Abstract
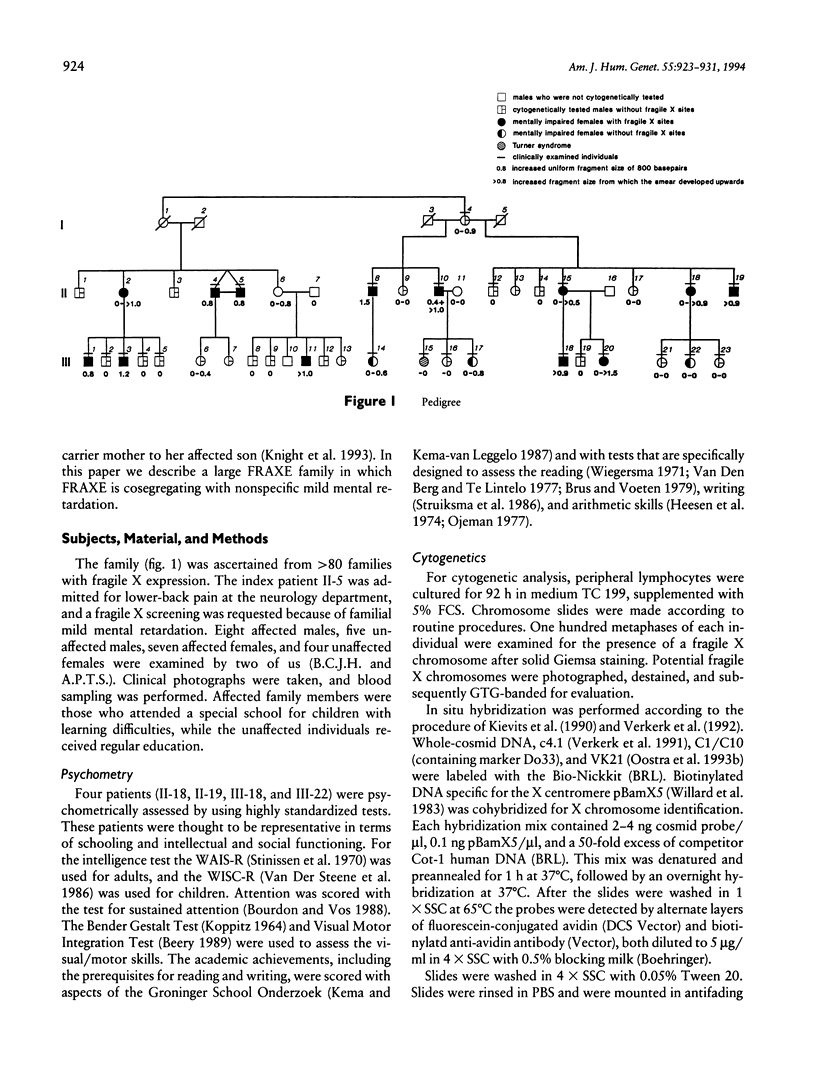
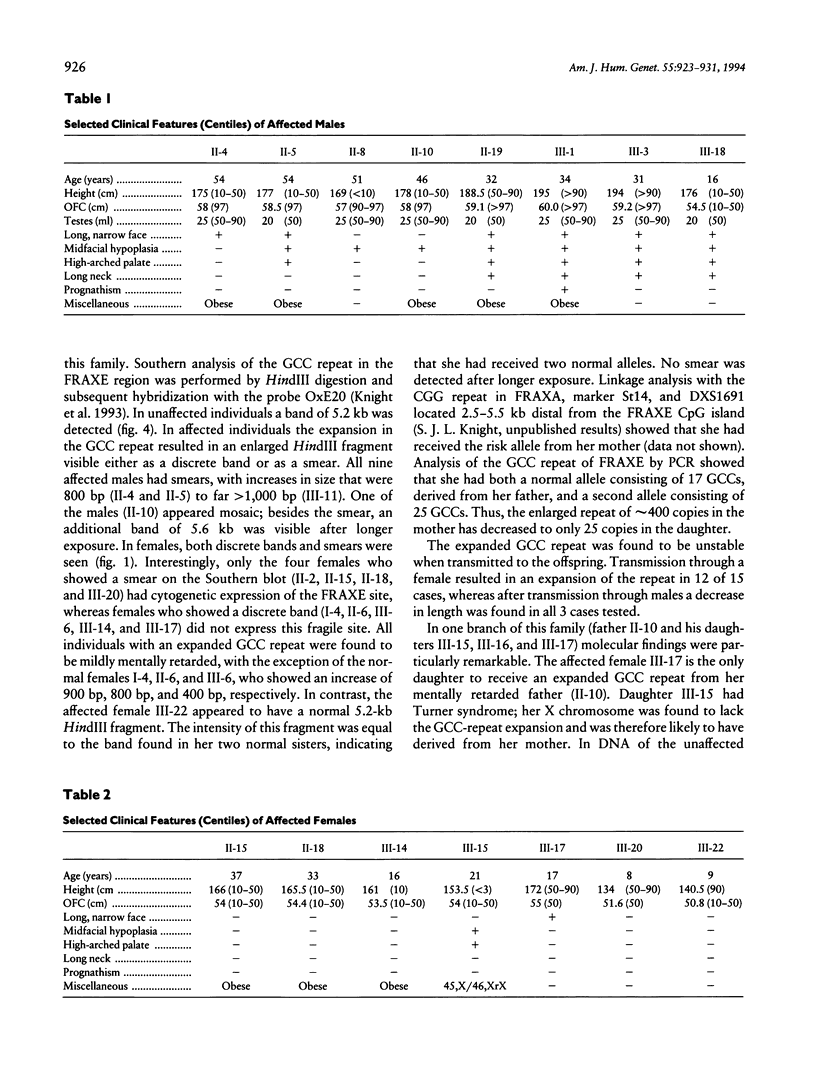
During an ongoing study on X-linked mental retardation, we ascertained a large family in which mild mental retardation was cosegregating with a fragile site at Xq27-28. Clinical, psychometric, cytogenetic, and molecular studies were performed. Apart from mild mental retardation, affected males and females did not show a specific clinical phenotype. Psychometric assessment of four representative affected individuals revealed low academic achievements, with verbal and performance IQs of 61-75 and 70-82, respectively. Cytogenetically the fragile site was always present in affected males and was not always present in affected females. With FISH the fragile site was located within the FRAXE region. The expanded GCC repeat of FRAXE was seen in affected males and females either as a discrete band or as a broad smear. No expansion was seen in unaffected males, whereas three unaffected females did have an enlarged GCC repeat. Maternal transmission of FRAXE may lead to expansion or contraction of the GCC repeat length, whereas in all cases of paternal transmission contraction was seen. In striking contrast to the situation in fragile X syndrome, affected males may have affected daughters. In addition, there appears to be no premutation of the FRAXE GCC repeat, since in the family studied here all males lacking the normal allele were found to be affected.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dennis N. R., Curtis G., Macpherson J. N., Jacobs P. A. Two families with Xq27.3 fragility, no detectable insert in the FMR-1 gene, mild mental impairment, and absence of the Martin-Bell phenotype. 1992 Apr 15-May 1Am J Med Genet. 43(1-2):232–236. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn G. A., Hirst M. C., Knight S. J., Macpherson J. N., Barber J. C., Flannery A. V., Davies K. E., Buckle V. J. Identification of the FRAXE fragile site in two families ascertained for X linked mental retardation. J Med Genet. 1993 Feb;30(2):97–100. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.2.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Kuhl D. P., Pizzuti A., Pieretti M., Sutcliffe J. S., Richards S., Verkerk A. J., Holden J. J., Fenwick R. G., Jr, Warren S. T. Variation of the CGG repeat at the fragile X site results in genetic instability: resolution of the Sherman paradox. