Abstract
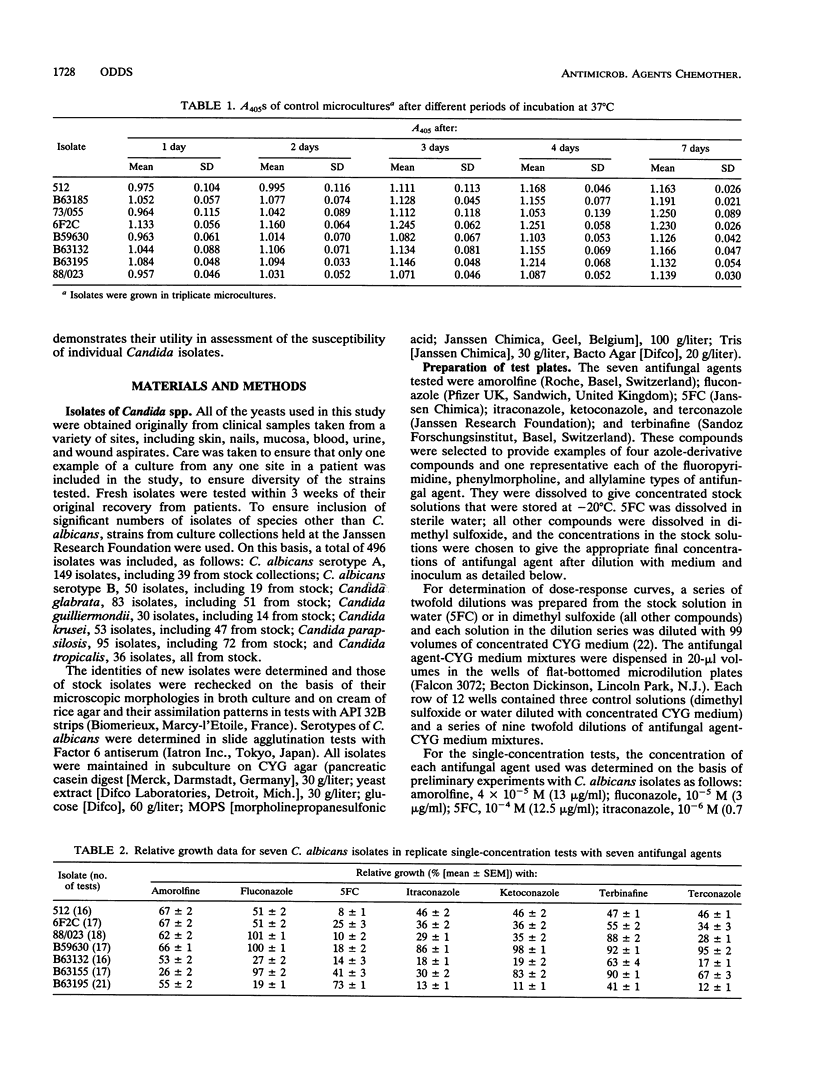
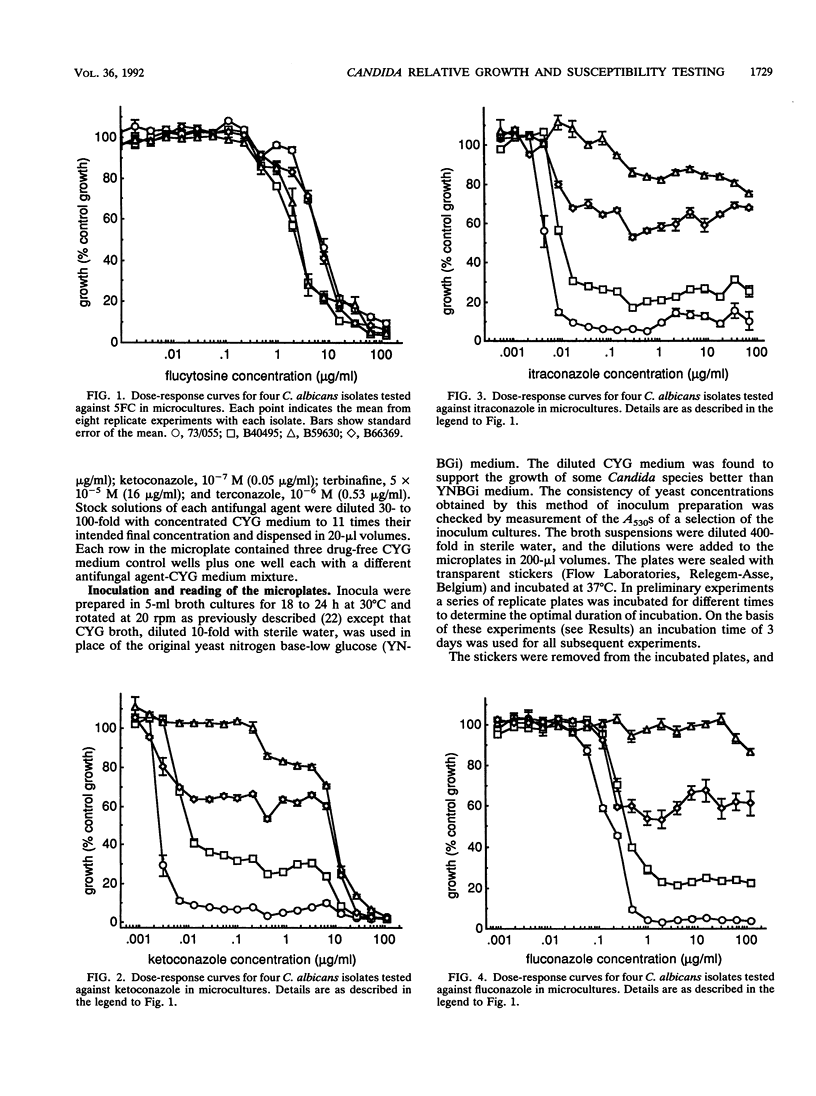
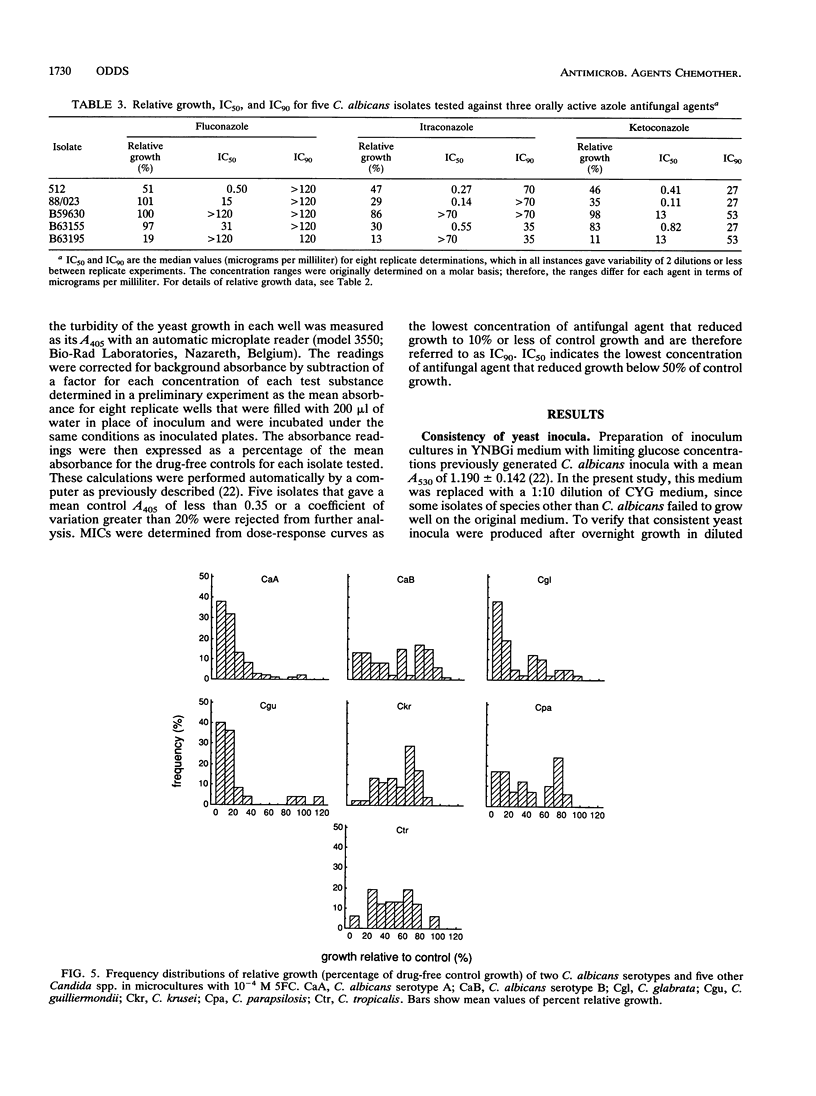
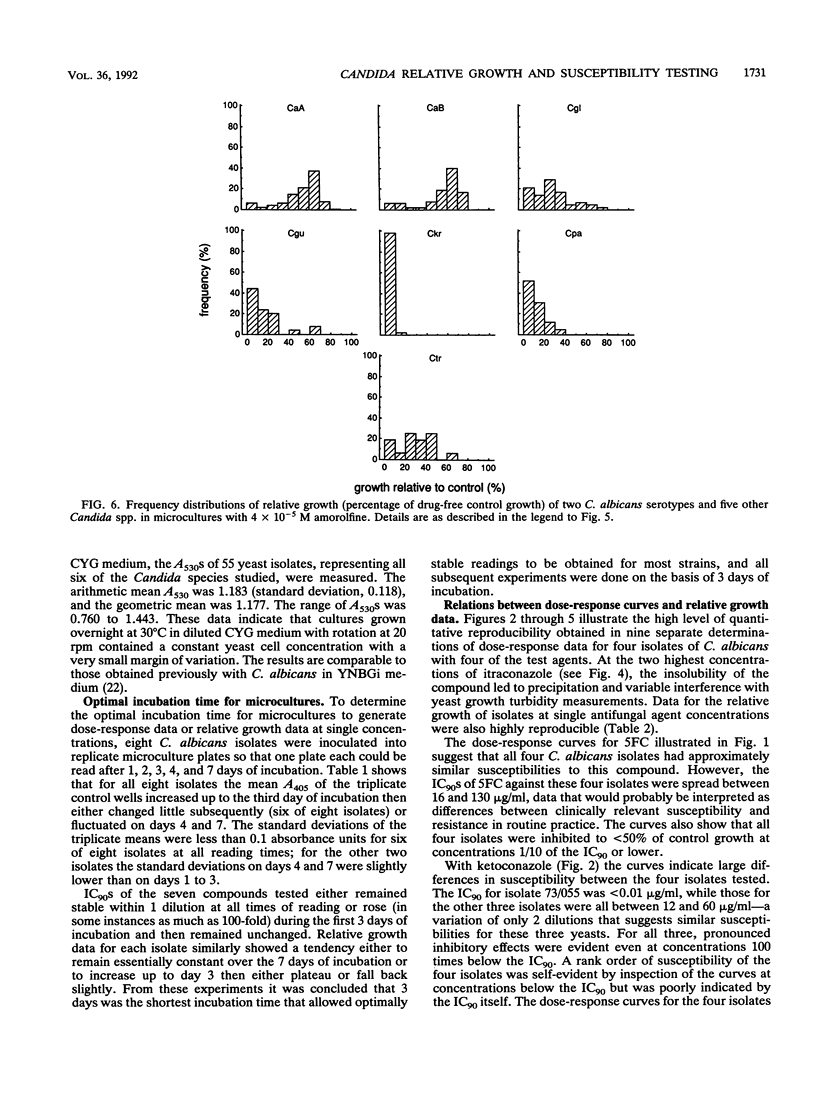
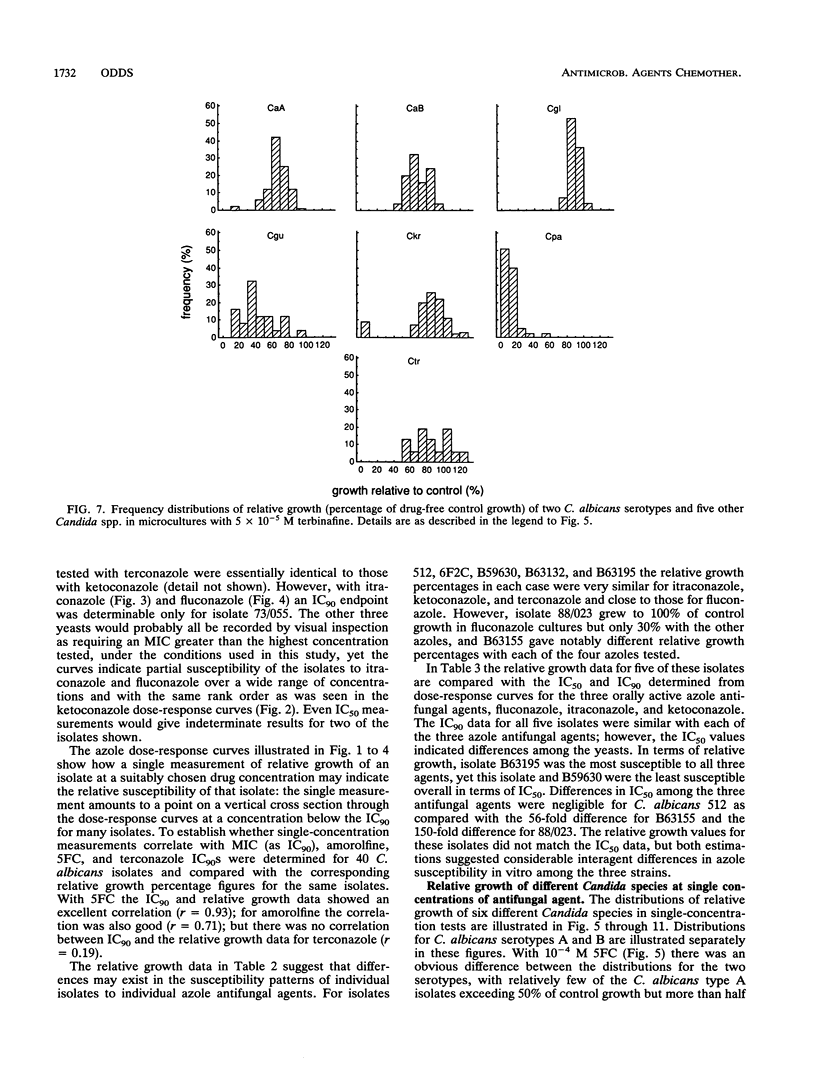
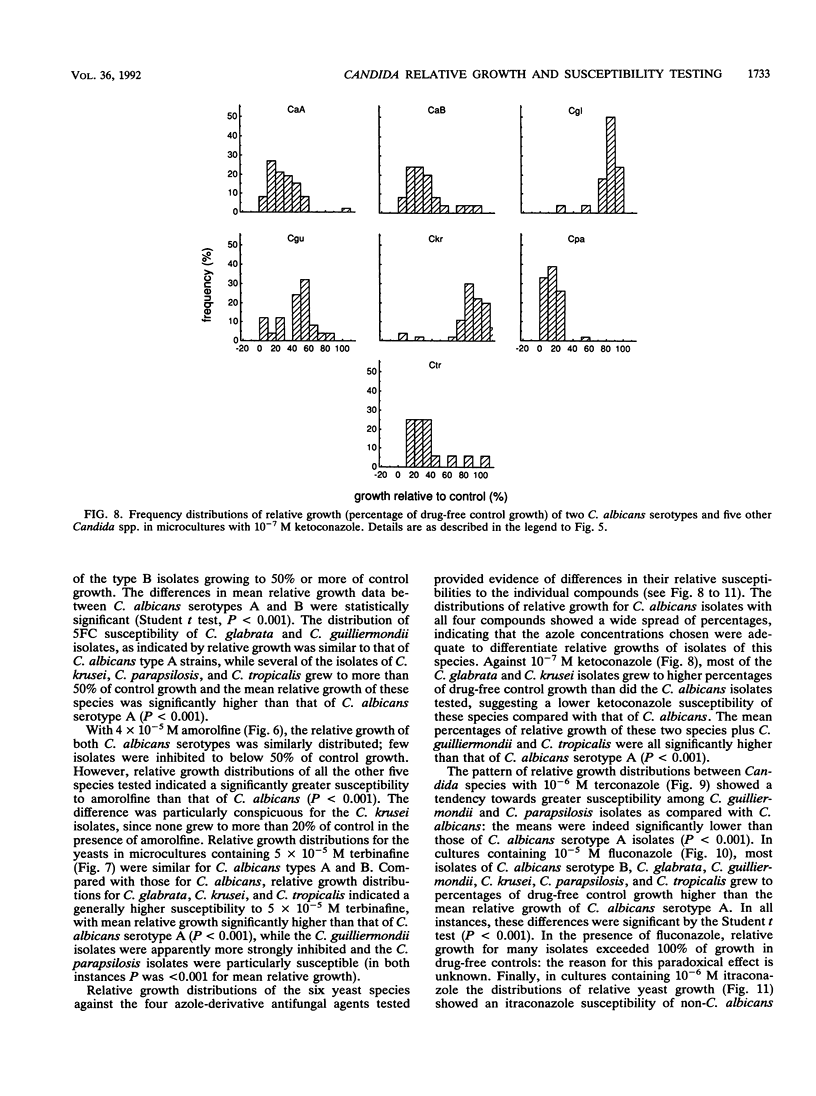
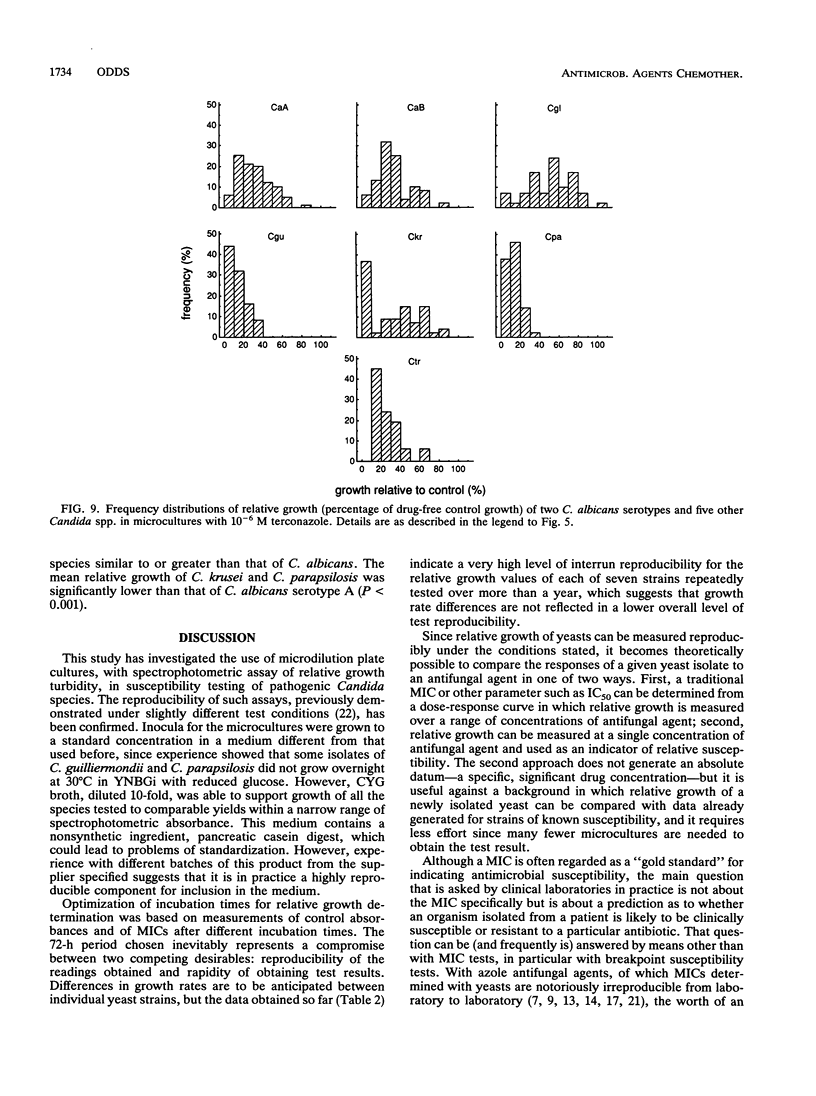
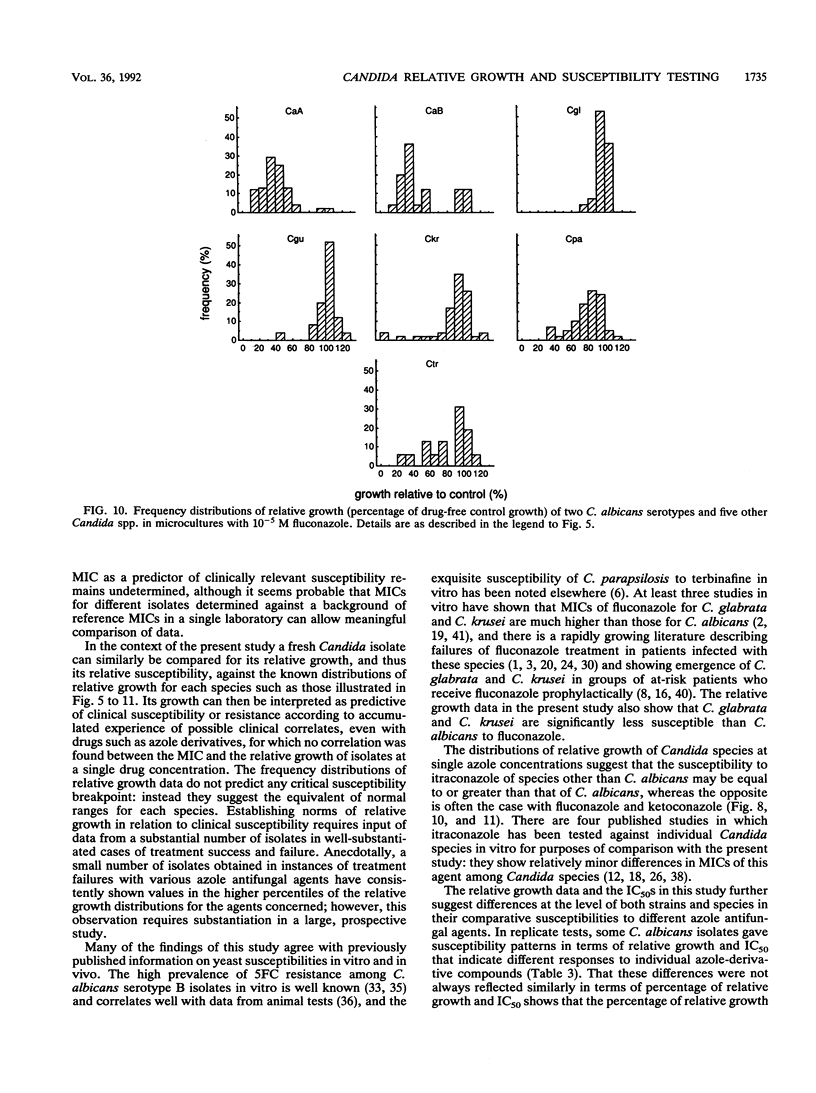
The relative growth (percentage of growth relative to control growth) of 496 isolates representing six Candida species was assessed as a means of determining in vitro susceptibilities of the isolates in microdilution plate wells containing single concentrations of each of seven antifungal agents. The relative growth data were highly reproducible. With flucytosine and amorolfine they correlated well with MICs, but for an azole antifungal agent, terconazole, they did not correlate with MICs. Distributions of relative growth percentages for different Candida spp. showed significant differences in species susceptibility to individual agents. For example, C. albicans was less susceptible than the other species to amorolfine; C. parapsilosis isolates were particularly susceptible to terbinafine; and C. glabrata, C. guilliermondii, and C. krusei isolates were less susceptible than C. albicans to