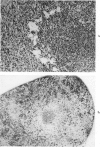
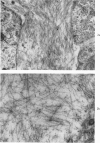
Full text
PDF









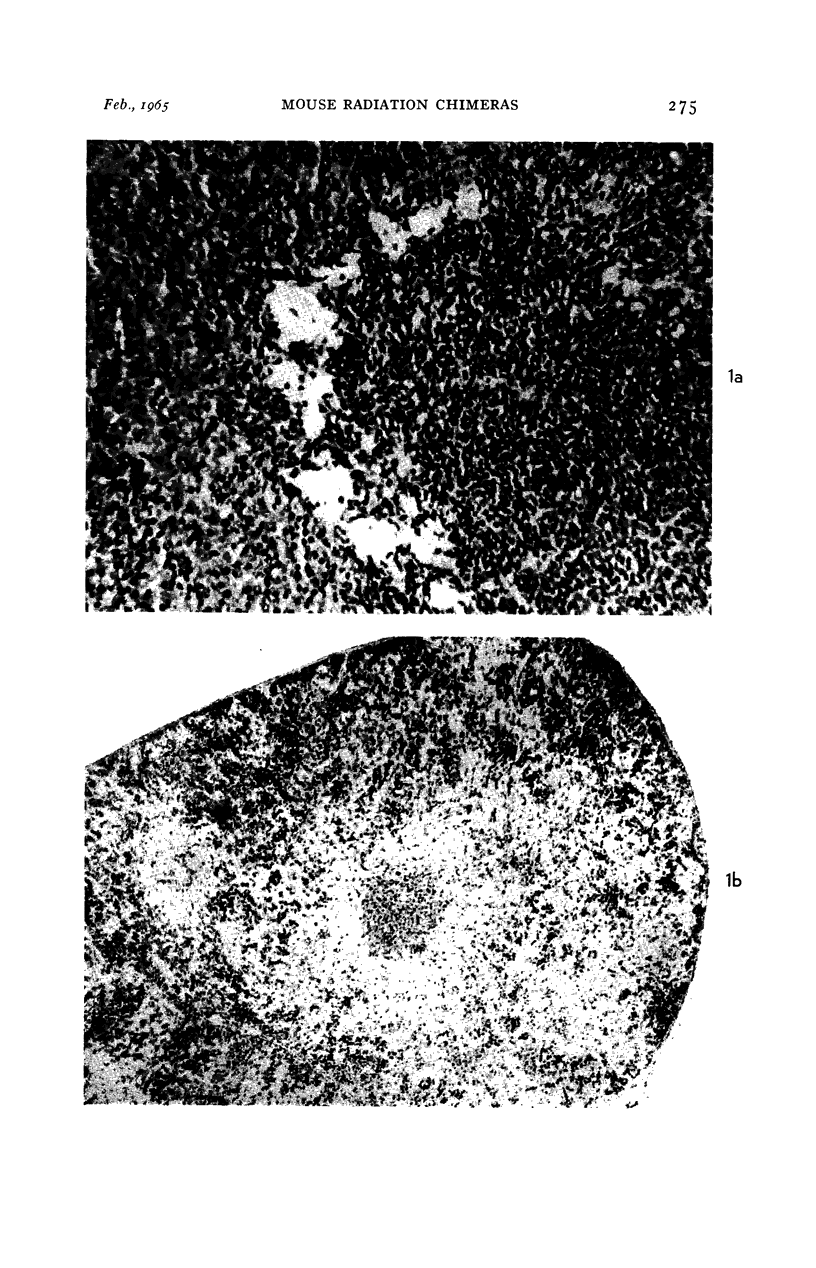

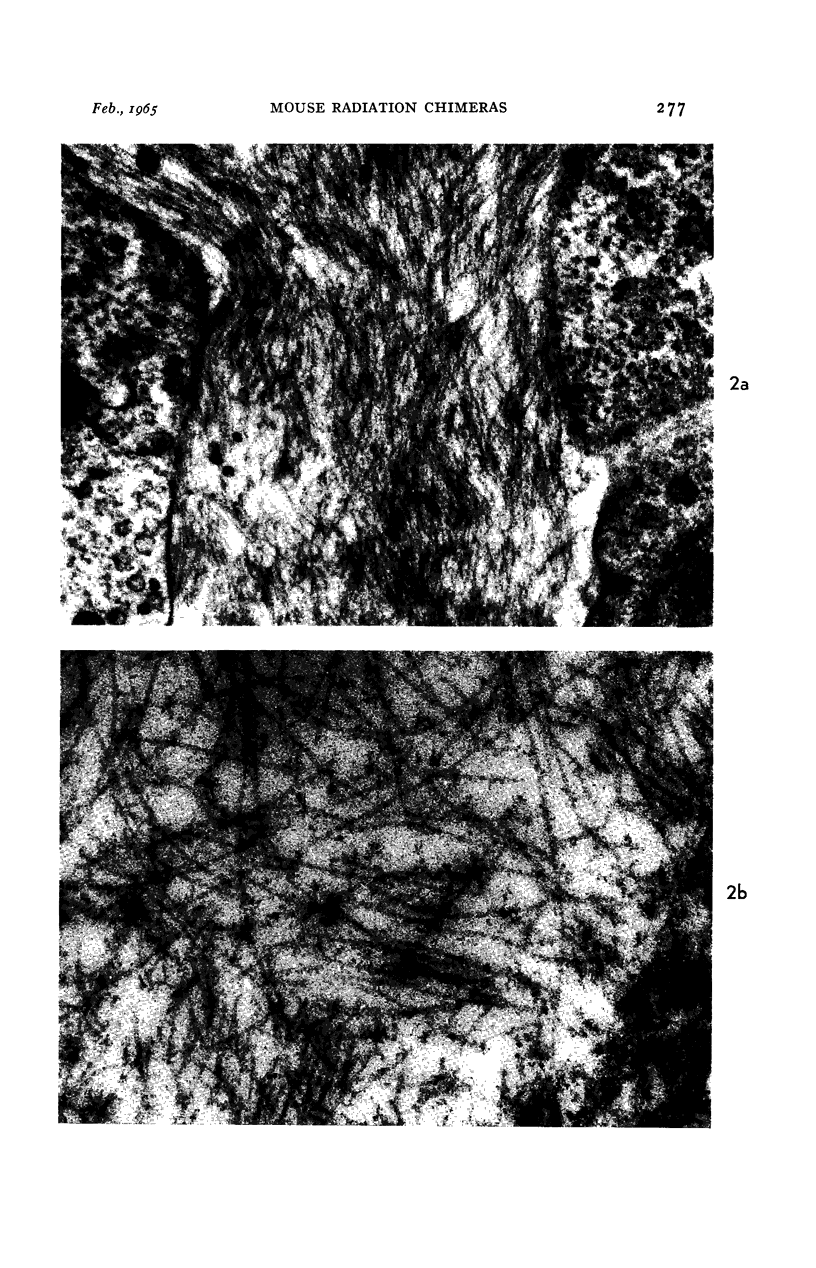
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARNES D. W., LOUTIT J. F., MICKLEM H. S. "Secondary disease" of radiation chimeras: a syndrome due to lymphoid aplasia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1962 Oct 24;99:374–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb45321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUNSTEIN H., BUERGER L. A study of the histochemical and staining characteristics of amyloid. Am J Pathol. 1959 Jul-Aug;35(4):791–800. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CALKINS E., COHEN A. S., LARSEN B. Amyloidosis: preliminary clinical, chemical, and experimental observations. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jun 30;86:1033–1042. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN A. S., CALKINS E. Electron microscopic observations on a fibrous component in amyloid of diverse origins. Nature. 1959 Apr 25;183(4669):1202–1203. doi: 10.1038/1831202a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN A. S., FRENSDORFF A., LAMPRECHT S., CALKINS E. A study of the fine structure of the amyloid associated with familial Mediterranean fever. Am J Pathol. 1962 Nov;41:567–578. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick G. F., Leiter L. Some factors in the development, localization and reabsorption of experimental amyloidosis in the rabbit. Am J Pathol. 1941 Sep;17(5):741–754.1. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORD C. E., HAMERTON J. L., BARNES D. W., LOUTIT J. F. Cytological identification of radiation-chimaeras. Nature. 1956 Mar 10;177(4506):452–454. doi: 10.1038/177452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORD C. E., MICKLEM H. S. The thymus and lymph-nodes in radiation chimaeras. Lancet. 1963 Feb 16;1(7277):359–362. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91385-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOWANS J. L. The fate of parental strain small lymphocytes in F1 hybrid rats. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1962 Oct 24;99:432–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb45326.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ILBERY P. L., KOLLER P. C., LOUTIT J. F. Immunological characteristics of radiation chimaeras. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1958 Jun;20(6):1051–1089. doi: 10.1093/jnci/20.6.1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEBLOND C. P., GLEGG R. E., EIDINGER D. Presence of carbohydrates with free 1,2-glycol groups in sites stained by the periodic acid-Schiff technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1957 Sep;5(5):445–458. doi: 10.1177/5.5.