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1047–1058. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst M. C., Barnicoat A., Flynn G., Wang Q., Daker M., Buckle V. J., Davies K. E., Bobrow M. The identification of a third fragile site, FRAXF, in Xq27--q28 distal to both FRAXA and FRAXE. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Feb;2(2):197–200. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.2.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight S. J., Flannery A. V., Hirst M. C., Campbell L., Christodoulou Z., Phelps S. R., Pointon J., Middleton-Price H. R., Barnicoat A., Pembrey M. E. Trinucleotide repeat amplification and hypermethylation of a CpG island in FRAXE mental retardation. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90300-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight S. J., Voelckel M. A., Hirst M. C., Flannery A. V., Moncla A., Davies K. E. Triplet repeat expansion at the FRAXE locus and X-linked mild mental handicap. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Jul;55(1):81–86. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahori Y., Knight S. J., Holland J., Schwartz C., Roche A., Tarleton J., Wong S., Flint T. J., Froster-Iskenius U., Bentley D. Molecular heterogeneity of the fragile X syndrome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4355–4359. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Boué J., Croquette M. F., Voelckel M. A., Mattei M. G., Mandel J. L. Three families with high expression of a fragile site at Xq27.3, lack of anomalies at the FMR-1 CpG island, and no clear phenotypic association. 1992 Apr 15-May 1Am J Med Genet. 43(1-2):224–231. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Rousseau F., Heitz D., Kretz C., Devys D., Hanauer A., Boué J., Bertheas M. F., Mandel J. L. Instability of a 550-base pair DNA segment and abnormal methylation in fragile X syndrome. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1097–1102. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieretti M., Zhang F. P., Fu Y. H., Warren S. T., Oostra B. A., Caskey C. T., Nelson D. L. Absence of expression of the FMR-1 gene in fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):817–822. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90125-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyniers E., Vits L., De Boulle K., Van Roy B., Van Velzen D., de Graaff E., Verkerk A. J., Jorens H. Z., Darby J. K., Oostra B. The full mutation in the FMR-1 gene of male fragile X patients is absent in their sperm. Nat Genet. 