Abstract
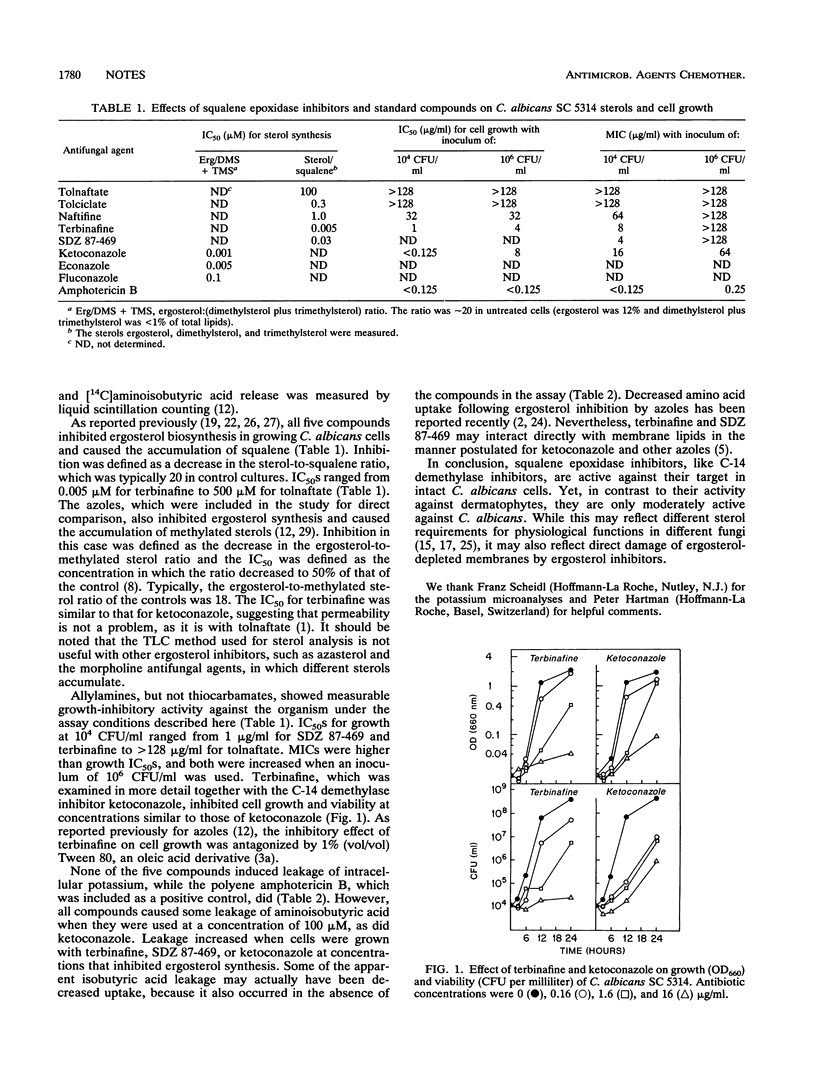
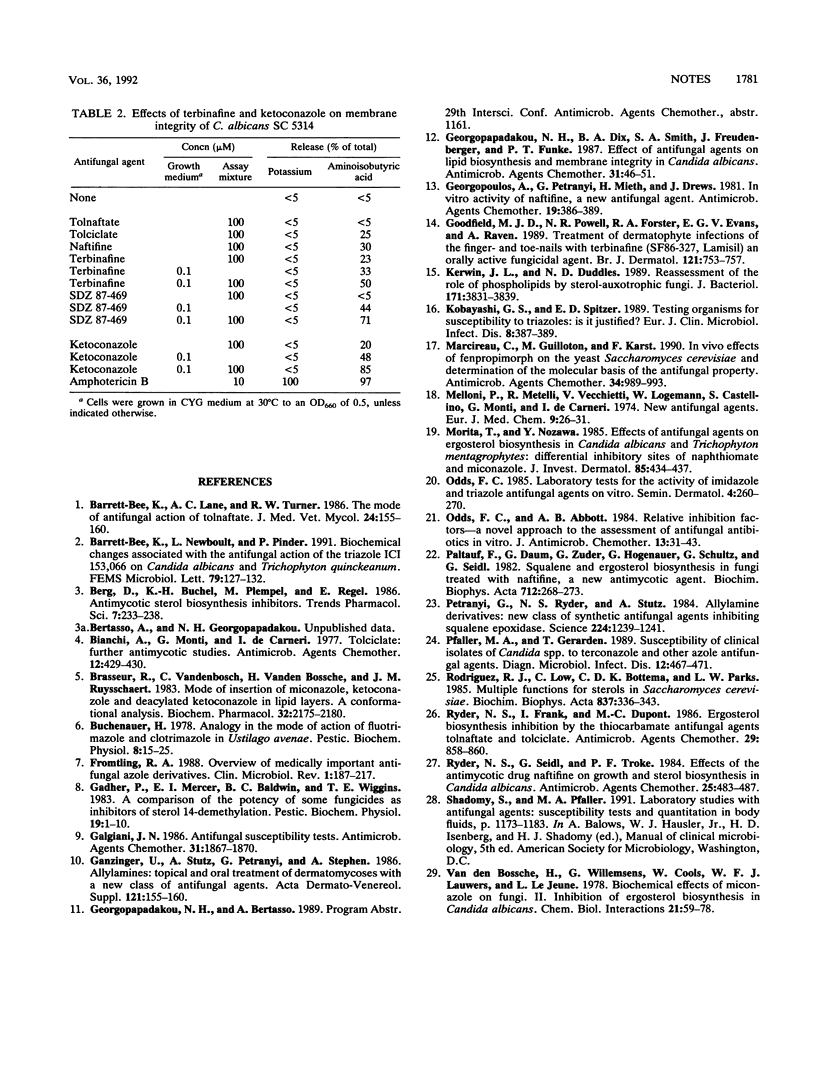
The relationship between sterol biosynthesis inhibition, membrane integrity, and cell growth inhibition in Candida albicans was examined for five squalene epoxidase inhibitors. The compounds were the thiocarbamates tolnaftate and tolciclate and the allylamines naftifine, terbinafine, and SDZ 87-469. All compounds inhibited sterol biosynthesis, with the concentrations that caused a 50% decrease in the total sterol-to-squalene ratio ranging from less than or equal to 0.01 microM for terbinafine and SDZ 87-469 to 500 microM for tolnaftate. At 100 microM, the compounds also caused up to a 30% release of intracellular [14C]aminoisobutyric acid. With terbinafine and SD2 87-469, aminoisobutyric acid release further increased in cells grown at concentrations that inhibited ergosterol biosynthesis. It is suggested that inhibition of ergosterol synthesis may render the C. albicans membrane susceptible to further damage, including direct damage from squalene epoxidase inhibitors.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett-Bee K. J., Lane A. C., Turner R. W. The mode of antifungal action of tolnaftate. J Med Vet Mycol. 1986 Apr;24(2):155–160. doi: 10.1080/02681218680000221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett-Bee K., Newboult L., Pinder P. Biochemical changes associated with the antifungal action of the triazole ICI 153,066 on Candida albicans and Trichophyton quinckeanum. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Apr 15;63(2-3):127–131. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90074-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi A., Monti G., de Carneri I. Tolciclate: further antimycotic studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Sep;12(3):429–430. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.3.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasseur R., Vandenbosch C., Van den Bossche H., Ruysschaert J. M. Mode of insertion of miconazole, ketoconazole and deacylated ketoconazole in lipid layers. A conformational analysis. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Jul 15;32(14):2175–2180. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90223-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromtling R. A. Overview of medically important antifungal azole derivatives. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Apr;1(2):187–217. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galgiani J. N. Antifungal susceptibility tests. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Dec;31(12):1867–1870. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.12.1867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganzinger U., Stutz A., Petranyi G., Stephen A. Allylamines: topical and oral treatment of dermatomycoses with a new class of antifungal agents. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh) 1986;121:155–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Dix B. A., Smith S. A., Freudenberger J., Funke P. T. Effect of antifungal agents on lipid biosynthesis and membrane integrity in Candida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jan;31(1):46–51. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos A., Petranyi G., Mieth H., Drews J. In vitro activity of naftifine, a new antifungal agent. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Mar;19(3):386–389. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.3.386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfield M. J., Rowell N. R., Forster R. A., Evans E. G., Raven A. Treatment of dermatophyte infection of the finger- and toe-nails with terbinafine (SF 86-327, Lamisil), an orally active fungicidal agent. Br J Dermatol. 1989 Dec;121(6):753–757. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1989.tb08217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerwin J. L., Duddles N. D. Reassessment of the role of phospholipids in sexual reproduction by sterol-auxotrophic fungi. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3831–3839. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3831-3839.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi G. S., Spitzer E. D. Testing of organisms for susceptibility to triazoles: is it justified? Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 May;8(5):387–389. doi: 10.1007/BF01964051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcireau C., Guilloton M., Karst F. In vivo effects of fenpropimorph on the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and determination of the molecular basis of the antifungal property. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):989–993. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T., Nozawa Y. Effects of antifungal agents on ergosterol biosynthesis in Candida albicans and Trichophyton mentagrophytes: differential inhibitory sites of naphthiomate and miconazole. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Nov;85(5):434–437. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12277141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odds F. C., Abbott A. B. Relative inhibition factors--a novel approach to the assessment of antifungal antibiotics in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Jan;13(1):31–43. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petranyi G., Ryder N. S., Stütz A. Allylamine derivatives: new class of synthetic antifungal agents inhibiting fungal squalene epoxidase. Science. 1984 Jun 15;224(4654):1239–1241. doi: 10.1126/science.6547247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller M. A., Gerarden T. Susceptibility of clinical isolates of Candida spp. to terconazole and other azole antifungal agents. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Nov-Dec;12(6):467–471. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(89)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez R. J., Low C., Bottema C. D., Parks L. W. Multiple functions for sterols in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 4;837(3):336–343. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder N. S., Frank I., Dupont M. C. Ergosterol biosynthesis inhibition by the thiocarbamate antifungal agents tolnaftate and tolciclate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):858–860. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder N. S., Seidl G., Troke P. F. Effect of the antimycotic drug naftifine on growth of and sterol biosynthesis in Candida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):483–487. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bossche H., Willemsens G., Cools W., Lauwers W. F., Le Jeune L. Biochemical effects of miconazole on fungi. II. Inhibition of ergosterol biosynthesis in Candida albicans. Chem Biol Interact. 1978 Apr;21(1):59–78. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(78)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