fluconazole and ketoconazole but equally susceptible as or more susceptible than C. albicans to itraconazole. Differential patterns of susceptibility to individual azole antifungal agents were noted for some individual strains as well as for Candida spp.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akova M., Akalin H. E., Uzun O., Gür D. Emergence of Candida krusei infections after therapy of oropharyngeal candidiasis with fluconazole. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Jul;10(7):598–599. doi: 10.1007/BF01967286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blancard A., Moulin-Traffort J., Regli P., Sarzier J. M., Quilici M. Apport du laboratoire dans la surveillance du traitement antifongique par le fluconazole des candidoses chez les immunodéprimés. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1991 May;39(5):534–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boag F. C., Houang E. T., Westrom R., McCormack S. M., Lawrence A. G. Comparison of vaginal flora after treatment with a clotrimazole 500 mg vaginal pessary or a fluconazole 150 mg capsule for vaginal candidosis. Genitourin Med. 1991 Jun;67(3):232–234. doi: 10.1136/sti.67.3.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casals J. B. Tablet sensitivity testing on pathogenic fungi. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Jul;32(7):719–722. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.7.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton Y. M. In vitro activity of terbinafine. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1989 Mar;14(2):101–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1989.tb00901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook R. A., McIntyre K. A., Galgiani J. N. Effects of incubation temperature, inoculum size, and medium on agreement of macro- and microdilution broth susceptibility test results for yeasts. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Aug;34(8):1542–1545. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.8.1542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drutz D. J. In vitro antifungal susceptibility testing and measurement of levels of antifungal agents in body fluids. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Mar-Apr;9(2):392–397. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.2.