseudoachondroplasia (PSACH) to markers in the pericentromeric region of chromosome 19. Genomics. 1993 Dec;18(3):656–660. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80369-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetow K. H., Weber J. L., Ludwigsen S., Scherpbier-Heddema T., Duyk G. M., Sheffield V. C., Wang Z., Murray J. C. Integrated human genome-wide maps constructed using the CEPH reference panel. Nat Genet. 1994 Apr;6(4):391–393. doi: 10.1038/ng0494-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins A., Keats B. J., Dracopoli N., Shields D. C., Morton N. E. Integration of gene maps: chromosome 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4598–4602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doege K. J., Sasaki M., Kimura T., Yamada Y. Complete coding sequence and deduced primary structure of the human cartilage large aggregating proteoglycan, aggrecan. Human-specific repeats, and additional alternatively spliced forms. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):894–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht J. T., Francomano C. A., Briggs M. D., Deere M., Conner B., Horton W. A., Warman M., Cohn D. H., Blanton S. H. Linkage of typical pseudoachondroplasia to chromosome 19. Genomics. 1993 Dec;18(3):661–666. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry I., Bernheim A., Bernard M., van der Rest M., Kimura T., Jeanpierre C., Barichard F., Berger R., Olsen B. R., Ramirez F. Mapping of a human fibrillar collagen gene, pro alpha 1 (XI) (COL11A1), to the p21 region of chromosome 1. Genomics. 1988 Jul;3(1):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90165-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins R. N., Osborne-Lawrence S. L., Sinclair A. K., Eddy R. L., Jr, Byers M. G., Shows T. B., Duby A. D. Structure and chromosomal location of the human gene encoding cartilage matrix protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19624–19631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura T., Mattei M. G., Stevens J. W., Goldring M. B., Ninomiya Y., Olsen B. R. Molecular cloning of rat and human type IX collagen cDNA and localization of the alpha 1(IX) gene on the human chromosome 6. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 15;179(1):71–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14522.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Chen X. N., Doege K., Grover J., Roughley P. J. Assignment of the human aggrecan gene (AGC1) to 15q26 using fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis. Genomics. 1993 May;16(2):546–548. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):482–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroteaux P., Stanescu R., Stanescu V., Fontaine G. The mild form of pseudoachondroplasia. Identity of the morphological and biochemical alterations of growth cartilage with those of typical pseudoachondroplasia. Eur J Pediatr. 1980 May;133(3):227–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00496081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard J. A., Cooper R. R., Ponseti I. V. A unique rough surfaced endoplasmic reticulum inclusion in pseudoachondroplasia. Lab Invest. 1972 Jan;26(1):40–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä T. P., Hellsten E., Vesa J., Alitalo K., Peltonen L. An Alu variable polyA repeat polymorphism upstream of L-myc at 1p32. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Jun;1(3):217–217. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.3.217-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata K., Ono K., Miyazaki J., Olsen B. R., Muragaki Y., Adachi E., Yamamura K., Kimura T. Osteoarthritis associated with mild chondrodysplasia in transgenic mice expressing alpha 1(IX) collagen chains with a central deletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2870–2874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nau M. M., Brooks B. J., Battey J., Sausville E., Gazdar A. F., Kirsch I. R., McBride O. W., Bertness V., Hollis G. F., Minna J. D. L-myc, a new myc-related gene amplified and expressed in human small cell lung cancer. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):69–73. doi: 10.1038/318069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehlmann R., Summerville G. P., Yeh G., Weaver E. J., Jimenez S. A., Knowlton R. G. Genetic linkage mapping of multiple epiphyseal dysplasia to the pericentromeric region of chromosome 19. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Jan;54(1):3–10. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimoin D. L., Rasmussen I. M., Briggs M. D., Roughley P. J., Gruber H. E., Warman M. L., Olsen B. R., Hsia Y. E., Yuen J., Reinker K. A large family with features of pseudoachondroplasia and multiple epiphyseal dysplasia: exclusion of seven candidate gene loci that encode proteins of the cartilage extracellular matrix. Hum Genet. 1994 Mar;93(3):236–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00212015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw L. M., Olsen B. R. FACIT collagens: diverse molecular bridges in extracellular matrices. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 May;16(5):191–194. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanescu R., Stanescu V., Muriel M. P., Maroteaux P. Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia, Fairbank type: morphologic and biochemical study of cartilage. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Feb 15;45(4):501–507. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320450420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanescu V., Maroteaux P., Stanescu R. The biochemical defect of pseudoachondroplasia. Eur J Pediatr. 1982 May;138(3):221–225. doi: 10.1007/BF00441206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan L., Mendler M., Huber S., Bruckner P., Winterhalter K. H., Irwin M. I., Mayne R. D-periodic distribution of collagen type IX along cartilage fibrils. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):991–997. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuorio E., de Crombrugghe B. The family of collagen genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:837–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warman M. L., Tiller G. E., Polumbo P. A., Seldin M. F., Rochelle J. M., Knoll J. H., Cheng S. D., Olsen B. R. Physical and linkage mapping of the human and murine genes for the alpha 1 chain of type IX collagen (COL9A1). Genomics. 1993 Sep;17(3):694–698. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., Wang Z., Hansen K., Stephenson M., Kappel C., Salzman S., Wilkie P. J., Keats B., Dracopoli N. C., Brandriff B. F. Evidence for human meiotic recombination interference obtained through construction of a short tandem repeat-polymorphism linkage map of chromosome 19. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Nov;53(5):1079–1095. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Gyapay G., Dib C., Vignal A., Morissette J., Millasseau P., Vaysseix G., Lathrop M. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):794–801. doi: 10.1038/359794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. J., Woods P. E., Eyre D. R. Identification of cross-linking sites in bovine cartilage type IX collagen reveals an antiparallel type II-type IX molecular relationship and type IX to type IX bonding. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23007–23014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Rest M., Mayne R., Ninomiya Y., Seidah N. G., Chretien M., Olsen B. R. The structure of type IX collagen. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):220–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Rest M., Mayne R. Type IX collagen proteoglycan from cartilage is covalently cross-linked to type II collagen. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1615–1618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


