Abstract
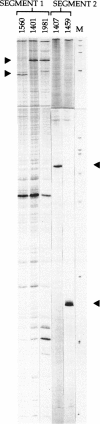
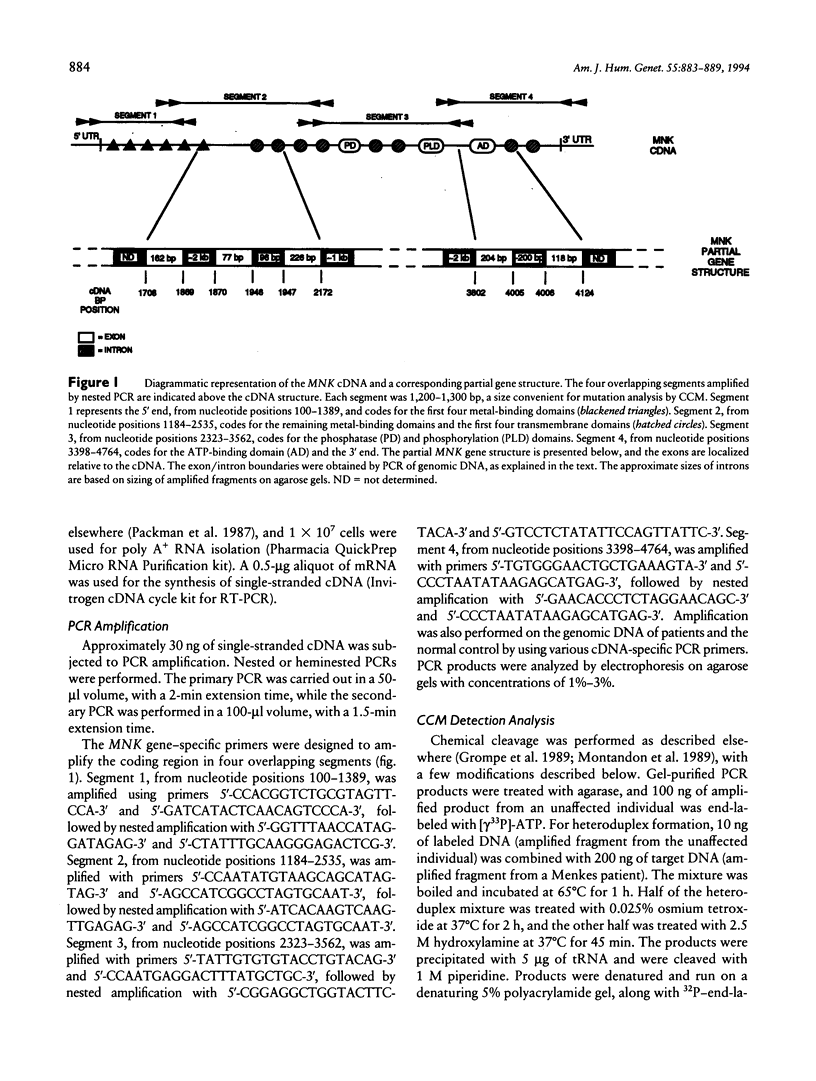
Fibroblast cultures from 12 unrelated patients with classical Menkes disease were analyzed for mutations in the MNK gene, by reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) and chemical cleavage mismatch detection. Mutations were observed in 10 patients, and in each case a different mutation was present. All of the mutations would be predicted to have adverse effects on protein expression. Mutations that resulted in splicing abnormalities, detected by RT-PCR alone, were observed in six patients and included two splice-site changes, a nonsense mutation, a missense mutation, a small duplication, and a small deletion. Chemical cleavage analysis of the remaining six patients revealed the presence of one nonsense mutation, two adjacent 5-bp deletions, and one missense mutation. A valine/leucine polymorphism was also observed. These findings, combined with the prior observation of deletions in 15%-20% of Menkes patients, suggest that Southern blot hybridization and RT-PCR will identify mutations in the majority of patients.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chelly J., Tümer Z., Tønnesen T., Petterson A., Ishikawa-Brush Y., Tommerup N., Horn N., Monaco A. P. Isolation of a candidate gene for Menkes disease that encodes a potential heavy metal binding protein. Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):14–19. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condie A., Eeles R., Borresen A. L., Coles C., Cooper C., Prosser J. Detection of point mutations in the p53 gene: comparison of single-strand conformation polymorphism, constant denaturant gel electrophoresis, and hydroxylamine and osmium tetroxide techniques. Hum Mutat. 1993;2(1):58–66. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380020111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton R. G., Rodrigues N. R., Campbell R. D. Reactivity of cytosine and thymine in single-base-pair mismatches with hydroxylamine and osmium tetroxide and its application to the study of mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4397–4401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz H. C., Valle D., Francomano C. A., Kendzior R. J., Jr, Pyeritz R. E., Cutting G. R. The skipping of constitutive exons in vivo induced by nonsense mutations. Science. 1993 Jan 29;259(5095):680–683. doi: 10.1126/science.8430317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P. J., Schmeissner U., Hofer M., Miller J. H. Genetic studies of the lac repressor. VII. On the molecular nature of spontaneous hotspots in the lacI gene of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda I., Ogawa K. Alternatively-spliced p53 mRNA in the FAA-HTC1 rat hepatoma cell line without the splice site mutations. Cell Struct Funct. 1992 Dec;17(6):427–432. doi: 10.1247/csf.17.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes A. M., Tønnesen T., Pergament E., Sander C., Baerlocher K. E., Wartha R., Güttler F., Horn N. Variability in clinical expression of Menkes syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 1988 Nov;148(2):132–135. doi: 10.1007/BF00445920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson R. A., Hajianpour A., Murer-Orlando M., Buchwald M., Mathew C. G. A nonsense mutation and exon skipping in the Fanconi anaemia group C gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jun;2(6):797–799. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.6.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grompe M., Muzny D. M., Caskey C. T. Scanning detection of mutations in human ornithine transcarbamoylase by chemical mismatch cleavage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5888–5892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas R. H., Robinson A., Evans K., Lascelles P. T., Dubowitz V. An X-linked disease of the nervous system with disordered copper metabolism and features differing from Menkes disease. Neurology. 