Abstract
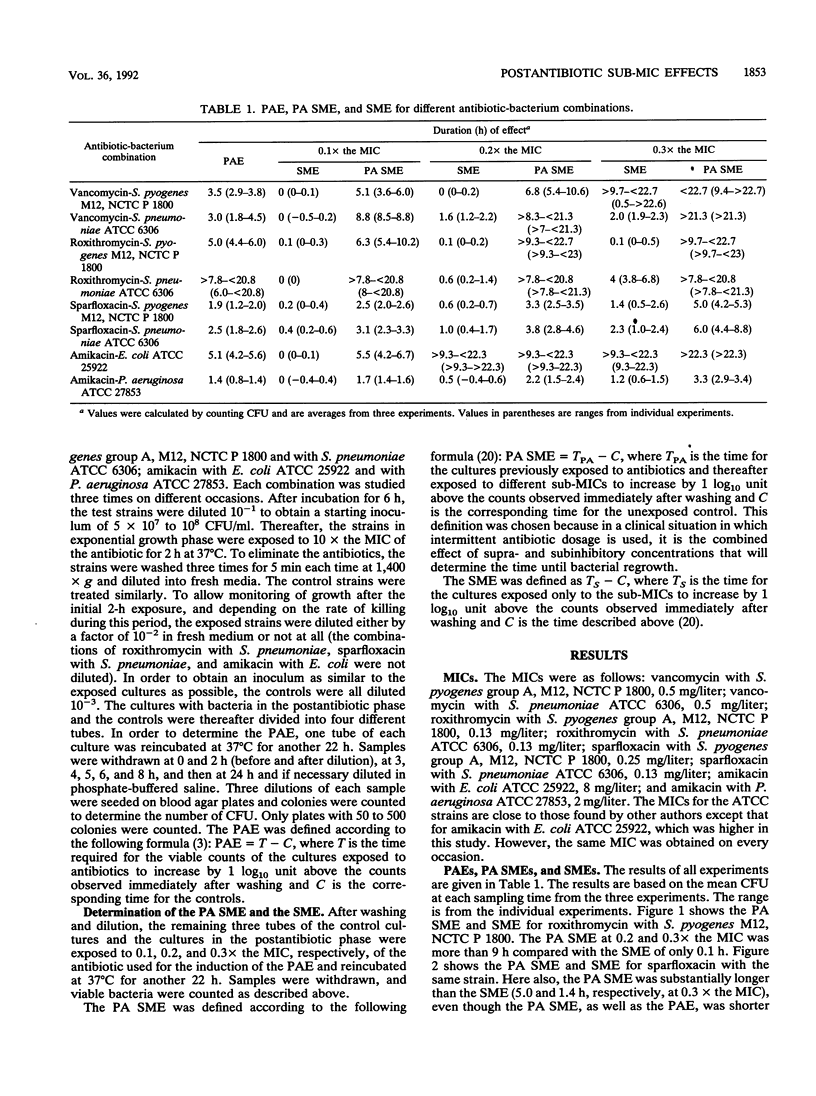
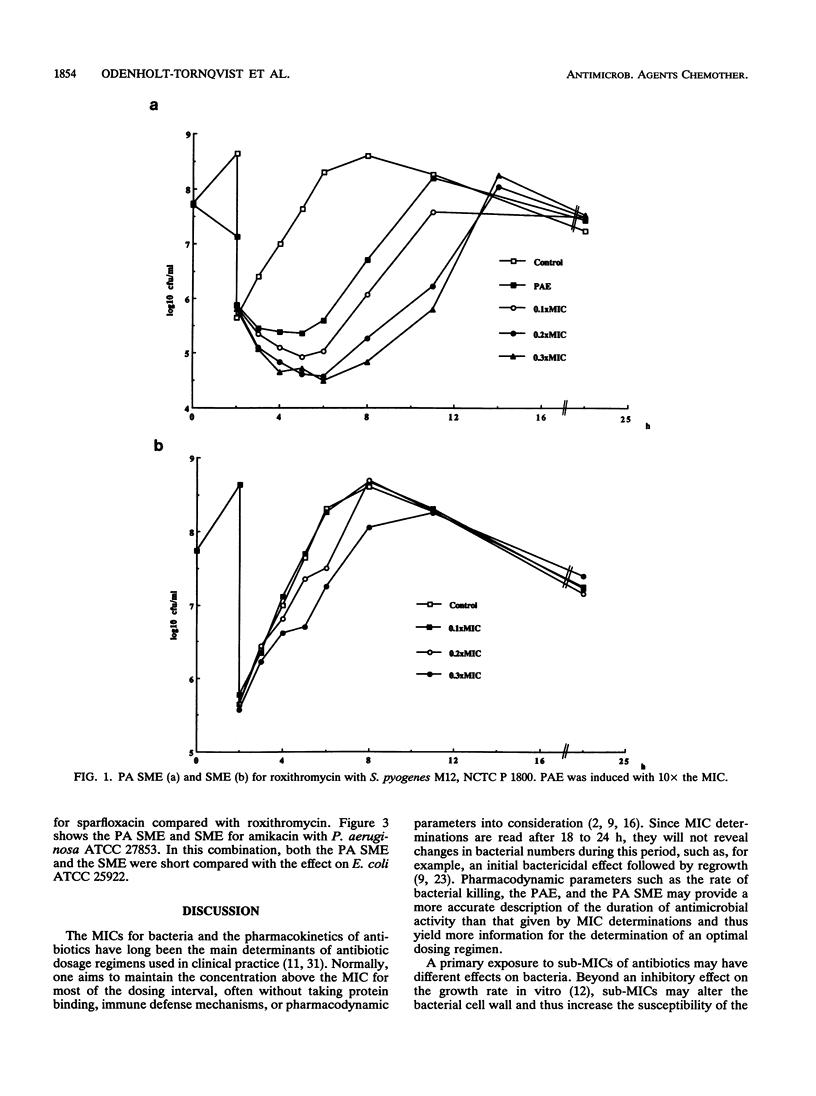
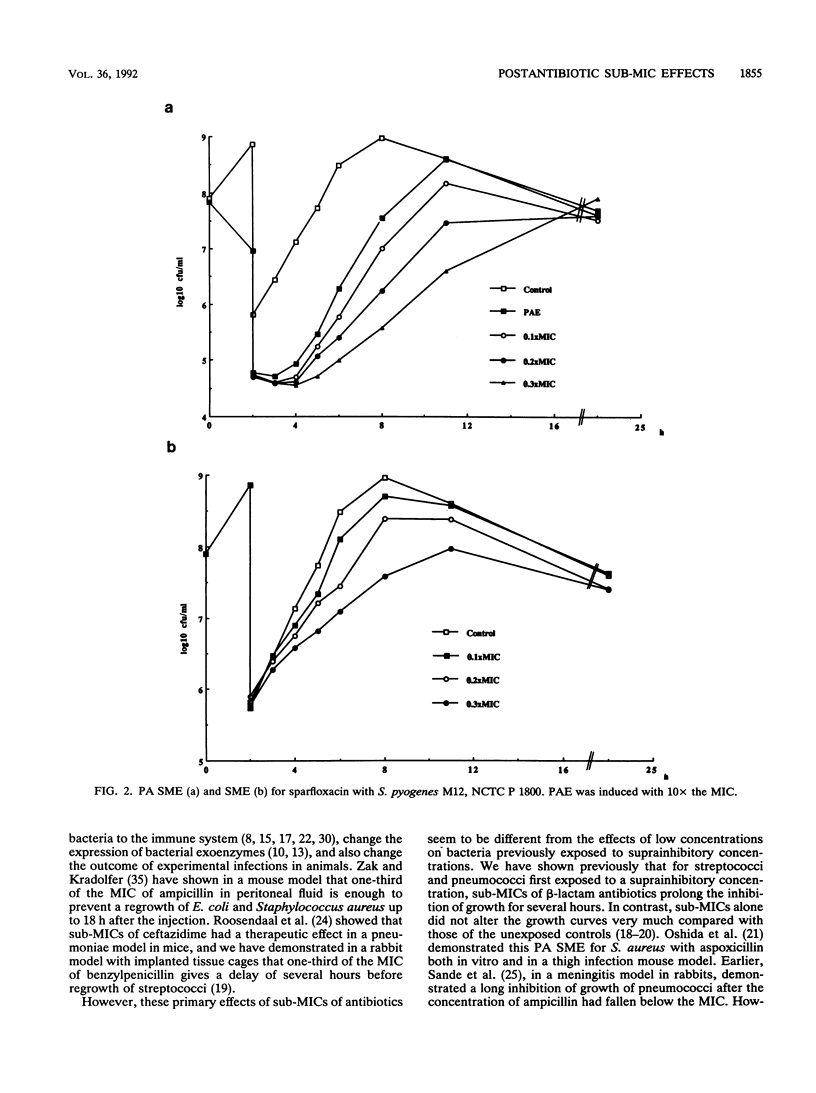
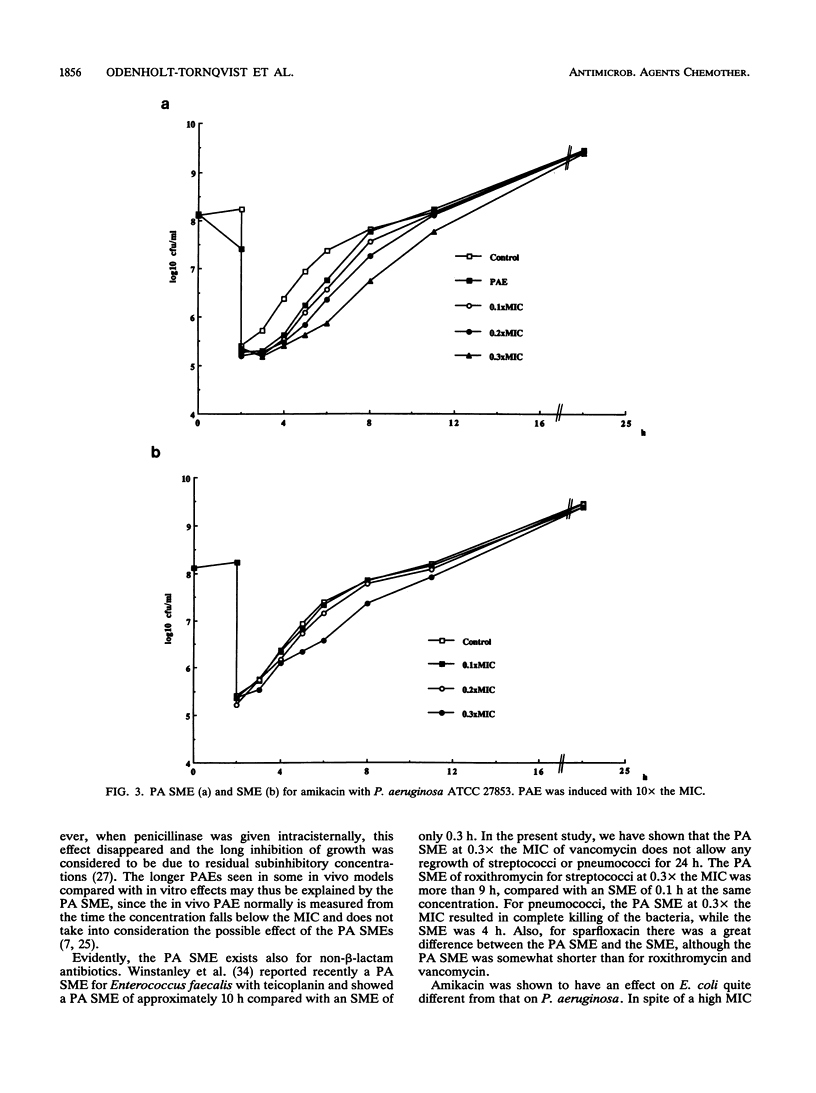
The sub-MIC effects (SMEs) and the postantibiotic sub-MIC effects (PA SMEs) of vancomycin, roxithromycin, and sparfloxacin for Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus pneumoniae and of amikacin for Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa were investigated. A postantibiotic effect was induced by exposing strains to 10x the MIC of the antibiotic for 2 h in vitro. After the induction, the exposed cultures were washed to eliminate the antibiotics. Unexposed controls were treated similarly. Thereafter, the exposed cultures (PA SME) and the controls (SME) were exposed to different subinhibitory concentrations (0.1, 0.2, and 0.3x the MIC) of the same drug and growth curves for a period of 24 h were compared. In general, the PA SMEs were much more pronounced than the SMEs. However, for amikacin and E. coli the SME of 0.2 and 0.3x the MIC also had an initial bactericidal effect. The longest PA SMEs were demonstrated for the combinations with the most pronounced killing during the induction and for the combinations which exhibited the longest PAEs.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altemeier W. A. Penicillin Therapy with Prolonged Interval Dosage Schedules. Ann Surg. 1948 Oct;128(4):708–713. doi: 10.1097/00000658-194810000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barza M. A critique of animal models in antibiotic research. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):109–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H., FLEISCHMAN R., LEVY M. "Continuous" vs. "discontinuous" therapy with penicillin; the effect of the interval between injections on therapeutic efficacy. N Engl J Med. 1953 Mar 19;248(12):481–488. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195303192481201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H., FLEISCHMAN R., MUSSELMAN A. D. The bactericidal action of penicillin in vivo: the participation of the host, and the slow recovery of the surviving organisms. Ann Intern Med. 1950 Sep;33(3):544–571. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-33-3-544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagle H., Musselman A. D. THE SLOW RECOVERY OF BACTERIA FROM THE TOXIC EFFECTS OF PENICILLIN. J Bacteriol. 1949 Oct;58(4):475–490. doi: 10.1128/jb.58.4.475-490.