Abstract
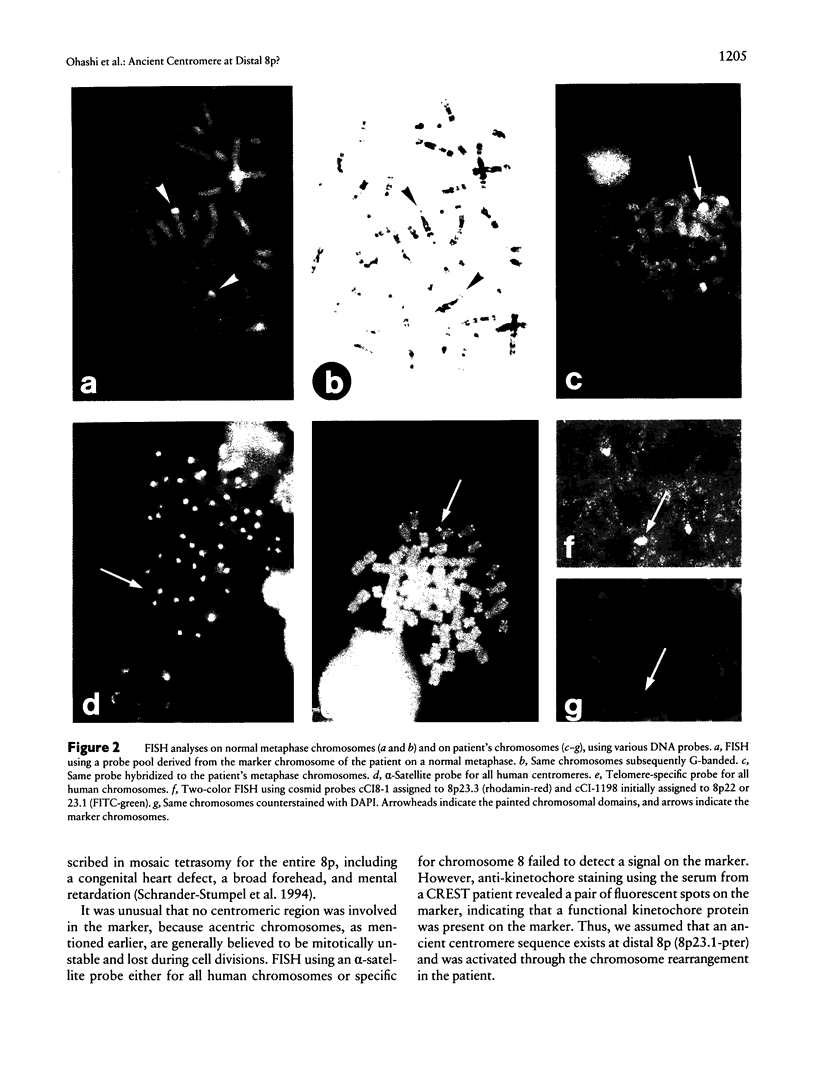
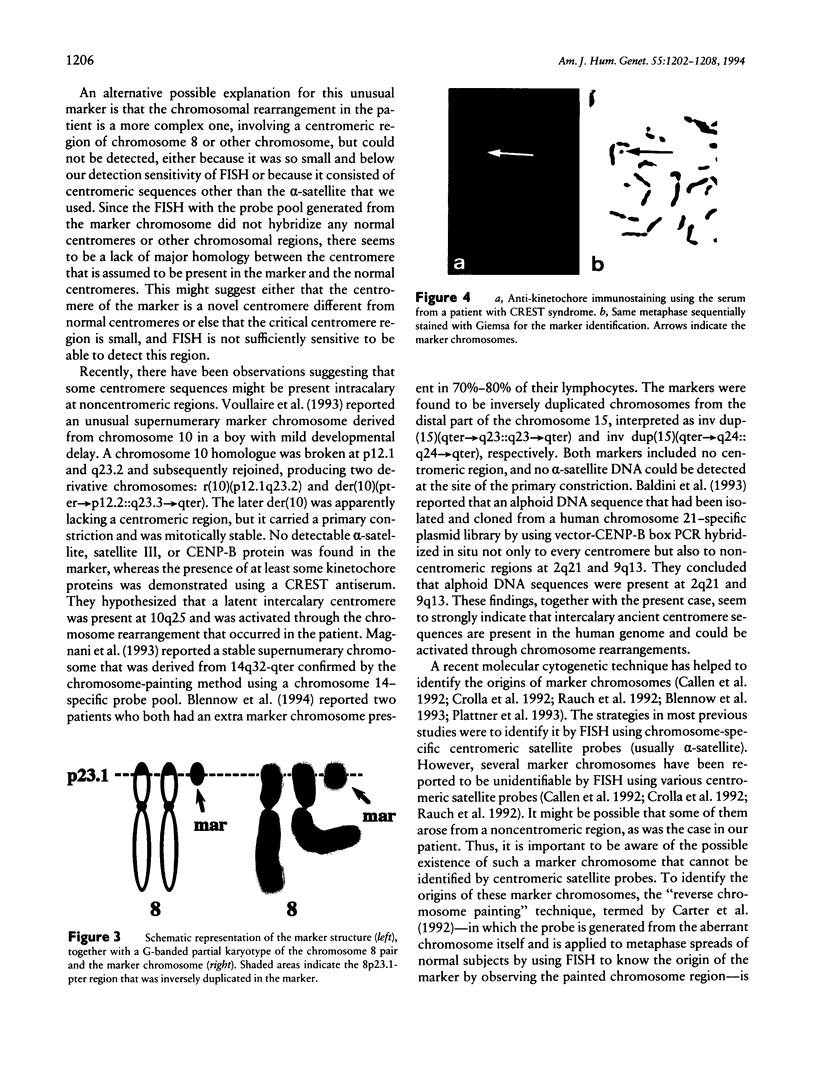
A centromere is considered to be an essential chromosomal component where microtubule-kinetochore interaction occurs to segregate sister chromatids faithfully and acentric chromosomes are unstable and lost through cell divisions. We report a novel marker chromosome that was acentric but stable through cell divisions. The patient was a 2-year-old girl with mental retardation, patent ductus arteriosus, and mild dysmorphic features. G-banded chromosome analysis revealed that an additional small marker chromosome was observed in all 100 cells examined. By the reverse-chromosome-painting method, the marker was found to originate from the distal region of 8p, and a subsequent two-color FISH analysis with cosmid probes around the region revealed that the marker was an inverted duplication interpreted as 8pter-->p23.1::p23.1-->8pter. No centromeric region was involved in the marker. By FISH, no alpha-satellite sequence was detected on the marker, while a telomere sequence was detected at each end. Anti-kinetochore immunostaining, using a serum from a patient with CREST (calcinosis, Raynaud syndrome, esophageal dismotility, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasia) syndrome, showed a pair of signals on the marker, which indicated that a functional kinetochore was present on the marker. The analysis of this patient might suggest the possibility that an ancient centromere sequence exists at distal 8p (8p23.1-pter) and was activated through the chromosome rearrangement in the patient.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldini A., Ried T., Shridhar V., Ogura K., D'Aiuto L., Rocchi M., Ward D. C. An alphoid DNA sequence conserved in all human and great ape chromosomes: evidence for ancient centromeric sequences at human chromosomal regions 2q21 and 9q13. Hum Genet. 1993 Feb;90(6):577–583. doi: 10.1007/BF00202474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blennow E., Annerén G., Bui T. H., Berggren E., Asadi E., Nordenskjöld M. Characterization of supernumerary ring marker chromosomes by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Aug;53(2):433–442. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blennow E., Telenius H., Larsson C., de Vos D., Bajalica S., Ponder B. A., Nordenskjöld M. Complete characterization of a large marker chromosome by reverse and forward chromosome painting. Hum Genet. 1992 Dec;90(4):371–374. doi: 10.1007/BF00220461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blennow E., Telenius H., de Vos D., Larsson C., Henriksson P., Johansson O., Carter N. P., Nordenskjöld M. Tetrasomy 15q: two marker chromosomes with no detectable alpha-satellite DNA. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 May;54(5):877–883. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom K. The centromere frontier: kinetochore components, microtubule-based motility, and the CEN-value paradox. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):621–624. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90242-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callen D. F., Eyre H., Yip M. Y., Freemantle J., Haan E. A. Molecular cytogenetic and clinical studies of 42 patients with marker chromosomes. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Jul 1;43(4):709–715. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter N. P., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Perryman M. T., Telenius H., Pelmear A. H., Leversha M. A., Glancy M. T., Wood S. L., Cook K., Dyson H. M. Reverse chromosome painting: a method for the rapid analysis of aberrant chromosomes in clinical cytogenetics. J Med Genet. 1992 May;29(5):299–307. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.5.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crolla J. A., Dennis N. R., Jacobs P. A. A non-isotopic in situ hybridisation study of the chromosomal origin of 15 supernumerary marker chromosomes in man. J Med Genet. 1992 Oct;29(10):699–703. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.10.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng H. X., Yoshiura K., Dirks R. W., Harada N., Hirota T., Tsukamoto K., Jinno Y., Niikawa N. Chromosome-band-specific painting: chromosome in situ suppression hybridization using PCR products from a microdissected chromosome band as a probe pool. Hum Genet. 1992 Apr;89(1):13–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00207034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima Y., Ohashi H., Wakui K., Nishida T., Oh-ishi T. A rapid method for starting a culture for the establishment of Epstein-Barr virus-transformed human lymphoblastoid cell lines. Jpn J Hum Genet. 1992 Jun;37(2):149–150. doi: 10.1007/BF01899737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan X. Y., Trent J. M., Meltzer P. S. Generation of band-specific painting probes from a single microdissected chromosome. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1117–1121. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haaf T., Schmid M. Analysis of double minutes and double minute-like chromatin in human and murine tumor cells using antikinetochore antibodies. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988 Jan;30(1):73–82. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(88)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota T., Tsukamoto K., Deng H. X., Yoshiura K., Ohta T., Tohma T., Kibe T., Harada N., Jinno Y., Niikawa N. Microdissection of human chromosomal regions 8q23.3-q24.11 and 2q33-qter: construction of DNA libraries and isolation of their clones. Genomics. 1992 Jun;13(2):349–354. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90252-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeuchi T. Inhibitory effect of ethidium bromide on mitotic chromosome condensation and its application to high-resolution chromosome banding. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;38(1):56–61. doi: 10.1159/000132030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inazawa J., Ariyama T., Tokino T., Tanigami A., Nakamura Y., Abe T. High resolution ordering of DNA markers by multi-color fluorescent in situ hybridization of prophase chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1994;65(1-2):130–135. doi: 10.1159/000133618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jinno Y., Harada N., Yoshiura K., Ohta T., Tohma T., Hirota T., Tsukamoto K., Deng H. X., Oshimura M., Niikawa N. A simple and efficient amplification method of DNA with unknown sequences and its application to microdissection/microcloning. J Biochem. 1992 Jul;112(1):75–80. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. C., Meyne J., Sasi R., Moyzis R. K. Apparent lack of telomere sequences on double minute chromosomes. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1990 Sep;48(2):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(90)90131-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnani I., Sacchi N., Darfler M., Nisson P. E., Tornaghi R., Fuhrman-Conti A. M. Identification of the chromosome 14 origin of a C-negative marker associated with a 14q32 deletion by chromosome painting. Clin Genet. 1993 Apr;43(4):180–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1993.tb04444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masumoto H., Masukata H., Muro Y., Nozaki N., Okazaki T. A human centromere antigen (CENP-B) interacts with a short specific sequence in alphoid DNA, a human centromeric satellite. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):1963–1973. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merry D. E., Pathak S., Hsu T. C., Brinkley B. R. Anti-kinetochore antibodies: use as probes for inactive centromeres. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Mar;37(2):425–430. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T., Tohma T., Soejima H., Fukushima Y., Nagai T., Yoshiura K., Jinno Y., Niikawa N. The origin of cytologically unidentifiable chromosome abnormalities: six cases ascertained by targeted chromosome-band painting. Hum Genet. 1993 Aug;92(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/BF00216136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plattner R., Heerema N. A., Yurov Y. B., Palmer C. G. Efficient identification of marker chromosomes in 27 patients by stepwise hybridization with alpha-satellite DNA probes. Hum Genet. 1993 Mar;91(2):131–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00222713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrander-Stumpel C. T., Govaerts L. C., Engelen J. J., van der Blij-Philipsen M., Borghgraef M., Loots W. J., Peters J. J., Rijnvos W. P., Smeets D. F., Fryns J. P. Mosaic tetrasomy 8p in two patients: clinical data and review of the literature. Am J Med Genet. 1994 May 1;50(4):377–380. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320500416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voullaire L. E., Slater H. R., Petrovic V., Choo K. H. A functional marker centromere with no detectable alpha-satellite, satellite III, or CENP-B protein: activation of a latent centromere? Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jun;52(6):1153–1163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]