Abstract
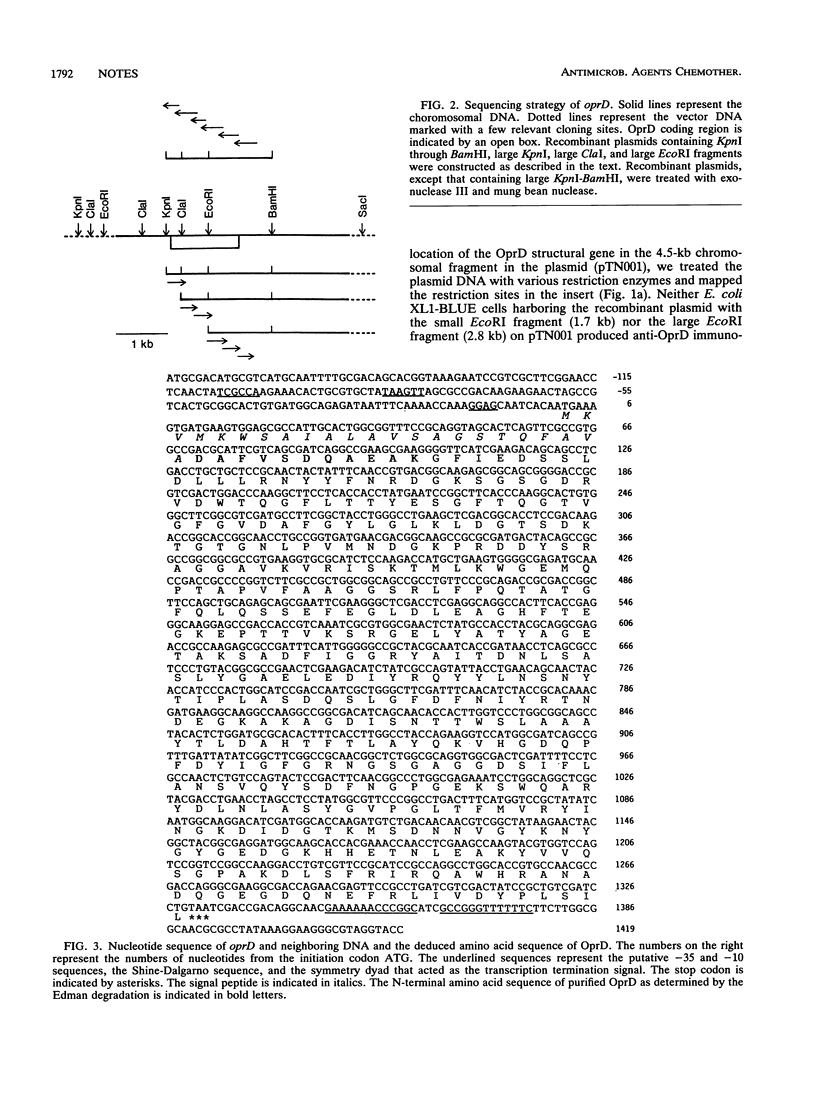
Protein D2 of the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa was shown to form the imipenem-permeable pore. We cloned and sequenced the protein D2 gene. The protein D2 gene encodes a polypeptide with 443 amino acids consisting of 23 and 420 amino acid residues for the signal peptide and mature polypeptide (M(r), 46,010), respectively. Protein D2 contains the highest molar ratio of glycine and no cysteine. The polar amino acids are scattered throughout the sequence.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Büscher K. H., Cullmann W., Dick W., Wendt S., Opferkuch W. Imipenem resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa is due to diminished expression of outer membrane proteins. J Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;156(4):681–684. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.4.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuoka T., Masuda N., Takenouchi T., Sekine N., Iijima M., Ohya S. Increase in susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to carbapenem antibiotics in low-amino-acid media. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Mar;35(3):529–532. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.3.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerbl-Rieger S., Peters J., Kellermann J., Lottspeich F., Baumeister W. Nucleotide and derived amino acid sequences of the major porin of Comamonas acidovorans and comparison of porin primary structures. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(7):2196–2205. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.7.2196-2205.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Halvorson H. O. A putative signal peptidase recognition site and sequence in eukaryotic and prokaryotic signal peptides. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):391–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. P., Darzins A., Miyashiro D., Ripp S., Miller R. V. Imipenem resistance in pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO: mapping of the OprD2 gene. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Apr;35(4):753–755. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.4.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn J. P., Dudek E. J., DiVincenzo C. A., Lucks D. A., Lerner S. A. Emergence of resistance to imipenem during therapy for Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. J Infect Dis. 1986 Aug;154(2):289–294. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satake S., Yoneyama H., Nakae T. Role of OmpD2 and chromosomal beta-lactamase in carbapenem resistance in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Aug;28(2):199–207. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.2.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satake S., Yoshihara E., Nakae T. Diffusion of beta-lactam antibiotics through liposome membranes reconstituted from purified porins of the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 May;34(5):685–690. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.5.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trias J., Nikaido H. Outer membrane protein D2 catalyzes facilitated diffusion of carbapenems and penems through the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):52–57. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trias J., Nikaido H. Protein D2 channel of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane has a binding site for basic amino acids and peptides. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15680–15684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. E., Iglewski B. H. Codon usage in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9323–9335. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoneyama H., Nakae T. Cloning of the protein D2 gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its functional expression in the imipenem-resistant host. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jun 3;283(2):177–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80582-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshihara E., Nakae T. Identification of porins in the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa that form small diffusion pores. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6297–6301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]