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupouy-Camet J., Paugam A., Di Donato C., Viguié C., Vicens I., Volle P. J., Tourte-Schaefer C. Résistance au fluconazole en milieu hospitalier. Concordance entre la résistance de Candida albicans in vitro et l'échec thérapeutique. Presse Med. 1991 Sep 14;20(28):1341–1341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espinel-Ingroff A., Shadomy S., Gebhart R. J. In vitro studies with R 51,211 (itraconazole). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):5–9. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espinel-Ingroff A., Shadomy S. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of antifungal agents. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Apr;8(4):352–361. doi: 10.1007/BF01963469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N., Reiser J., Brass C., Espinel-Ingroff A., Gordon M. A., Kerkering T. M. Comparison of relative susceptibilities of Candida species to three antifungal agents as determined by unstandardized methods. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1343–1347. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N., Stevens D. A. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of yeasts: a turbidimetric technique independent of inoculum size. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):721–728. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Just-Nübling G., Gentschew G., Döhle M., Böttinger C., Helm E. B., Stille W. Fluconazole in the treatment of oropharyngeal candidosis in HIV-positive patients. Mycoses. 1990 Sep-Oct;33(9-10):435–440. doi: 10.1111/myc.1990.33.9-10.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi G. S., Spitzer E. D. Testing of organisms for susceptibility to triazoles: is it justified? Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 May;8(5):387–389. doi: 10.1007/BF01964051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi G., Gramegna G., Cavanna C., Poma G., Marangoni E., Michelone G. Itraconazole vs amphotericin B: in vitro comparative evaluation of the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) against clinically isolated yeasts. Mycopathologia. 1989 Apr;106(1):31–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00436923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlroy M. A. Failure of fluconazole to suppress fungemia in a patient with fever, neutropenia, and typhlitis. J Infect Dis. 1991 Feb;163(2):420–421. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.2.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., Abbott A. B. Relative inhibition factors--a novel approach to the assessment of antifungal antibiotics in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Jan;13(1):31–43. