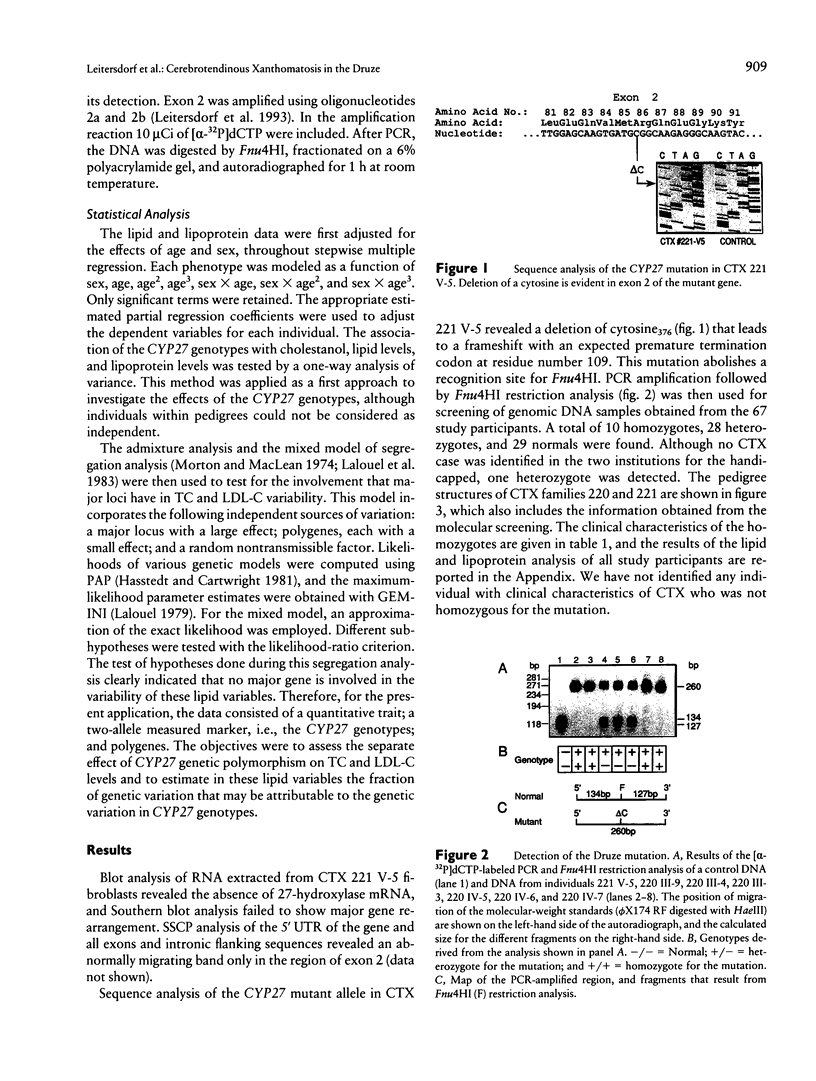
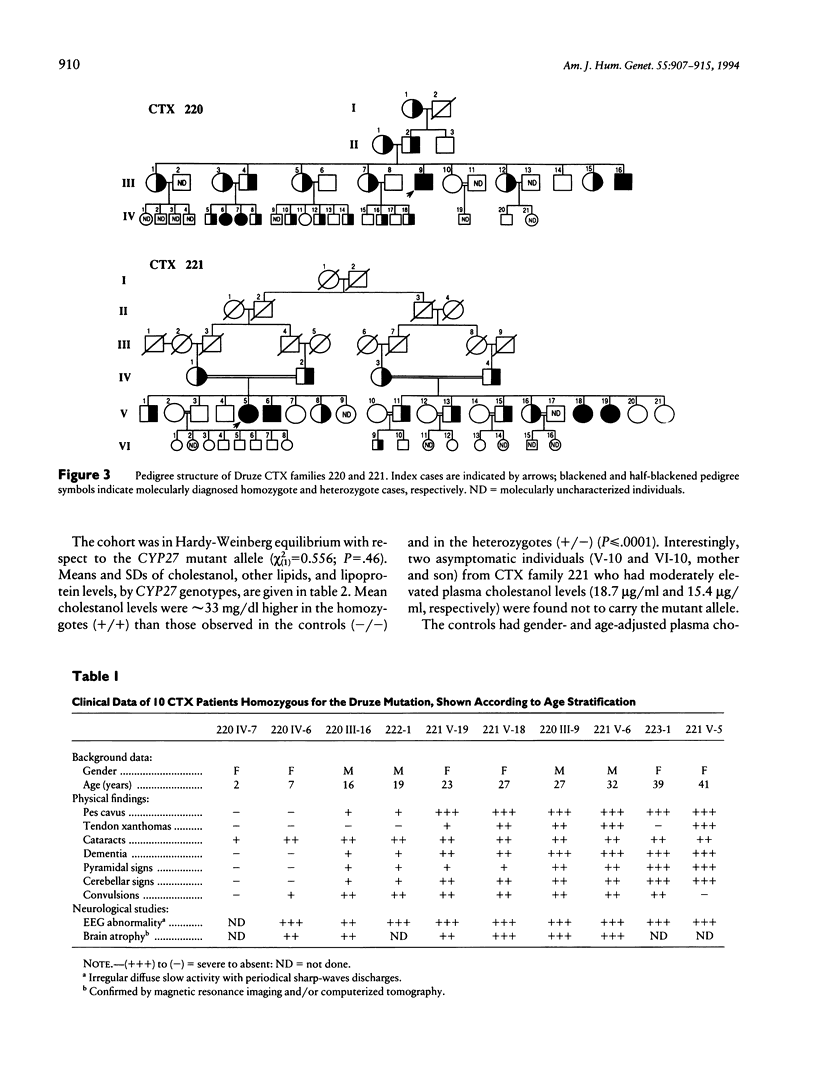
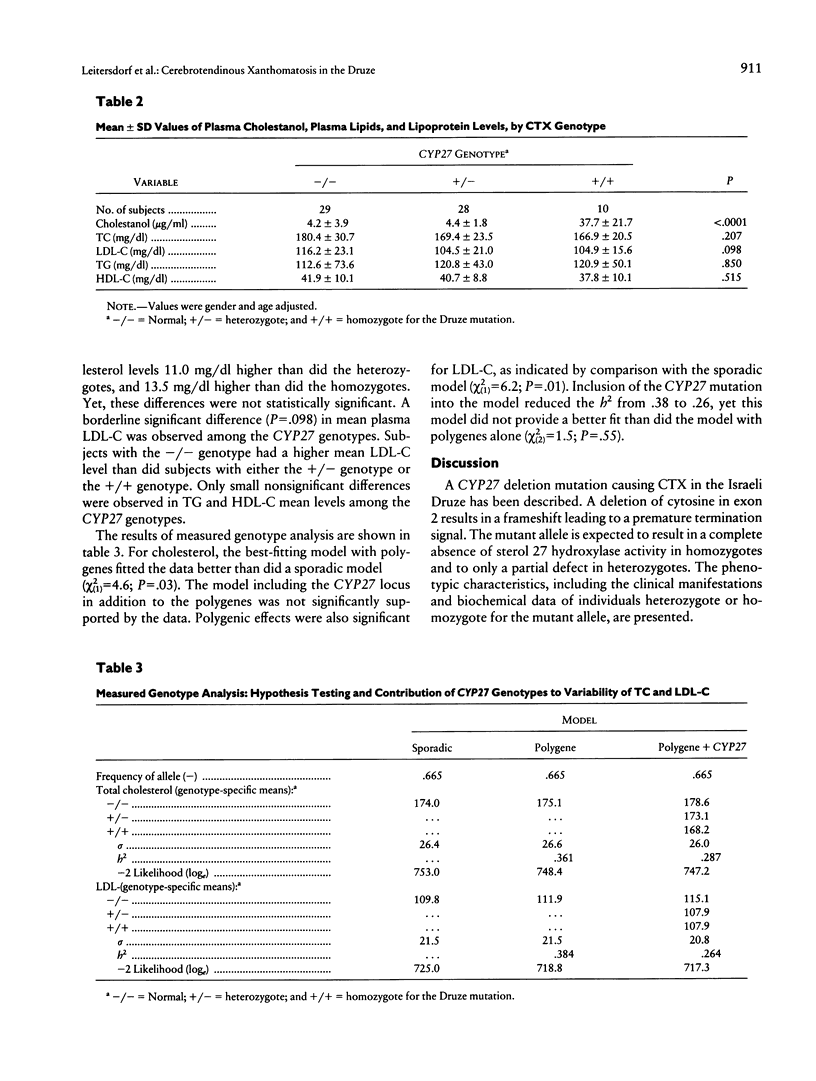
Abstract
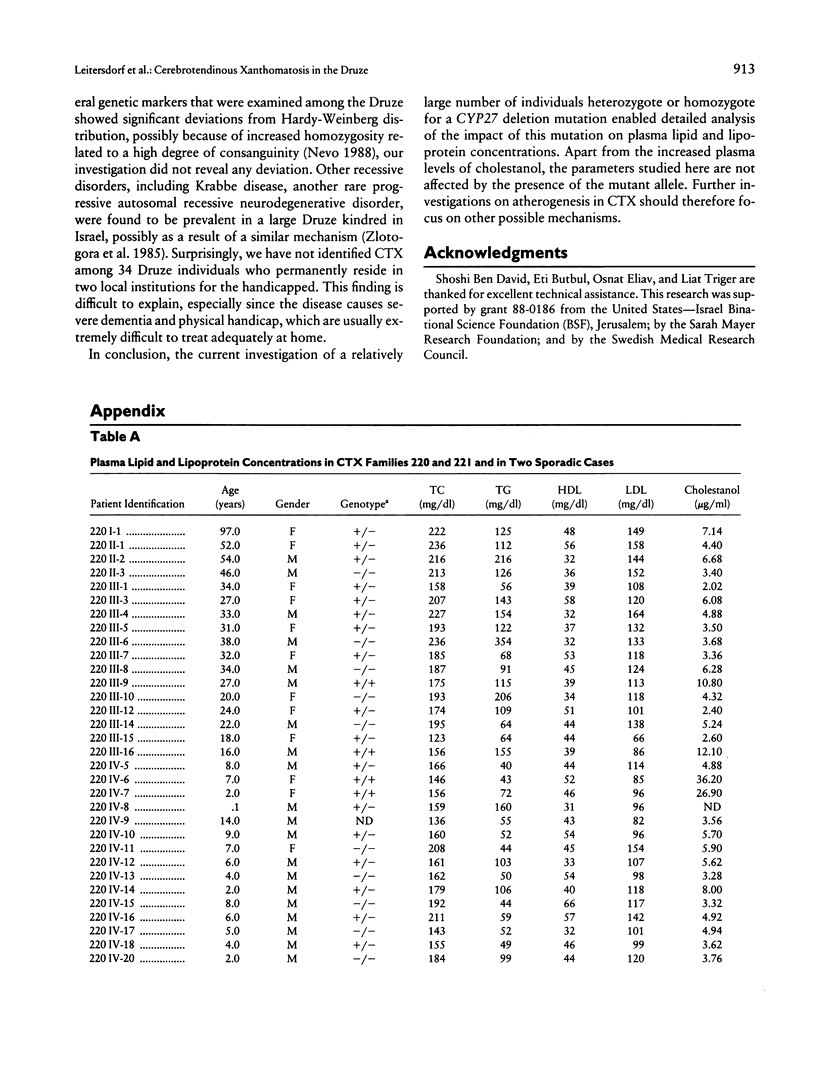
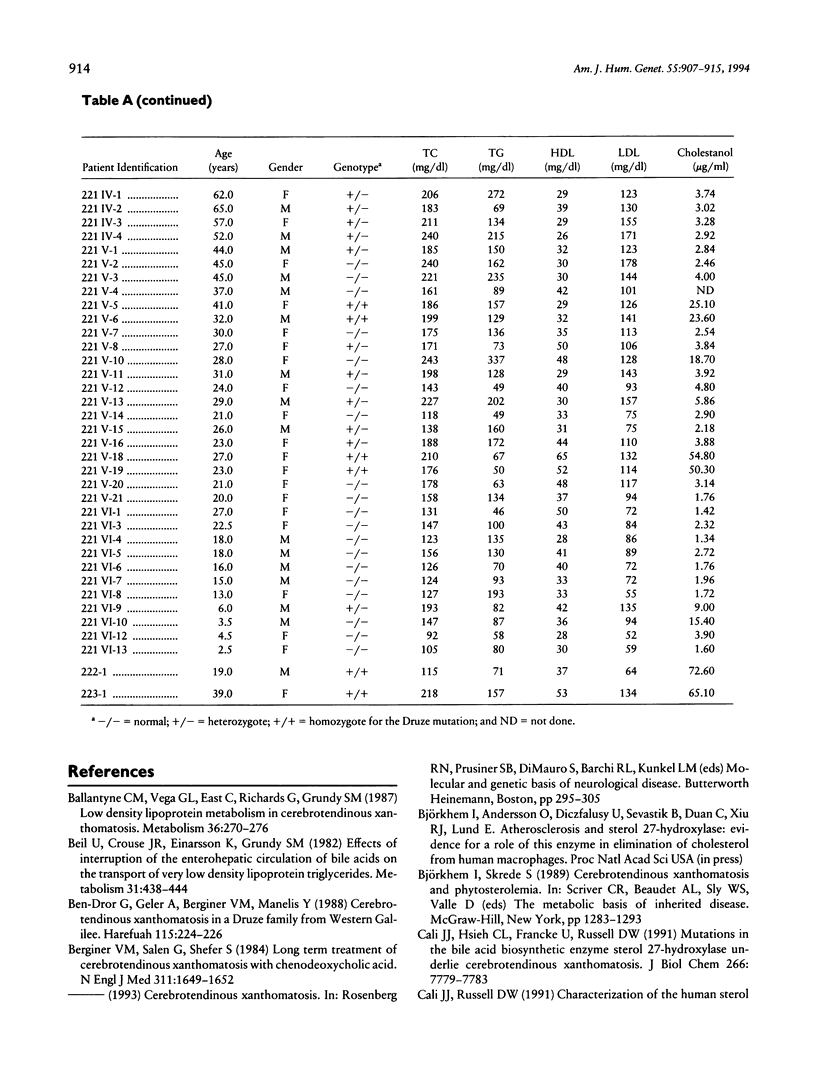
Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX) is an autosomal recessive lipid-storage disease caused by mutations in the sterol 27 hydroxylase gene (CYP27). Clinically, a multitude of neurological, skeletal, and vascular manifestations are usually present. Premature atherosclerosis has been reported in CTX and may be related to the metabolic derangement caused by the deficiency of the enzyme. A CYP27 nonsense mutation created by the deletion of cytosine376 has been identified in four Israeli Druze CTX patients residing in the same village. Molecular screening for this mutation in families of two probands revealed a total of 10 homozygotes and 28 heterozygotes whose clinical and biochemical characteristics are described. Overall, except for tendon xanthomas, most of the clinical manifestations progress with age. The CYP27 mutation was associated with modest differences in the levels of plasma total cholesterol (TC) and LDL cholesterol (LDL-C). The distribution of plasma concentrations of TC and LDL-C in the CTX families was consistent with a polygenic model. A similar model that includes also the effects of the CYP27 genotypes was not better supported by the data. It may be concluded that, in CTX, the presence of a CYP27 mutation does not significantly affect the plasma concentrations of lipids and lipoproteins. Therefore, the reported increased prevalence of atherosclerosis in this disease must be related to other factors.