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOUTIT J. F., MICKLEM H. S. "Secondary disease" among lethally irradiated mice restored with haematopoietic tissues from normal or iso-immunized foreign mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Feb;43:77–87. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MISSMAHL H. P., HARTWIG M. Polarisationsoptische Untersuchungen an der Amyloidsubstanz. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat Physiol Klin Med. 1953;324(4):489–508. doi: 10.1007/BF00954791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALADE G. E. A study of fixation for electron microscopy. J Exp Med. 1952 Mar;95(3):285–298. doi: 10.1084/jem.95.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REECE J. M., REYNOLDS T. B. Amyloidosis complicating rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med Sci. 1954 Nov;228(5):554–559. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195411000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIRO D. The structural basis of proteinuria in man; electron microscopic studies of renal biopsy specimens from patients with lipid nephrosis, amyloidosis, and subacute and chronic glomerulonephritis. Am J Pathol. 1959 Jan-Feb;35(1):47–73. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEILUM G. Cortisone-ascorbic acid interaction and the pathogenesis of amyloidosis; mechanism of action of cortisone on mesenchymal tissue. Ann Rheum Dis. 1952 Jun;11(2):119–136. doi: 10.1136/ard.11.2.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEILUM G., LINDAHL A. Frequency and significance of amyloid changes in rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Med Scand. 1954;149(6):449–455. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1954.tb11456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEILUM G. Periodic acid-Schiff-positive reticulo-endothelial cells producing glycoprotein; functional significance during formation of amyloid. Am J Pathol. 1956 Sep-Oct;32(5):945–959. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON S. W., 2nd, GEIL R. G., YAMANAKA H. S. A histochemical study of the protein nature of amyloid. Am J Pathol. 1961 Jun;38:737–747. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINDRUM G. M., KRAMER H. Some observations on the histochemical reactions of amyloid. AMA Arch Pathol. 1957 Apr;63(4):373–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de JAGER, STAM F. C. Pathology and histochemistry of amyloidosis in old age. Gerontologia. 1962;6:19–35. doi: 10.1159/000211103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]