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C. Quantitative microculture system with standardized inocula for strain typing, susceptibility testing, and other physiologic measurements with Candida albicans and other yeasts. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2735–2740. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2735-2740.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persons D. A., Laughlin M., Tanner D., Perfect J., Gockerman J. P., Hathorn J. W. Fluconazole and Candida krusei fungemia. N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 31;325(18):1315–1315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller M. A., Rinaldi M. G., Galgiani J. N., Bartlett M. S., Body B. A., Espinel-Ingroff A., Fromtling R. A., Hall G. S., Hughes C. E., Odds F. C. Collaborative investigation of variables in susceptibility testing of yeasts. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1648–1654. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radetsky M., Wheeler R. C., Roe M. H., Todd J. K. Microtiter broth dilution method for yeast susceptibility testing with validation by clinical outcome. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Oct;24(4):600–606. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.4.600-606.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryley J. F., Wilson R. G., Barrett-Bee K. J. Azole resistance in Candida albicans. Sabouraudia. 1984;22(1):53–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Røder B. L., Sonnenschein C., Hartzen S. H. Failure of fluconazole therapy in Candida krusei fungemia. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;10(3):173–173. doi: 10.1007/BF01964453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiller R. L., Bennett J. E., Scholer H. J., Wall M., Polak A., Stevens D. A. Correlation of in vitro susceptibility test results with in vivo response: flucytosine therapy in a systemic candidiasis model. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jun;147(6):1070–1077. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.6.1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiller R. L., Bennett J. E., Scholer H. J., Wall M., Polak A., Stevens D. A. Susceptibility to 5-fluorocytosine and prevalence of serotype in 402 Candida albicans isolates from the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):482–487. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troke P. F., Marriott M. S., Richardson K., Tarbit M. H. In vitro potency and in vivo activity of azoles. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;544:284–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb40414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock D. W., Burke J., Cope N. J., Johnson E. M., von Fraunhofer N. A., Williams E. W. Fluconazole resistance in Candida glabrata. Lancet. 1988 Dec 3;2(8623):1310–1310. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92919-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingard J. R., Merz W. G., Rinaldi M. G., Johnson T. R., Karp J. E., Saral R. Increase in Candida krusei infection among patients with bone marrow transplantation and neutropenia treated prophylactically with fluconazole. N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 31;325(18):1274–1277. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199110313251803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Uchida K., Kawasaki K., Matsunaga T. [In vitro activity of fluconazole, a novel bistriazole antifungal agent]. Jpn J Antibiot. 1989 Jan;42(1):1–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



