Abstract
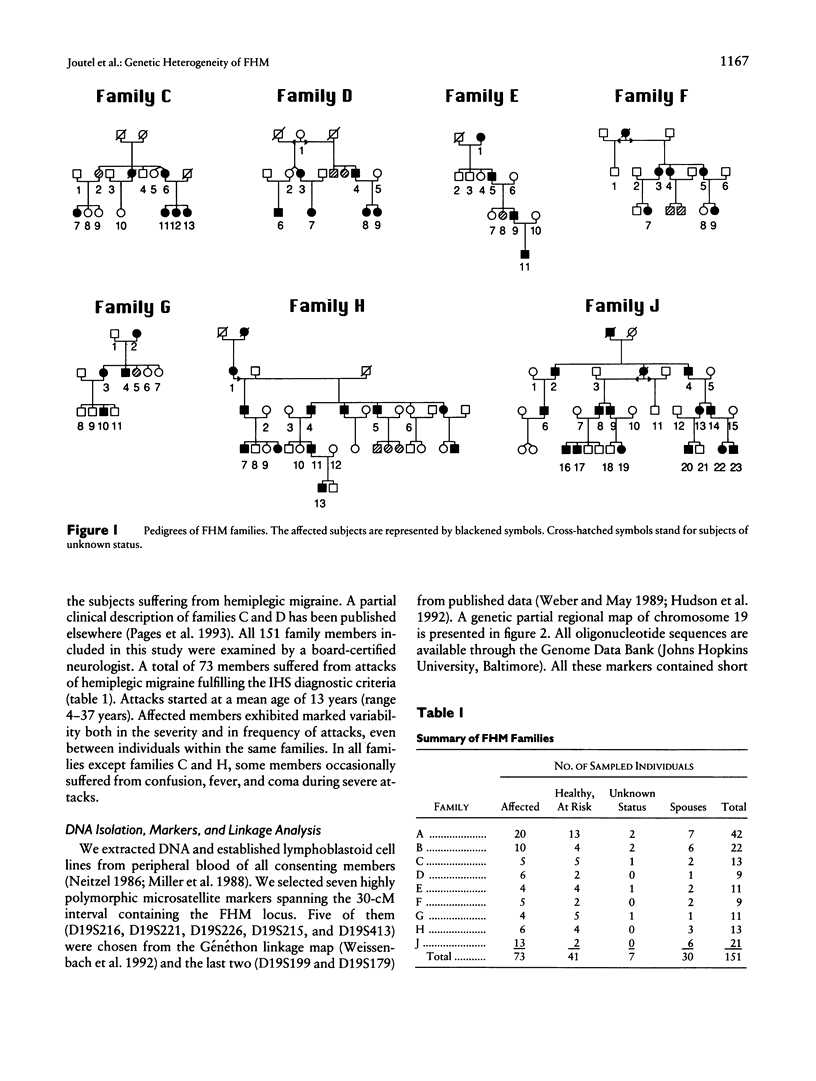
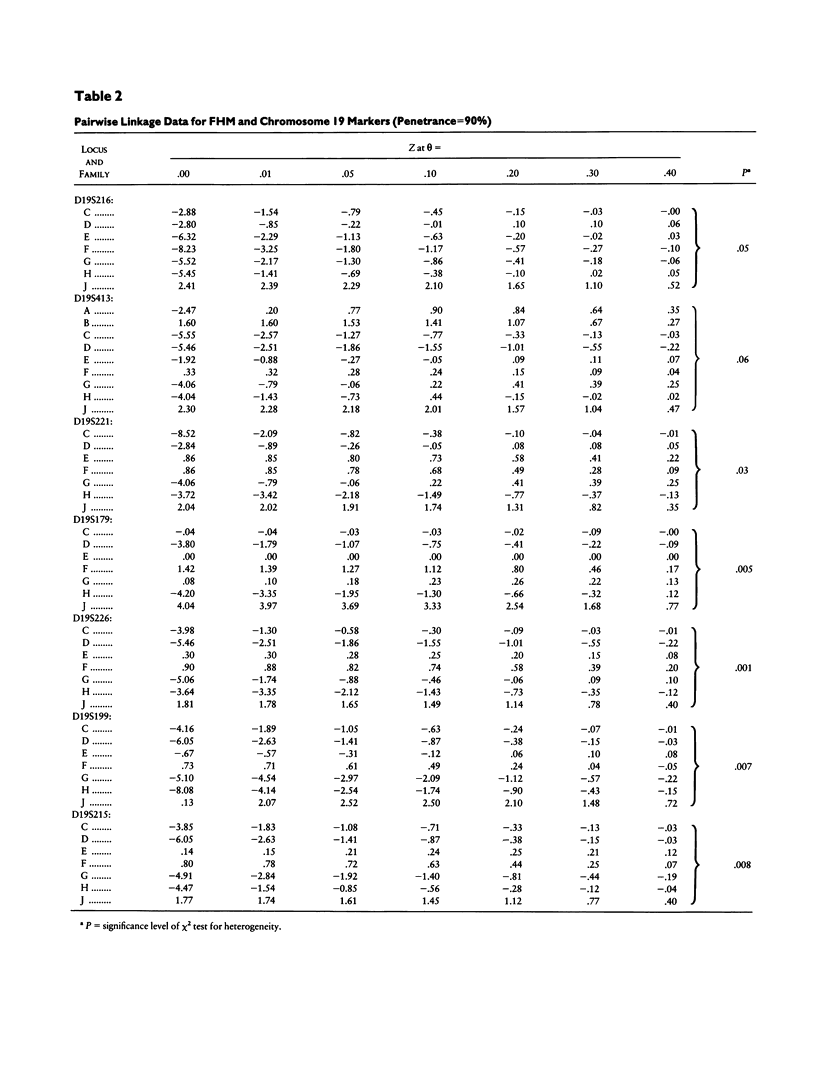
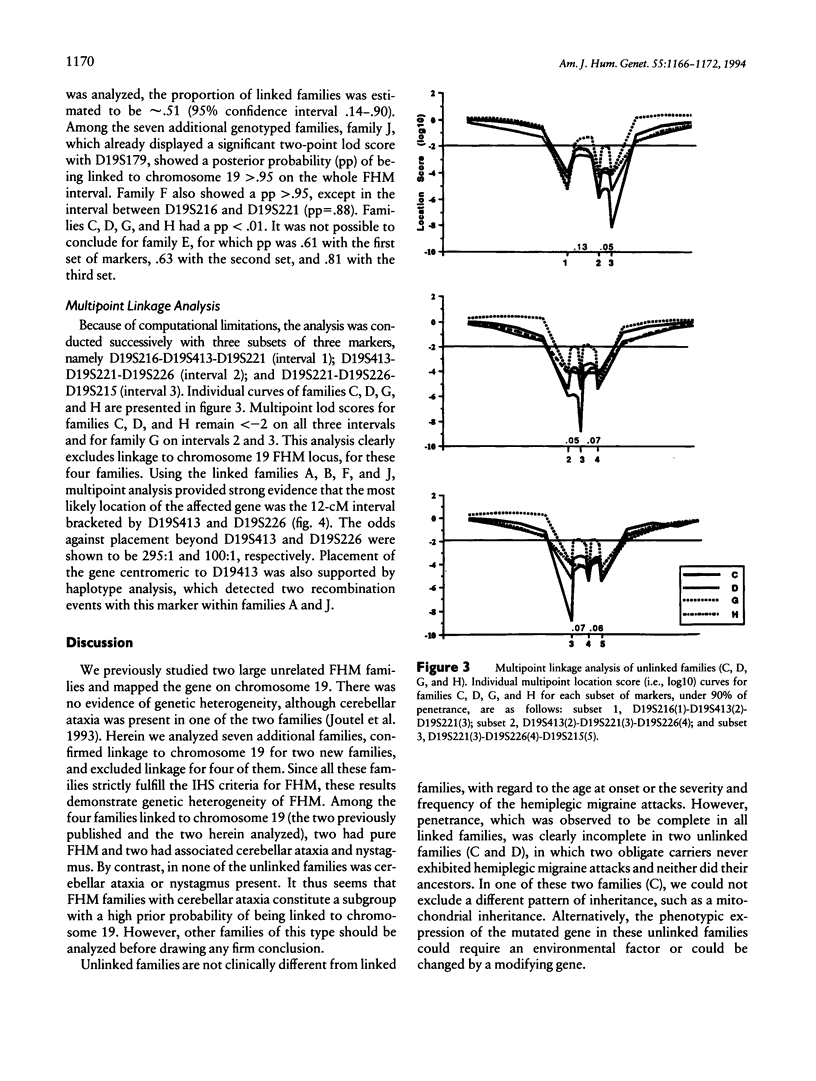
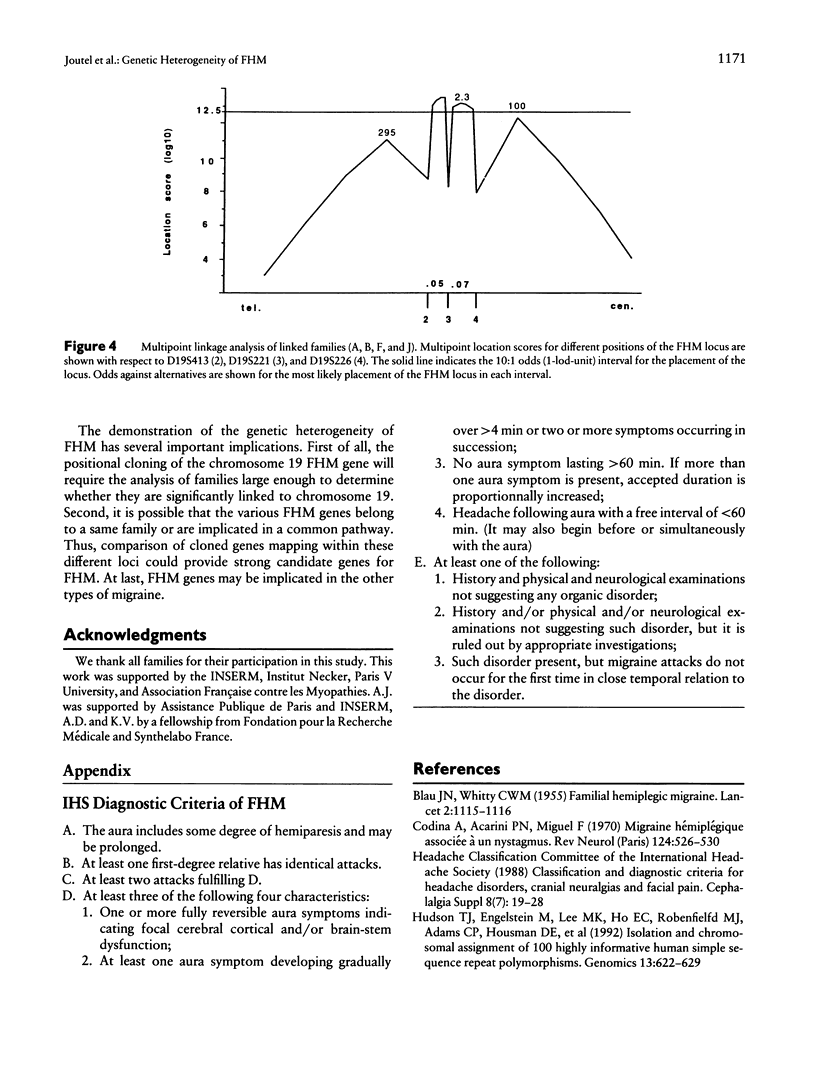
Familial hemiplegic migraine (FHM) is an autosomal dominant variety of migraine with aura. We previously mapped a gene responsible for this disorder to the short arm of chromosome 19, within a 30-cM interval bracketed by D19S216 and D19S215. Linkage analysis conducted on two large pedigrees did not show any evidence of heterogeneity, despite their clinical differences due to the presence, in one family, of cerebellar ataxia and nystagmus. Herein we report linkage data on seven additional FHM families including another one with cerebellar ataxia. Analysis was conducted with a set of seven markers spanning the D19S216-D19S215 interval. Two-point and multipoint lod score analyses as well as HOMOG testing provided strong evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Strong evidence of linkage was obtained in two families and of absence of linkage in four families. The posterior probability of being of the linked type was >.95 in the first two families and <.01 in four other ones. It was not possible to draw any firm conclusion for the last family. Thus, within the nine families so far tested, four were linked, including those with associated cerebellar ataxia. We could not find any clinical difference between the pure FHM families regardless of whether they were linked. In addition to the demonstration of genetic heterogeneity of FHM, this study also allowed us to establish that the most likely location of the gene was within an interval of 12 cM between D19S413 and D19S226.