Full text
PDF

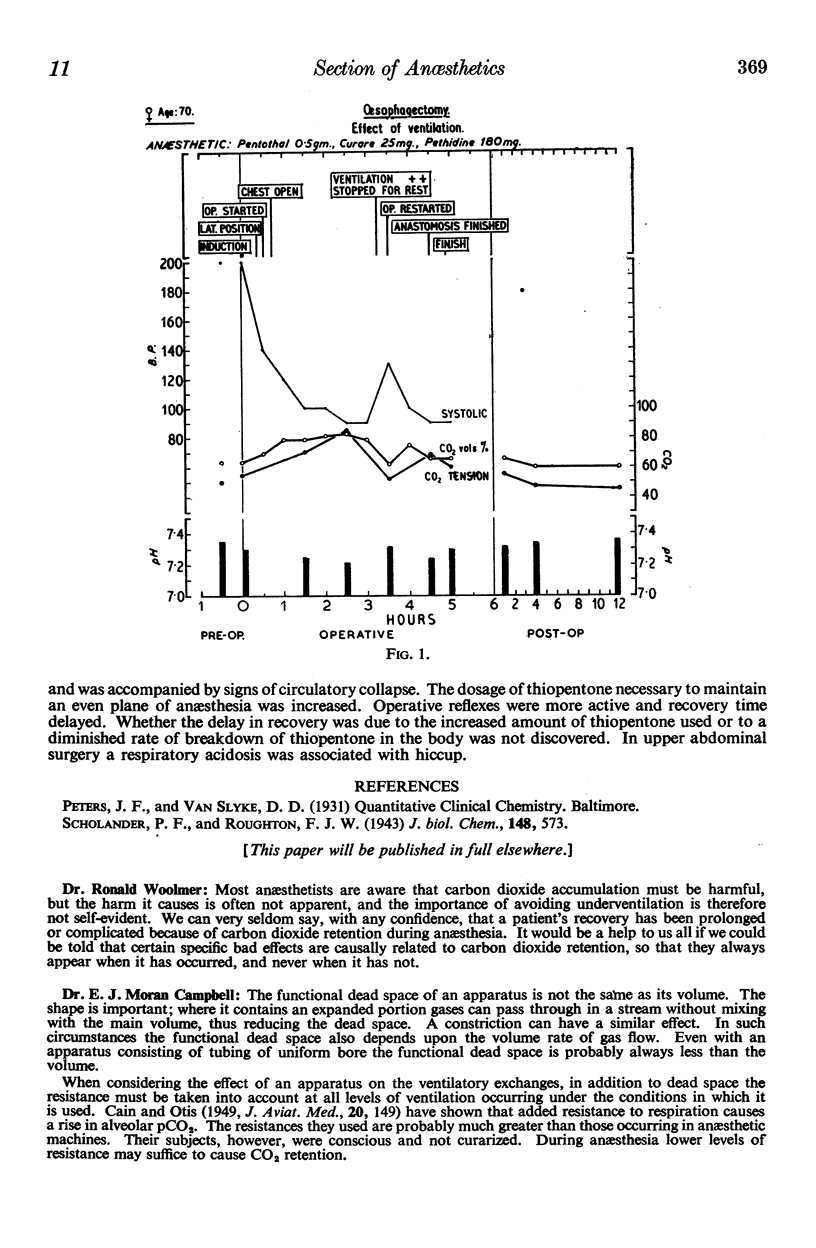

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENSON J. H., REEVE E. B., TAYLOR G. W. A simple apparatus for the continuous quantitative recording of the respiration during anaesthesia. Guys Hosp Rep. 1951;100(1-2):129–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS A. B., BRITT A. G., FENN W. O. Alveolar CO2 during the respiratory cycle. J Appl Physiol. 1952 Jan;4(7):535–548. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1952.4.7.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale H. H., Evans C. L. Effects on the circulation of changes in the carbon-dioxide content of the blood. J Physiol. 1922 May 16;56(3-4):125–145. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1922.sp001997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kety S. S., Schmidt C. F. THE EFFECTS OF ACTIVE AND PASSIVE HYPERVENTILATION ON CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW, CEREBRAL OXYGEN CONSUMPTION, CARDIAC OUTPUT, AND BLOOD PRESSURE OF NORMAL YOUNG MEN. J Clin Invest. 1946 Jan;25(1):107–119. doi: 10.1172/JCI101680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRIME F. J. Volumetric determination of either or cyclopropane, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide and oxygen in anaesthetic mixtures. Br J Anaesth. 1950 Jul;22(3):162–170. doi: 10.1093/bja/22.3.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]