Abstract
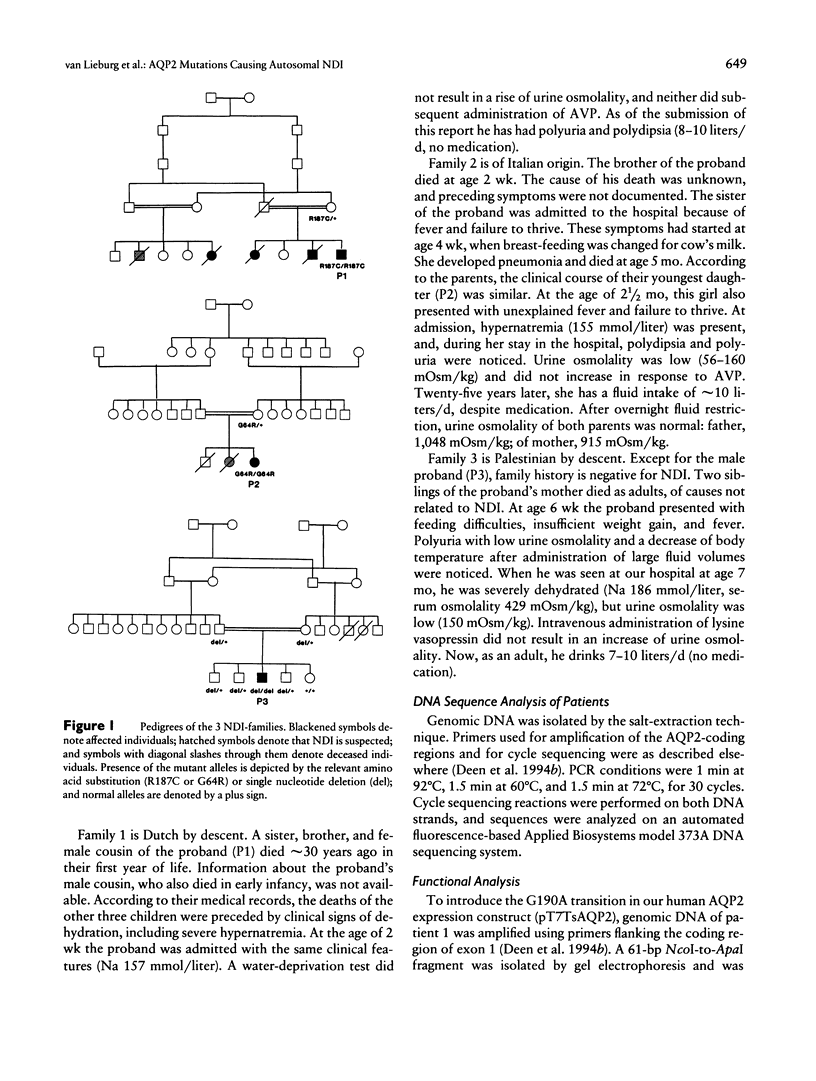
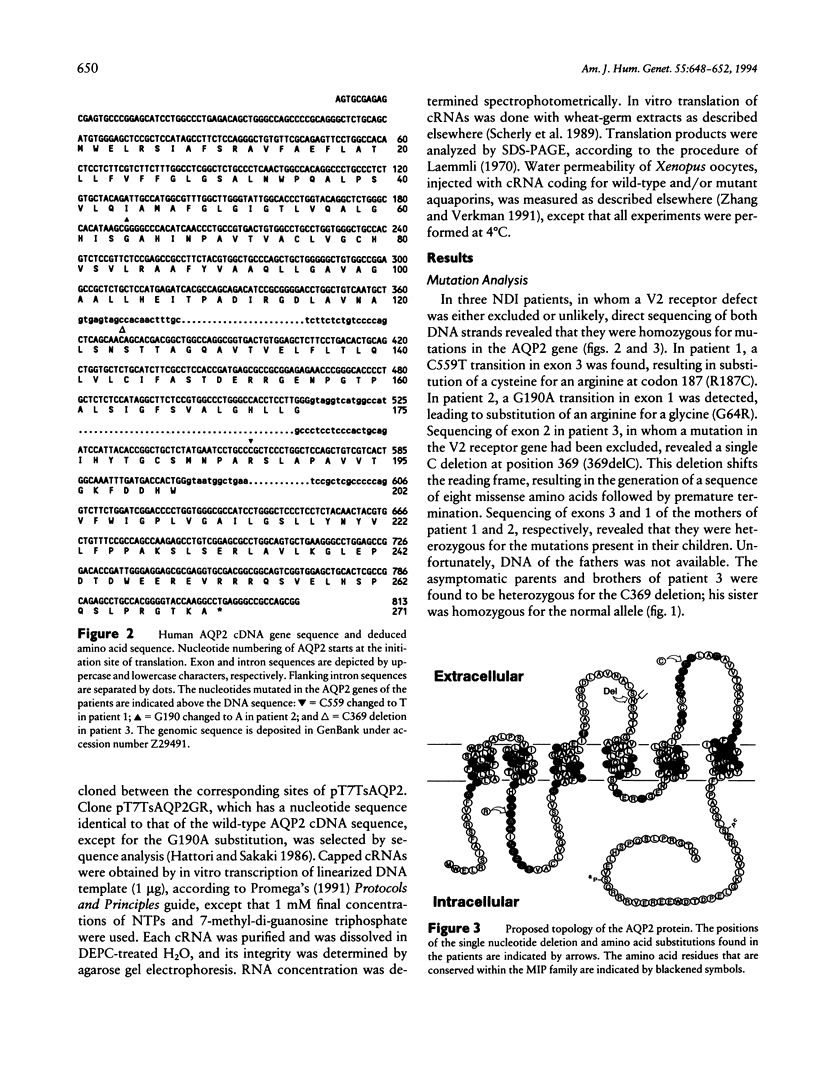
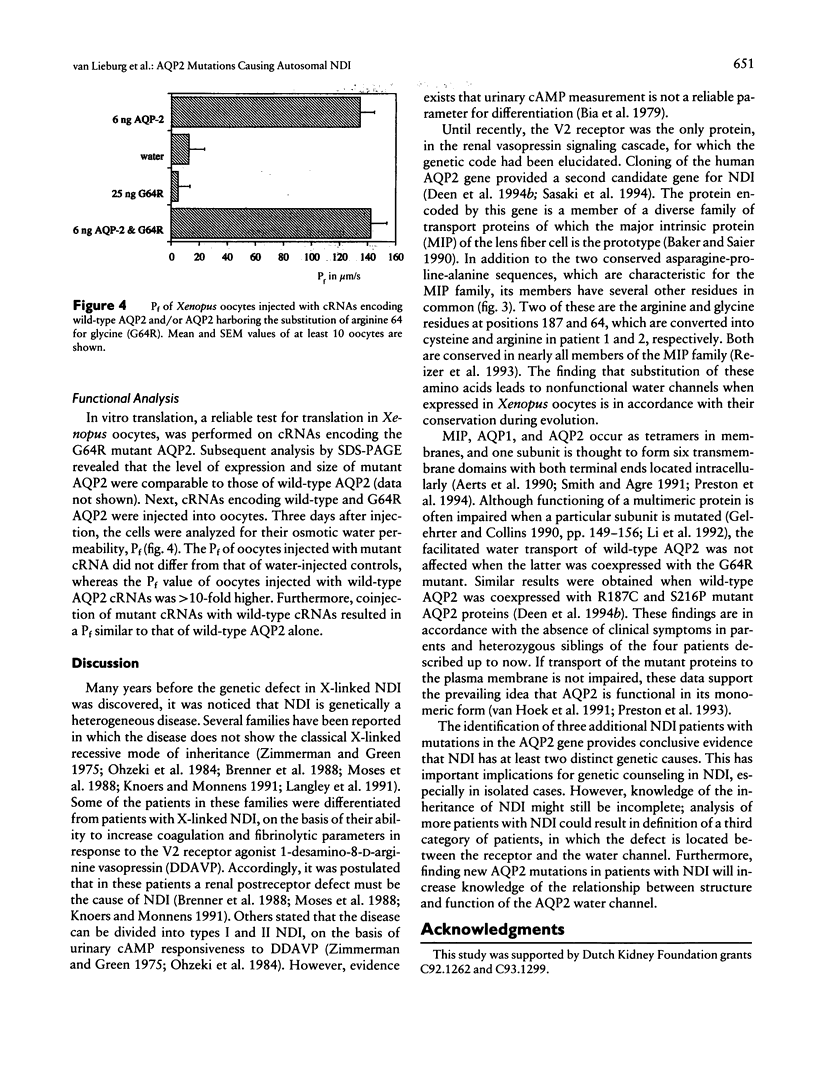
Mutations in the X-chromosomal V2 receptor gene are known to cause nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (NDI). Besides the X-linked form, an autosomal mode of inheritance has been described. Recently, mutations in the autosomal gene coding for water-channel aquaporin 2 (AQP2) of the renal collecting duct were reported in an NDI patient. In the present study, missense mutations and a single nucleotide deletion in the aquaporin 2 gene of three NDI patients from consanguineous matings are described. Expression studies in Xenopus oocytes showed that the missense AQP2 proteins are nonfunctional. These results prove that mutations in the AQP2 gene cause autosomal recessive NDI.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aerts T., Xia J. Z., Slegers H., de Block J., Clauwaert J. Hydrodynamic characterization of the major intrinsic protein from the bovine lens fiber membranes. Extraction in n-octyl-beta-D-glucopyranoside and evidence for a tetrameric structure. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8675–8680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker M. E., Saier M. H., Jr A common ancestor for bovine lens fiber major intrinsic protein, soybean nodulin-26 protein, and E. coli glycerol facilitator. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):185–186. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90731-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bia M. J., Dewitt S., Forrest J. N., Jr Dissociation between plasma, urine, and renal papillary cyclic AMP content following vasopressin and DDAVP. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):F218–F225. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1979.237.3.F218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichet D. G., Arthus M. F., Lonergan M., Hendy G. N., Paradis A. J., Fujiwara T. M., Morgan K., Gregory M. C., Rosenthal W., Didwania A. X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus mutations in North America and the Hopewell hypothesis. J Clin Invest. 1993 Sep;92(3):1262–1268. doi: 10.1172/JCI116698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Seligsohn U., Hochberg Z. Normal response of factor VIII and von Willebrand factor to 1-deamino-8D-arginine vasopressin in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Jul;67(1):191–193. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-1-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen P. M., Verdijk M. A., Knoers N. V., Wieringa B., Monnens L. A., van Os C. H., van Oost B. A. Requirement of human renal water channel aquaporin-2 for vasopressin-dependent concentration of urine. Science. 1994 Apr 1;264(5155):92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.8140421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen P. M., Weghuis D. O., Sinke R. J., Geurts van Kessel A., Wieringa B., van Os C. H. Assignment of the human gene for the water channel of renal collecting duct Aquaporin 2 (AQP2) to chromosome 12 region q12-->q13. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1994;66(4):260–262. doi: 10.1159/000133707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fushimi K., Uchida S., Hara Y., Hirata Y., Marumo F., Sasaki S. Cloning and expression of apical membrane water channel of rat kidney collecting tubule. Nature. 1993 Feb 11;361(6412):549–552. doi: 10.1038/361549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman E. J., Harris H. W., Jr, Kolakowski L. F., Jr, Guay-Woodford L. M., Botelho B., Ausiello D. A. Brief report: a molecular defect in the vasopressin V2-receptor gene causing nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. N Engl J Med. 1993 May 27;328(21):1534–1537. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199305273282105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoers N., Monnens L. A. A variant of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus: V2 receptor abnormality restricted to the kidney. Eur J Pediatr. 1991 Mar;150(5):370–373. doi: 10.1007/BF01955943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoers N., van den Ouweland A., Dreesen J., Verdijk M., Monnens L. A., van Oost B. A. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus: identification of the genetic defect. Pediatr Nephrol. 1993 Oct;7(5):685–688. doi: 10.1007/BF00852579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley J. M., Balfe J. W., Selander T., Ray P. N., Clarke J. T. Autosomal recessive inheritance of vasopressin-resistant diabetes insipidus. Am J Med Genet. 