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLAU J. N., WHITTY C. W. Familial hemiplegic migraine. Lancet. 1955 Nov 26;269(6900):1115–1116. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(55)92952-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina A., Acarin P. N., Miquel F., Noguera M. Migraine hémiplégique familiale associée à un nystagmus. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1971 Jun;124(6):526–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson T. J., Engelstein M., Lee M. K., Ho E. C., Rubenfield M. J., Adams C. P., Housman D. E., Dracopoli N. C. Isolation and chromosomal assignment of 100 highly informative human simple sequence repeat polymorphisms. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):622–629. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90133-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joutel A., Bousser M. G., Biousse V., Labauge P., Chabriat H., Nibbio A., Maciazek J., Meyer B., Bach M. A., Weissenbach J. A gene for familial hemiplegic migraine maps to chromosome 19. Nat Genet. 1993 Sep;5(1):40–45. doi: 10.1038/ng0993-40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neitzel H. A routine method for the establishment of permanent growing lymphoblastoid cell lines. Hum Genet. 1986 Aug;73(4):320–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00279094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta M., Araki S., Kuroiwa Y. Familial occurrence of migraine with a hemiplegic syndrome and cerebellar manifestations. Neurology. 1967 Aug;17(8 Pt 1):813–817. doi: 10.1212/wnl.17.8.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTY C. W. Familial hemiplegic migraine. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1953 Aug;16(3):172–177. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.16.3.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., May P. E. Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):388–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Gyapay G., Dib C., Vignal A., Morissette J., Millasseau P., Vaysseix G., Lathrop M. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):794–801. doi: 10.1038/359794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young G. F., Leon-Barth C. A., Green J. Familial hemiplegic migraine, retinal degeneration, deafness, and nystagmus. Arch Neurol. 1970 Sep;23(3):201–209. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480270011002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zifkin B., Andermann E., Andermann F., Kirkham T. An autosomal dominant syndrome of hemiplegic migraine, nystagmus, and tremor. Ann Neurol. 1980 Sep;8(3):329–332. doi: 10.1002/ana.410080319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