1981 Jul;31(7):852–859. doi: 10.1212/wnl.31.7.852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson B., Gitschier J., Vulpe C., Whitney S., Yang S., Packman S. Are X-linked cutis laxa and Menkes disease allelic? Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):6–6. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligtenberg M. J., Gennissen A. M., Vos H. L., Hilkens J. A single nucleotide polymorphism in an exon dictates allele dependent differential splicing of episialin mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 25;19(2):297–301. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo M., Masumura T., Nishio H., Nakajima T., Kitoh Y., Takumi T., Koga J., Nakamura H. Exon skipping during splicing of dystrophin mRNA precursor due to an intraexon deletion in the dystrophin gene of Duchenne muscular dystrophy kobe. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):2127–2131. doi: 10.1172/JCI115244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer J. F., Livingston J., Hall B., Paynter J. A., Begy C., Chandrasekharappa S., Lockhart P., Grimes A., Bhave M., Siemieniak D. Isolation of a partial candidate gene for Menkes disease by positional cloning. Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):20–25. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon A. J., Green P. M., Giannelli F., Bentley D. R. Direct detection of point mutations by mismatch analysis: application to haemophilia B. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3347–3358. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor J. A., Green P. M., Rizza C. R., Giannelli F. Analysis of factor VIII mRNA reveals defects in everyone of 28 haemophilia A patients. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jan;2(1):11–17. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odermatt A., Suter H., Krapf R., Solioz M. An ATPase operon involved in copper resistance by Enterococcus hirae. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Nov 30;671:484–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb43836.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman S., Palmiter R. D., Karin M., O'Toole C. Metallothionein messenger RNA regulation in the mottled mouse and Menkes kinky hair syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1338–1342. doi: 10.1172/JCI112959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steingrimsdottir H., Rowley G., Dorado G., Cole J., Lehmann A. R. Mutations which alter splicing in the human hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1201–1208. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tønnesen T., Petterson A., Kruse T. A., Gerdes A. M., Horn N. Multipoint linkage analysis in Menkes disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 May;50(5):1012–1017. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vulpe C., Levinson B., Whitney S., Packman S., Gitschier J. Isolation of a candidate gene for Menkes disease and evidence that it encodes a copper-transporting ATPase. Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):7–13. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakamatsu N., Kobayashi H., Miyatake T., Tsuji S. A novel exon mutation in the human beta-hexosaminidase beta subunit gene affects 3' splice site selection. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2406–2413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yandell D. W., Campbell T. A., Dayton S. H., Petersen R., Walton D., Little J. B., McConkie-Rosell A., Buckley E. G., Dryja T. P. Oncogenic point mutations in the human retinoblastoma gene: their application to genetic counseling. N Engl J Med. 1989 Dec 21;321(25):1689–1695. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198912213212501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]