1991 Jan;38(1):90–94. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320380120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Specification of subunit assembly by the hydrophilic amino-terminal domain of the Shaker potassium channel. Science. 1992 Aug 28;257(5074):1225–1230. doi: 10.1126/science.1519059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merendino J. J., Jr, Speigel A. M., Crawford J. D., O'Carroll A. M., Brownstein M. J., Lolait S. J. Brief report: a mutation in the vasopressin V2-receptor gene in a kindred with X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. N Engl J Med. 1993 May 27;328(21):1538–1541. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199305273282106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. M., Miller J. L., Levine M. A. Two distinct pathophysiological mechanisms in congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Jun;66(6):1259–1264. doi: 10.1210/jcem-66-6-1259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., DiGiovanni S. R., Christensen E. I., Knepper M. A., Harris H. W. Cellular and subcellular immunolocalization of vasopressin-regulated water channel in rat kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11663–11667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohzeki T., Igarashi T., Okamoto A. Familial cases of congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus type II: Remarkable increment of urinary adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in response to antidiuretic hormone. J Pediatr. 1984 Apr;104(4):593–595. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80556-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan Y., Metzenberg A., Das S., Jing B., Gitschier J. Mutations in the V2 vasopressin receptor gene are associated with X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):103–106. doi: 10.1038/ng1092-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston G. M., Jung J. S., Guggino W. B., Agre P. The mercury-sensitive residue at cysteine 189 in the CHIP28 water channel. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):17–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Reizer A., Saier M. H., Jr The MIP family of integral membrane channel proteins: sequence comparisons, evolutionary relationships, reconstructed pathway of evolution, and proposed functional differentiation of the two repeated halves of the proteins. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1993;28(3):235–257. doi: 10.3109/10409239309086796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal W., Seibold A., Antaramian A., Lonergan M., Arthus M. F., Hendy G. N., Birnbaumer M., Bichet D. G. Molecular identification of the gene responsible for congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nature. 1992 Sep 17;359(6392):233–235. doi: 10.1038/359233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki S., Fushimi K., Saito H., Saito F., Uchida S., Ishibashi K., Kuwahara M., Ikeuchi T., Inui K., Nakajima K. Cloning, characterization, and chromosomal mapping of human aquaporin of collecting duct. J Clin Invest. 1994 Mar;93(3):1250–1256. doi: 10.1172/JCI117079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Boelens W., van Venrooij W. J., Dathan N. A., Hamm J., Mattaj I. W. Identification of the RNA binding segment of human U1 A protein and definition of its binding site on U1 snRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4163–4170. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. L., Agre P. Erythrocyte Mr 28,000 transmembrane protein exists as a multisubunit oligomer similar to channel proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6407–6415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang R. B., Verkman A. S. Water and urea permeability properties of Xenopus oocytes: expression of mRNA from toad urinary bladder. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jan;260(1 Pt 1):C26–C34. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.1.C26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hoek A. N., Hom M. L., Luthjens L. H., de Jong M. D., Dempster J. A., van Os C. H. Functional unit of 30 kDa for proximal tubule water channels as revealed by radiation inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16633–16635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Ouweland A. M., Dreesen J. C., Verdijk M., Knoers N. V., Monnens L. A., Rocchi M., van Oost B. A. Mutations in the vasopressin type 2 receptor gene (AVPR2) associated with nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):99–102. doi: 10.1038/ng1092-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


