Abstract
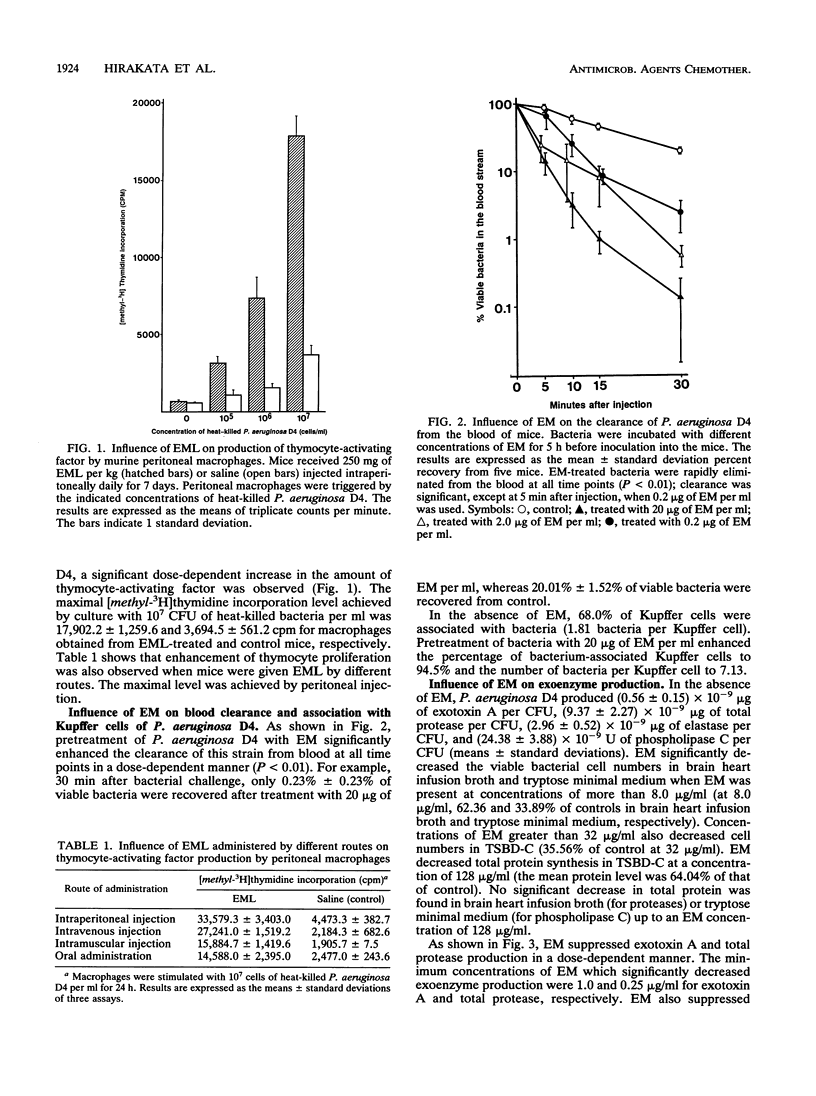
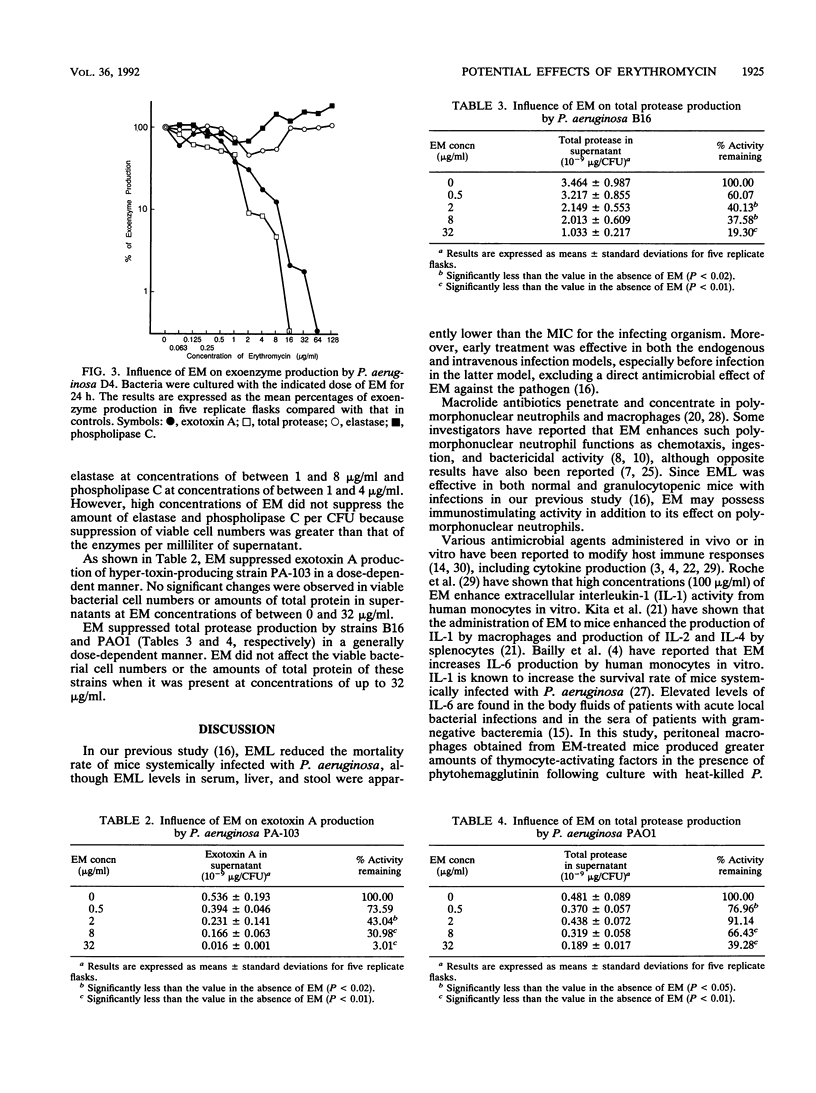
We evaluated several potential effects of erythromycin (EM) on host defense systems and the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Peritoneal macrophages obtained from mice given 250 mg of EM per kg of body weight for 7 days by the intraperitoneal, intravenous, subcutaneous, or oral route produced significantly greater amounts of thymocyte-activating factors. These data suggest that EM enhances the in vivo production of cytokines, such as interleukins 1 and 6. Treatment of P. aeruginosa D4 with subinhibitory concentrations of EM enhanced the association of bacteria with murine Kupffer cells in vitro and increased bacterial clearance from the blood in mice. EM suppressed the in vitro production of exotoxin A, total protease, elastase, and phospholipase C by P. aeruginosa D4; exotoxin A production by P. aeruginosa PA-103; and total protease production by P. aeruginosa B16 and PAO1 in a generally dose-dependent manner. These data demonstrate that EM produces various effects in addition to its direct antimicrobial activity, suggesting that it has potential as an immunomodulator or bacterial virulence-suppressing agent against P. aeruginosa and other infections.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adinolfi L. E., Bonventre P. F. Enhanced phagocytosis, killing, and serum sensitivity of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus treated with sub-MICs of imipenem. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jul;32(7):1012–1018. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.7.1012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreana A., Perna P., Utili R., Dilillo M., Ruggiero G. Increased phagocytosis and killing of Escherichia coli treated with subinhibitory concentrations of cefamandole and gentamicin in isolated rat livers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Feb;25(2):182–186. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.2.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly S., Fay M., Roche Y., Gougerot-Pocidalo M. A. Effects of quinolones on tumor necrosis factor production by human monocytes. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1990;12(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(90)90065-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly S., Pocidalo J. J., Fay M., Gougerot-Pocidalo M. A. Differential modulation of cytokine production by macrolides: interleukin-6 production is increased by spiramycin and erythromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Oct;35(10):2016–2019. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.10.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berka R. M., Gray G. L., Vasil M. L. Studies of phospholipase C (heat-labile hemolysin) in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):1071–1074. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.1071-1074.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyraud A., Descotes J., Lombard J. Y., Laschi-Loquerie A., Tachon P., Veysseyre C., Evreux J. C. Effects of erythromycin, josamycin and spiramycin on rat polymorphonuclear leukocyte chemotaxis. Chemotherapy. 1986;32(4):379–382. doi: 10.1159/000238438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes A. C., Anderson R., Theron A. J., Jooné G., Van Rensburg C. E. Enhancement of human polymorphonuclear leucocyte motility by erythromycin in vitro and in vivo. S Afr Med J. 1984 Aug 4;66(5):173–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filice G. A. Antimicrobial properties of Kupffer cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1430–1435. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1430-1435.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraschini F., Scaglione F., Ferrara F., Marelli O., Braga P. C., Teodori F. Evaluation of the immunostimulating activity of erythromycin in man. Chemotherapy. 1986;32(3):286–290. doi: 10.1159/000238425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Gershon R. K., Waksman B. H. Potentiation of the T-lymphocyte response to mitogens. I. The responding cell. J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):128–142. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribble M. J., Chow A. W. Erythromycin. Med Clin North Am. 1982 Jan;66(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31443-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimwood K., To M., Rabin H. R., Woods D. E. Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme expression by subinhibitory antibiotic concentrations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):41–47. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser W. E., Jr, Remington J. S. Effect of antibiotics on the immune response. Am J Med. 1982 May;72(5):711–716. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90534-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfgott D. C., Tatter S. B., Santhanam U., Clarick R. H., Bhardwaj N., May L. T., Sehgal P. B. Multiple forms of IFN-beta 2/IL-6 in serum and body fluids during acute bacterial infection. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):948–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirakata Y., Kaku M., Tomono K., Tateda K., Furuya N., Matsumoto T., Araki R., Yamaguchi K. Efficacy of erythromycin lactobionate for treating Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jun;36(6):1198–1203. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.6.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirakata Y., Tomono K., Tateda K., Matsumoto T., Furuya N., Shimoguchi K., Kaku M., Yamaguchi K. Role of bacterial association with Kupffer cells in occurrence of endogenous systemic bacteremia. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):289–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.289-294.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Krishnapillai V., Morgan A. F. Chromosomal genetics of Pseudomonas. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Mar;43(1):73–102. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.1.73-102.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Sadoff J. C. Toxin inhibitors of protein synthesis: production, purification, and assay of Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin A. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:780–793. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro M., Koga H., Kohno S., Hayashi T., Yamaguchi K., Hirota M. Penetration of macrolides into human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Nov;24(5):719–729. doi: 10.1093/jac/24.5.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita E., Sawaki M., Nishikawa F., Mikasa K., Yagyu Y., Takeuchi S., Yasui K., Narita N., Kashiba S. Enhanced interleukin production after long-term administration of erythromycin stearate. Pharmacology. 1990;41(4):177–183. doi: 10.1159/000138716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita E., Sawaki M., Oku D., Hamuro A., Mikasa K., Konishi M., Emoto M., Takeuchi S., Narita N., Kashiba S. Suppression of virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by erythromycin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Mar;27(3):273–284. doi: 10.1093/jac/27.3.