1993 Jun;4(2):143–146. doi: 10.1038/ng0693-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romain D. R., Chapman C. J. Fragile site Xq27.3 in a family without mental retardation. Clin Genet. 1992 Jan;41(1):33–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1992.tb03625.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau F., Heitz D., Biancalana V., Blumenfeld S., Kretz C., Boué J., Tommerup N., Van Der Hagen C., DeLozier-Blanchet C., Croquette M. F. Direct diagnosis by DNA analysis of the fragile X syndrome of mental retardation. N Engl J Med. 1991 Dec 12;325(24):1673–1681. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199112123252401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkerk A. J., Eussen B. H., Van Hemel J. O., Oostra B. A. Limited size of the fragile X site shown by fluorescence in situ hybridization. 1992 Apr 15-May 1Am J Med Genet. 43(1-2):187–191. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkerk A. J., Pieretti M., Sutcliffe J. S., Fu Y. H., Kuhl D. P., Pizzuti A., Reiner O., Richards S., Victoria M. F., Zhang F. P. Identification of a gene (FMR-1) containing a CGG repeat coincident with a breakpoint cluster region exhibiting length variation in fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):905–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90397-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Heitz D., Petit C., Kretz C., Oberlé I., Mandel J. L. Abnormal pattern detected in fragile-X patients by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):624–626. doi: 10.1038/349624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voelckel M. A., Philip N., Piquet C., Pellissier M. C., Oberlé I., Birg F., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F. Study of a family with a fragile site of the X chromosome at Xq27-28 without mental retardation. Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;81(4):353–357. doi: 10.1007/BF00283690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S., Pritchard M., Kremer E., Lynch M., Nancarrow J., Baker E., Holman K., Mulley J. C., Warren S. T., Schlessinger D. Fragile X genotype characterized by an unstable region of DNA. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1179–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]