Abstract
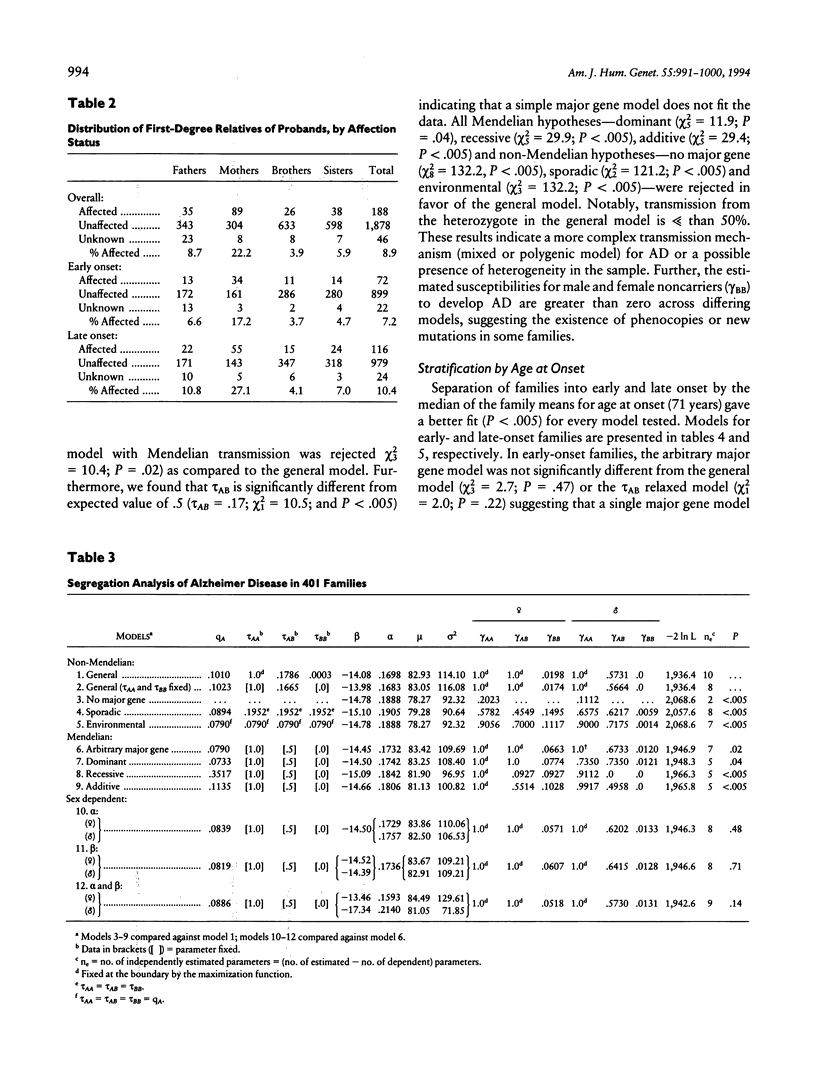
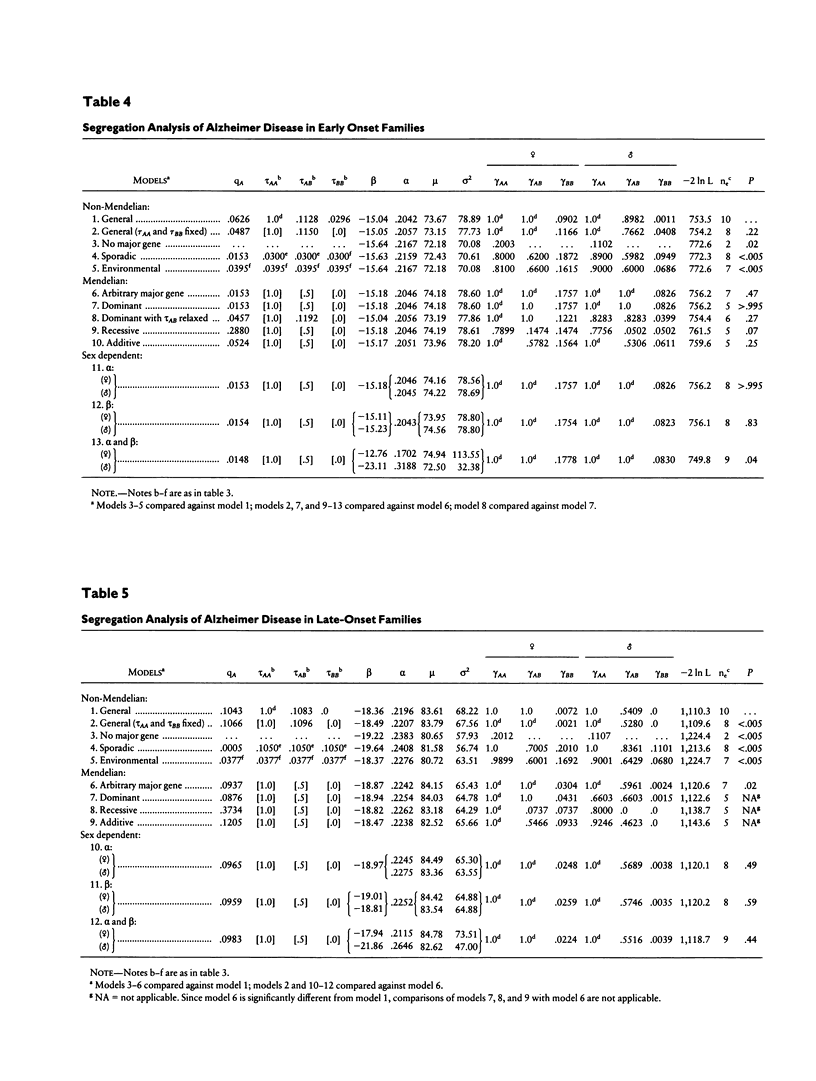
We have evaluated several transmission models for Alzheimer disease (AD), using the logistic regressive approach in 401 nuclear families of consecutively ascertained and rigorously diagnosed probands. Models postulating no major gene effect, random environmental transmission, recessive inheritance, and sporadic occurrence were rejected under varied assumptions regarding the associations among sex, age, and major gene susceptibility. Transmission of the disorder was not fully explained by a single Mendelian model for all families. Stratification of families as early- and late-onset by using the median of family mean onset ages showed that, regardless of the model studied, two groups of families fit better than a single group. AD in early-onset families is transmitted as an autosomal dominant trait with full penetrance in both sexes and has a gene frequency of 1.5%. Dominant inheritance also gave the best fit of the data in late-onset families, but this hypothesis was rejected, suggesting the presence of heterogeneity within this subset. Our study also revealed that genetically nonsusceptible males and females develop AD, indicating the presence of phenocopies within early-onset and late-onset groups. Moreover, our results suggest that the higher risk to females is not solely due to their increased longevity.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borgaonkar D. S., Schmidt L. C., Martin S. E., Kanzer M. D., Edelsohn L., Growdon J., Farrer L. A. Linkage of late-onset Alzheimer's disease with apolipoprotein E type 4 on chromosome 19. Lancet. 1993 Sep 4;342(8871):625–625. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91458-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitner J. C., Silverman J. M., Mohs R. C., Davis K. L. Familial aggregation in Alzheimer's disease: comparison of risk among relatives of early-and late-onset cases, and among male and female relatives in successive generations. Neurology. 1988 Feb;38(2):207–212. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breteler M. M., Claus J. J., van Duijn C. M., Launer L. J., Hofman A. Epidemiology of Alzheimer's disease. Epidemiol Rev. 1992;14:59–82. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corder E. H., Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D. E., Gaskell P. C., Small G. W., Roses A. D., Haines J. L., Pericak-Vance M. A. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science. 1993 Aug 13;261(5123):921–923. doi: 10.1126/science.8346443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demenais F. M., Laing A. E., Bonney G. E. Numerical comparisons of two formulations of the logistic regressive models with the mixed model in segregation analysis of discrete traits. Genet Epidemiol. 1992;9(6):419–435. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370090605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elandt-Johnson R. C. Segregation analysis for complex modes of inheritance. Am J Hum Genet. 1970 Mar;22(2):129–144. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston R. C., Sobel E. Sampling considerations in the gathering and analysis of pedigree data. Am J Hum Genet. 1979 Jan;31(1):62–69. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. A., Funkenstein H. H., Albert M. S., Scherr P. A., Cook N. R., Chown M. J., Hebert L. E., Hennekens C. H., Taylor J. O. Prevalence of Alzheimer's disease in a community population of older persons. Higher than previously reported. JAMA. 1989 Nov 10;262(18):2551–2556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrer L. A., Cupples L. A., Blackburn S., Kiely D. K., Auerbach S., Growdon J. H., Connor-Lacke L., Karlinsky H., Thibert A., Burke J. R. Interrater agreement for diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: the MIRAGE study. Neurology. 1994 Apr;44(4):652–656. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.4.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrer L. A., Cupples L. A., Connor L., Wolf P. A., Growdon J. H. Association of decreased paternal age and late-onset Alzheimer's disease. An example of genetic imprinting? Arch Neurol. 1991 Jun;48(6):599–604. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1991.00530180051017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrer L. A., Cupples L. A. Estimating the probability for major gene Alzheimer disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Feb;54(2):374–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrer L. A., Myers R. H., Connor L., Cupples L. A., Growdon J. H. Segregation analysis reveals evidence of a major gene for Alzheimer disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jun;48(6):1026–1033. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrer L. A., Myers R. H., Cupples L. A., St George-Hyslop P. H., Bird T. D., Rossor M. N., Mullan M. J., Polinsky R., Nee L., Heston L. Transmission and age-at-onset patterns in familial Alzheimer's disease: evidence for heterogeneity. Neurology. 1990 Mar;40(3 Pt 1):395–403. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.3_part_1.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrer L. A., O'Sullivan D. M., Cupples L. A., Growdon J. H., Myers R. H. Assessment of genetic risk for Alzheimer's disease among first-degree relatives. Ann Neurol. 1989 May;25(5):485–493. doi: 10.1002/ana.410250511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goate A., Chartier-Harlin M. C., Mullan M., Brown J., Crawford F., Fidani L., Giuffra L., Haynes A., Irving N., James L. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):704–706. doi: 10.1038/349704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heston L. L., Mastri A. R., Anderson V. E., White J. Dementia of the Alzheimer type. Clinical genetics, natural history, and associated conditions. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1981 Oct;38(10):1085–1090. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1981.01780350019001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joachim C. L., Morris J. H., Selkoe D. J. Clinically diagnosed Alzheimer's disease: autopsy results in 150 cases. Ann Neurol. 1988 Jul;24(1):50–56. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAY D. W., BEAMISH P., ROTH M. OLD AGE MENTAL DISORDERS IN NEWCASTLE UPON TYNE. I. A STUDY OF PREVALENCE. Br J Psychiatry. 1964 Mar;110:146–158. doi: 10.1192/bjp.110.465.146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachaturian Z. S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1985 Nov;42(11):1097–1105. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060100083029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokmen E., Chandra V., Schoenberg B. S. Trends in incidence of dementing illness in Rochester, Minnesota, in three quinquennial periods, 1960-1974. Neurology. 1988 Jun;38(6):975–980. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.6.