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert S. C., Leggett J., Vogelman B., Craig W. A. Evidence for a slow elimination phase for penicillin G. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):200–202. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmell C. G., Peterson P. K., Schmeling D., Kim Y., Mathews J., Wannamaker L., Quie P. G. Potentiation of opsonization and phagocytosis of Streptococcus pyogenes following growth in the presence of clindamycin. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1249–1256. doi: 10.1172/JCI110152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D. In vitro veritas? Antimicrobial susceptibility tests and their clinical relevance. J Infect Dis. 1981 Oct;144(4):380–385. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.4.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimwood K., To M., Rabin H. R., Woods D. E. Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme expression by subinhibitory antibiotic concentrations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):41–47. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M. Dosage schedules of antimicrobial agents: a historical review. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):4–11. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.1.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorian V., Waluschka A., Popoola B. Pneumococcal beta hemolysin produced under the effect of antibiotics. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Feb;25(2):290–294. doi: 10.1128/am.25.2.290-294.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald P. J., Craig W. A., Kunin C. M. Persistent effect of antibiotics on Staphylococcus aureus after exposure for limited periods of time. J Infect Dis. 1977 Feb;135(2):217–223. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald P. J., Wetherall B. L., Pruul H. Postantibiotic leukocyte enhancement: increased susceptibility of bacteria pretreated with antibiotics to activity of leukocytes. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):38–44. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrikin D., Rolinson G. N. Antibiotic levels in experimentally infected mice in relation to therapeutic effect and antibacterial activity in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1979 Jul;5(4):423–429. doi: 10.1093/jac/5.4.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milatovic D. Antibiotics and phagocytosis. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;2(5):414–425. doi: 10.1007/BF02013898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odenholt-Tornqvist I., Löwdin E., Cars O. Pharmacodynamic effects of subinhibitory concentrations of beta-lactam antibiotics in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Sep;35(9):1834–1839. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odenholt I., Holm S. E., Cars O. Effects of benzylpenicillin on Streptococcus pyogenes during the postantibiotic phase in vitro. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Aug;24(2):147–156. doi: 10.1093/jac/24.2.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odenholt I., Holm S. E., Cars O. Effects of supra- and sub-MIC benzylpenicillin concentrations on group A beta-haemolytic streptococci during the postantibiotic phase in vivo. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Aug;26(2):193–201. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshida T., Onta T., Nakanishi N., Matsushita T., Yamaguchi T. Activity of sub-minimal inhibitory concentrations of aspoxicillin in prolonging the postantibiotic effect against Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Jul;26(1):29–38. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raponi G., Keller N., Overbeek B. P., Rozenberg-Arska M., van Kessel K. P., Verhoef J. Enhanced phagocytosis of encapsulated Escherichia coli strains after exposure to sub-MICs of antibiotics is correlated to changes of the bacterial cell surface. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Feb;34(2):332–336. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.2.332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolinson G. N. Subinhibitory concentrations of antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Mar;3(2):111–113. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.2.111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roosendaal R., Bakker-Woudenberg I. A., van den Berghe-van Raffe M., Michel M. F. Continuous versus intermittent administration of ceftazidime in experimental Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia in normal and leukopenic rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Sep;30(3):403–408. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.3.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sande M. A., Korzeniowski O. M., Allegro G. M., Brennan R. O., Zak O., Scheld W. M. Intermittent or continuous therapy of experimental meningitis due to Streptococcus pneumoniae in rabbits: preliminary observations on the postantibiotic effect in vivo. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):98–109. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.1.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E. Newly made enzymes determine ongoing cell wall synthesis and the antibacterial effects of cell wall synthesis inhibitors. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):535–543. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.535-543.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Täuber M. G., Zak O., Scheld W. M., Hengstler B., Sande M. A. The postantibiotic effect in the treatment of experimental meningitis caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1984 Apr;149(4):575–583. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.4.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Auwera P. Interactions between antibiotics and phagocytosis in bacterial killing. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1990;74:42–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelman B., Craig W. A. Kinetics of antimicrobial activity. J Pediatr. 1986 May;108(5 Pt 2):835–840. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80754-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelman B., Gudmundsson S., Turnidge J., Leggett J., Craig W. A. In vivo postantibiotic effect in a thigh infection in neutropenic mice. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):287–298. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. A., Rolinson G. N. The recovery period following exposure of bacteria to penicillins. Chemotherapy. 1979;25(1):14–22. doi: 10.1159/000237817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winstanley T., Edwards C., Hastings M. Post-antibiotic effect of teicoplanin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 May;27(5):683–684. doi: 10.1093/jac/27.5.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zak O., Kradolfer F. Effects of subminimal inhibitory concentrations of antibiotics in experimental infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Sep-Oct;1(5):862–879. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.5.862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhanel G. G., Karlowsky J. A., Hoban D. J., Davidson R. J. Antimicrobial activity of subinhibitory concentrations of aminoglycosides against Pseudomonas aeruginosa as determined by the killing-curve method and the postantibiotic effect. Chemotherapy. 1991;37(2):114–121. doi: 10.1159/000238842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