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballantyne C. M., Vega G. L., East C., Richards G., Grundy S. M. Low-density lipoprotein metabolism in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Metabolism. 1987 Mar;36(3):270–276. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(87)90187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beil U., Crouse J. R., Einarsson K., Grundy S. M. Effects of interruption of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids on the transport of very low density-lipoprotein triglycerides. Metabolism. 1982 May;31(5):438–444. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90231-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben Dror G., Geller A., Berginer V., Manelis J. [Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis in a Druze family]. Harefuah. 1988 Nov 1;115(9):224–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berginer V. M., Salen G., Shefer S. Long-term treatment of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis with chenodeoxycholic acid. N Engl J Med. 1984 Dec 27;311(26):1649–1652. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198412273112601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cali J. J., Hsieh C. L., Francke U., Russell D. W. Mutations in the bile acid biosynthetic enzyme sterol 27-hydroxylase underlie cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7779–7783. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cali J. J., Russell D. W. Characterization of human sterol 27-hydroxylase. A mitochondrial cytochrome P-450 that catalyzes multiple oxidation reaction in bile acid biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7774–7778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedewald W. T., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 1972 Jun;18(6):499–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyama J., Kuriyama M., Arima S., Shibata Y., Nagata K., Takenaga S., Tanaka H., Osame M. Atherogenic risk factors in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Clin Chim Acta. 1991 Aug 15;200(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(91)90328-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kibe A., Nakai S., Kuramoto T., Hoshita T. Occurrence of bile alcohols in the bile of a patient with cholestasis. J Lipid Res. 1980 Jul;21(5):594–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyama M., Fujiyama J., Yoshidome H., Takenaga S., Matsumuro K., Kasama T., Fukuda K., Kuramoto T., Hoshita T., Seyama Y. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: clinical and biochemical evaluation of eight patients and review of the literature. J Neurol Sci. 1991 Apr;102(2):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(91)90073-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalouel J. M., Rao D. C., Morton N. E., Elston R. C. A unified model for complex segregation analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Sep;35(5):816–826. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitersdorf E., Reshef A., Meiner V., Levitzki R., Schwartz S. P., Dann E. J., Berkman N., Cali J. J., Klapholz L., Berginer V. M. Frameshift and splice-junction mutations in the sterol 27-hydroxylase gene cause cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis in Jews or Moroccan origin. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jun;91(6):2488–2496. doi: 10.1172/JCI116484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiner V., Marais D. A., Reshef A., Björkhem I., Leitersdorf E. Premature termination codon at the sterol 27-hydroxylase gene causes cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis in an Afrikaner family. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jan;3(1):193–194. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.1.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiner V., Meiner Z., Reshef A., Björkhem I., Leitersdorf E. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: molecular diagnosis enables presymptomatic detection of a treatable disease. Neurology. 1994 Feb;44(2):288–290. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.2.288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E., MacLean C. J. Analysis of family resemblance. 3. Complex segregation of quantitative traits. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Jul;26(4):489–503. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevo S. Genetic blood markers in Arab Druze of Israel. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1988 Oct;77(2):183–190. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330770206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Suzuki Y., Sekiya T., Hayashi K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):874–879. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reshef A., Meiner V., Berginer V. M., Leitersdorf E. Molecular genetics of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis in Jews of north African origin. J Lipid Res. 1994 Mar;35(3):478–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyama Y., Ichikawa K., Yamakawa T. Quantitative determination of cholestanol in plasma with mass fragmentography. Biochemical diagnosis of cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J Biochem. 1976 Aug;80(2):223–228. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore V., Salen G., Cheng F. W., Forte T., Shefer S., Tint G. S., Lindgren F. T. Abnormal high density lipoproteins in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1295–1304. doi: 10.1172/JCI110376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tint G. S., Ginsberg H., Salen G., Le N. A., Shefer S. Chenodeoxycholic acid normalizes elevated lipoprotein secretion and catabolism in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. J Lipid Res. 1989 May;30(5):633–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weydert-Huijghebaert S., Karlaganis G., Renner E. L., Preisig R. Increased urinary excretion of bile alcohol glucuronides in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. J Lipid Res. 1989 Nov;30(11):1673–1679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlotogora J., Regev R., Zeigler M., Iancu T. C., Bach G. Krabbe disease: increased incidence in a highly inbred community. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Aug;21(4):765–770. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320210420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]