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux R., Ottman R., Tang M. X., Noboa-Bauza L., Marder K., Gurland B., Stern Y. Genetic susceptibility and head injury as risk factors for Alzheimer's disease among community-dwelling elderly persons and their first-degree relatives. Ann Neurol. 1993 May;33(5):494–501. doi: 10.1002/ana.410330513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E. M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E., MacLean C. J. Analysis of family resemblance. 3. Complex segregation of quantitative traits. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Jul;26(4):489–503. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullan M., Houlden H., Windelspecht M., Fidani L., Lombardi C., Diaz P., Rossor M., Crook R., Hardy J., Duff K. A locus for familial early-onset Alzheimer's disease on the long arm of chromosome 14, proximal to the alpha 1-antichymotrypsin gene. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):340–342. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nee L. E., Eldridge R., Sunderland T., Thomas C. B., Katz D., Thompson K. E., Weingartner H., Weiss H., Julian C., Cohen R. Dementia of the Alzheimer type: clinical and family study of 22 twin pairs. Neurology. 1987 Mar;37(3):359–363. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi S., Murakami K., Yamada N. Apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1993 Sep 18;342(8873):737–737. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91728-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payami H., Kaye J., Heston L. L., Bird T. D., Schellenberg G. D. Apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1993 Sep 18;342(8873):738–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pericak-Vance M. A., Bebout J. L., Gaskell P. C., Jr, Yamaoka L. H., Hung W. Y., Alberts M. J., Walker A. P., Bartlett R. J., Haynes C. A., Welsh K. A. Linkage studies in familial Alzheimer disease: evidence for chromosome 19 linkage. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jun;48(6):1034–1050. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pericak-Vance M. A., Yamaoka L. H., Haynes C. S., Speer M. C., Haines J. L., Gaskell P. C., Hung W. Y., Clark C. M., Heyman A. L., Trofatter J. A. Genetic linkage studies in Alzheimer's disease families. Exp Neurol. 1988 Dec;102(3):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(88)90220-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier J., Davignon J., Bouthillier D., Kogan S., Bertrand P., Gauthier S. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1993 Sep 18;342(8873):697–699. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91705-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocca W. A., Hofman A., Brayne C., Breteler M. M., Clarke M., Copeland J. R., Dartigues J. F., Engedal K., Hagnell O., Heeren T. J. Frequency and distribution of Alzheimer's disease in Europe: a collaborative study of 1980-1990 prevalence findings. The EURODEM-Prevalence Research Group. Ann Neurol. 1991 Sep;30(3):381–390. doi: 10.1002/ana.410300310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D., George-Hyslop P. H., Pericak-Vance M. A., Joo S. H., Rosi B. L., Gusella J. F., Crapper-MacLachlan D. R., Alberts M. J. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1993 Aug;43(8):1467–1472. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.8.1467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellenberg G. D., Bird T. D., Wijsman E. M., Orr H. T., Anderson L., Nemens E., White J. A., Bonnycastle L., Weber J. L., Alonso M. E. Genetic linkage evidence for a familial Alzheimer's disease locus on chromosome 14. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):668–671. doi: 10.1126/science.1411576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenberg B. S., Kokmen E., Okazaki H. Alzheimer's disease and other dementing illnesses in a defined United States population: incidence rates and clinical features. Ann Neurol. 1987 Dec;22(6):724–729. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St George-Hyslop P. H., Haines J. L., Farrer L. A., Polinsky R., Van Broeckhoven C., Goate A., McLachlan D. R., Orr H., Bruni A. C., Sorbi S. Genetic linkage studies suggest that Alzheimer's disease is not a single homogeneous disorder. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):194–197. doi: 10.1038/347194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St George-Hyslop P. H., Myers R. H., Haines J. L., Farrer L. A., Tanzi R. E., Abe K., James M. F., Conneally P. M., Polinsky R. J., Gusella J. F. Familial Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems. Neurobiol Aging. 1989 Sep-Oct;10(5):417–425. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(89)90082-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St George-Hyslop P., Haines J., Rogaev E., Mortilla M., Vaula G., Pericak-Vance M., Foncin J. F., Montesi M., Bruni A., Sorbi S. Genetic evidence for a novel familial Alzheimer's disease locus on chromosome 14. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):330–334. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Saunders A. M., Schmechel D., Pericak-Vance M., Enghild J., Salvesen G. S., Roses A. D. Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Vaula G., Romano D. M., Mortilla M., Huang T. L., Tupler R. G., Wasco W., Hyman B. T., Haines J. L., Jenkins B. J. Assessment of amyloid beta-protein precursor gene mutations in a large set of familial and sporadic Alzheimer disease cases. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Aug;51(2):273–282. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treves T., Korczyn A. D., Zilber N., Kahana E., Leibowitz Y., Alter M., Schoenberg B. S. Presenile dementia in Israel. Arch Neurol. 1986 Jan;43(1):26–29. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1986.00520010022014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Broeckhoven C., Backhovens H., Cruts M., De Winter G., Bruyland M., Cras P., Martin J. J. Mapping of a gene predisposing to early-onset Alzheimer's disease to chromosome 14q24.3. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):335–339. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duijn C. M., Farrer L. A., Cupples L. A., Hofman A. Genetic transmission of Alzheimer's disease among families in a Dutch population based study. J Med Genet. 1993 Aug;30(8):640–646. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.8.640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duijn C. M., Hofman A. Relation between nicotine intake and Alzheimer's disease. BMJ. 1991 Jun 22;302(6791):1491–1494. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6791.1491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duijn C. M., de Knijff P., Cruts M., Wehnert A., Havekes L. M., Hofman A., Van Broeckhoven C. Apolipoprotein E4 allele in a population-based study of early-onset Alzheimer's disease. Nat Genet. 1994 May;7(1):74–78. doi: 10.1038/ng0594-74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