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. Extracellular toxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130 (Suppl)(0):S94–S99. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.supplement.s94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B. Interleukin 1 and T cell activation. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:51–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson S., Summer W. R., Terry P. B., Warr G. A., Jakab G. J. Erythromycin-induced suppression of pulmonary antibacterial defenses. A potential mechanism of superinfection in the lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Nov;136(5):1207–1212. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.5.1207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otterness I. G., Bliven M. L., Eskra J. D., Reinke M., Hanson D. C. The pharmacologic regulation of interleukin-1 production: the role of prostaglandins. Cell Immunol. 1988 Jul;114(2):385–397. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90330-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki Y., Ohashi T., Minami A., Nakamura S. Enhanced resistance of mice to bacterial infection induced by recombinant human interleukin-1a. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1436–1440. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1436-1440.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocidalo J. J., Albert F., Desnottes J. F., Kernbaum S. Intraphagocytic penetration of macrolides: in-vivo comparison of erythromycin and spiramycin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jul;16 (Suppl A):167–173. doi: 10.1093/jac/16.suppl_a.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche Y., Fay M., Gougerot-Pocidalo M. A. Interleukin-1 production by antibiotic-treated human monocytes. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 May;21(5):597–607. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.5.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche Y., Gougerot-Pocidalo M. A., Fay M., Etienne D., Forest N., Pocidalo J. J. Comparative effects of quinolones on human mononuclear leucocyte functions. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Jun;19(6):781–790. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.6.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozgonyi F., Papp-Falusi E., Varga J., Rozgonyi-Szitha K. In-vitro activity of cefetamet (Ro 15-8074) compared with other oral agents. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Oct;24(4):539–546. doi: 10.1093/jac/24.4.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Hayden C. Secretion of phospholipase C by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):558–564. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.558-564.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R. L., Baker N. R., Johnson J., Stapleton M. J. Selective inhibition of the accumulation of extracellular proteases of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by gentamicin and tobramycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):468–472. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. G., Clark S. C. Multiple actions of interleukin 6 within a cytokine network. Immunol Today. 1988 May;9(5):137–139. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91200-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Schaffer M. S., Rabin H. R., Campbell G. D., Sokol P. A. Phenotypic comparison of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from a variety of clinical sites. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Aug;24(2):260–264. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.2.260-264.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


