Abstract
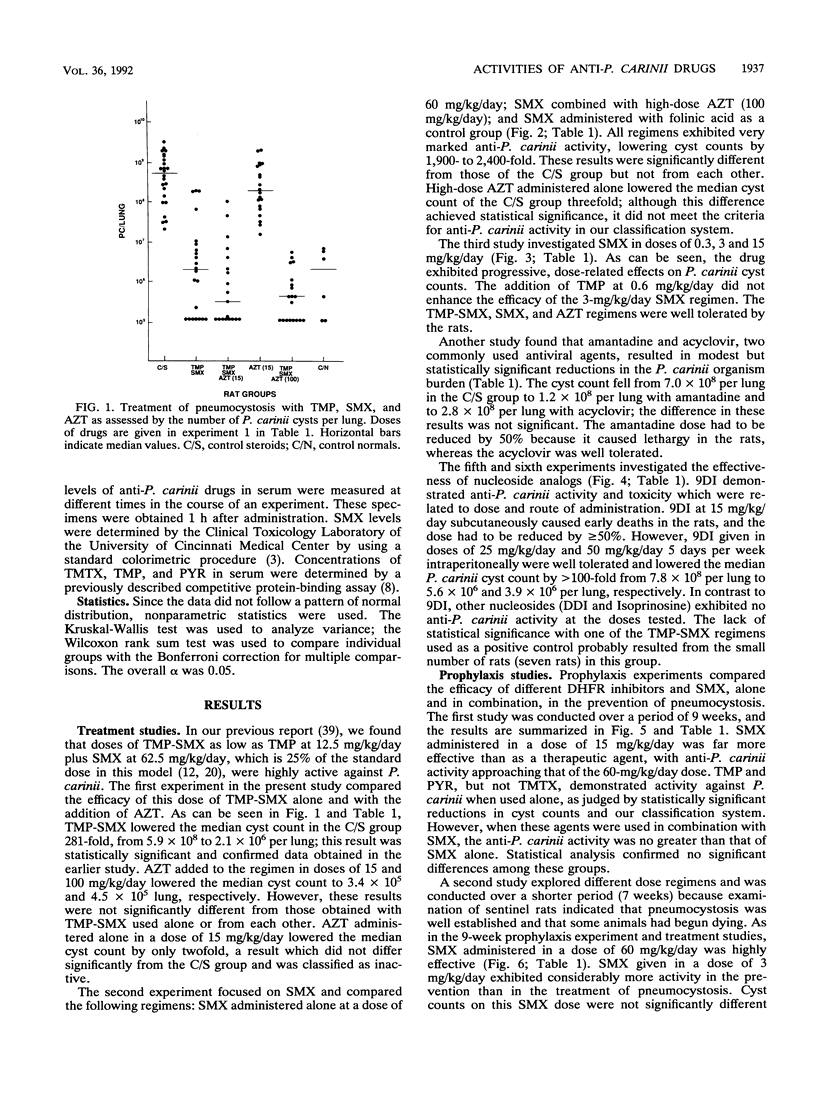
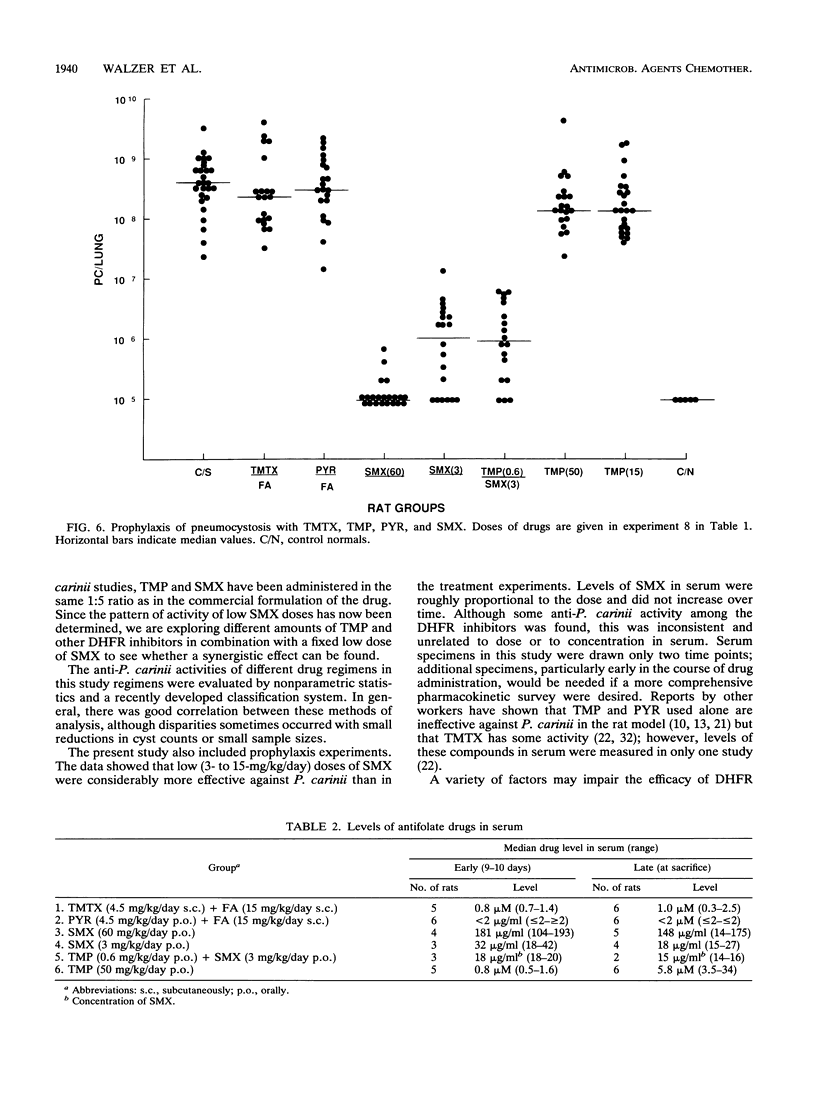
The efficacy of antifolate, antiviral, and other drugs was compared in an experimental model of pneumocystosis. Sulfamethoxazole (SMX) administered alone in doses of greater than or equal to 60 mg/kg/day was highly effective in treatment and prophylaxis. Low (less than or equal to 15 mg/kg/day) doses of SMX showed limited, dose-related anti-Pneumocystis carinii activity in therapy but were more effective in prophylaxis. The dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) inhibitors trimethoprim (TMP), pyrimethamine, and trimetrexate exhibited little anti-P. carinii activity when administered alone and did not enhance the efficacy of SMX; the effects of the DHFR inhibitors could not be related to the dose or the concentration in serum. These data suggested that the rat model is an excellent system for studying the anti-P. carinii activity of sulfonamides but is of limited value in studying DHFR inhibitors. The antiviral drugs azidothymidine, dideoxyinosine, inosine pranobex (Isoprinosine), amantadine, and acyclovir displayed little or no activity against P. carinii; however, azidothymidine did not impair the efficacy of SMX or TMP-SMX. These results supported the clinical practice of giving antiviral agents together with antifolate drugs to patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus and suggested that the beneficial effects of antiviral agents on the occurrence of pneumocystosis are due mainly to their effects on the virus or the host immune response. In contrast to the antiviral drugs, 9-deazainosine, a nucleoside analog with antiprotozoal properties, demonstrated marked activity against P. carinii which was related to dose and route of administration. These data raised the possibility that anti-P. carinii activity is a general property of purine nucleosides and suggested that further exploration of this class of compounds might lead to clinically useful agents.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allegra C. J., Chabner B. A., Tuazon C. U., Ogata-Arakaki D., Baird B., Drake J. C., Simmons J. T., Lack E. E., Shelhamer J. H., Balis F. Trimetrexate for the treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 15;317(16):978–985. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710153171602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allegra C. J., Kovacs J. A., Drake J. C., Swan J. C., Chabner B. A., Masur H. Activity of antifolates against Pneumocystis carinii dihydrofolate reductase and identification of a potent new agent. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):926–931. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder S., Mitsuya H., Yarchoan R., Pavlakis G. N. NIH conference. Antiretroviral therapy in AIDS. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Oct 15;113(8):604–618. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-8-604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushion M. T., Ruffolo J. J., Linke M. J., Walzer P. D. Pneumocystis carinii: growth variables and estimates in the A549 and WI-38 VA13 human cell lines. Exp Parasitol. 1985 Aug;60(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4894(85)80021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushion M. T., Stanforth D., Linke M. J., Walzer P. D. Method of testing the susceptibility of Pneumocystis carinii to antimicrobial agents in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Dec;28(6):796–801. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.6.796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Antonio R. G., Johnson D. B., Winn R. E., van Dellen A. F., Evans M. E. Effect of folinic acid on the capacity of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole to prevent and treat Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Feb;29(2):327–329. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake J. C., Allegra C. J., Curt G. A., Chabner B. A. Competitive protein-binding assay for trimetrexate. Cancer Treat Rep. 1985 Jun;69(6):641–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischl M. A., Richman D. D., Grieco M. H., Gottlieb M. S., Volberding P. A., Laskin O. L., Leedom J. M., Groopman J. E., Mildvan D., Schooley R. T. The efficacy of azidothymidine (AZT) in the treatment of patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 23;317(4):185–191. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707233170401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Good J. T., Shultz J. A. Latent Pneumocystis infection of rats, relapse, and chemotherapy. Lab Invest. 1966 Oct;15(10):1559–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman P. L., Remington J. S. The effect of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole on Toxoplasma gondii in vitro and in vivo. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1979 May;28(3):445–455. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1979.28.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Feldman S., Chaudhary S. C., Ossi M. J., Cox F., Sanyal S. K. Comparison of pentamidine isethionate and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in the treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. J Pediatr. 1978 Feb;92(2):285–291. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., McNabb P. C., Makres T. D., Feldman S. Efficacy of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole in the prevention and treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):289–293. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Smith-McCain B. L. Effects of sulfonylurea compounds on Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):944–947. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Smith B. L. Efficacy of diaminodiphenylsulfone and other drugs in murine Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Oct;26(4):436–440. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.4.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Smith B. L., Jacobus D. P. Successful treatment and prevention of murine Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis with 4,4'-sulfonylbisformanilide. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):509–510. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israelski D. M., Tom C., Remington J. S. Zidovudine antagonizes the action of pyrimethamine in experimental infection with Toxoplasma gondii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):30–34. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. K., Foy J. M., Cushion M. T., Stanforth D., Linke M. J., Hendrix H. L., Walzer P. D. Comparison of histologic and quantitative techniques in evaluation of therapy for experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):197–201. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluge R. M., Spaulding D. M., Spain A. J. Combination of pentamidine and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in therapy of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jun;13(6):975–978. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.6.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Allegra C. J., Kennedy S., Swan J. C., Drake J., Parrillo J. E., Chabner B., Masur H. Efficacy of trimetrexate, a potent lipid-soluble antifolate, in the treatment of rodent Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Nov;39(5):491–496. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.39.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert J. S., Seidlin M., Reichman R. C., Plank C. S., Laverty M., Morse G. D., Knupp C., McLaren C., Pettinelli C., Valentine F. T. 2',3'-dideoxyinosine (ddI) in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome or AIDS-related complex. A phase I trial. N Engl J Med. 1990 May 10;322(19):1333–1340. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199005103221901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr J. J., Berens R. L., Cohn N. K., Nelson D. J., Klein R. S. Biological action of inosine analogs in Leishmania and Trypanosoma spp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Feb;25(2):292–295. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.2.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medina I., Mills J., Leoung G., Hopewell P. C., Lee B., Modin G., Benowitz N., Wofsy C. B. Oral therapy for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. A controlled trial of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole versus trimethoprim-dapsone. N Engl J Med. 1990 Sep 20;323(12):776–782. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199009203231202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nottebrock H., Then R. Thymidine concentrations in serum and urine of different animal species and man. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Nov 15;26(22):2175–2179. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen C., Sandström E., Petersen C. S., Norkrans G., Gerstoft J., Karlsson A., Christensen K. C., Håkansson C., Pehrson P. O., Nielsen J. O. The efficacy of inosine pranobex in preventing the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. The Scandinavian Isoprinosine Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jun 21;322(25):1757–1763. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199006213222501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queener S. F., Bartlett M. S., Jay M. A., Durkin M. M., Smith J. W. Activity of lipid-soluble inhibitors of dihydrofolate reductase against Pneumocystis carinii in culture and in a rat model of infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1323–1327. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland S., Ferone R., Harvey R. J., Styles V. L., Morrison R. W. The characteristics and significance of sulfonamides as substrates for Escherichia coli dihydropteroate synthase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10337–10345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruprecht R. M., O'Brien L. G., Rossoni L. D., Nusinoff-Lehrman S. Suppression of mouse viraemia and retroviral disease by 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):467–469. doi: 10.1038/323467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattler F. R., Cowan R., Nielsen D. M., Ruskin J. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole compared with pentamidine for treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. A prospective, noncrossover study. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Aug 15;109(4):280–287. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-4-280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Bartlett M. S., Queener S. F., Durkin M. M., Jay M. A., Hull M. T., Klein R. S., Marr J. J. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia therapy with 9-deazainosine in rats. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;7(2):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(87)90028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Foy J., Steele P., White M. Treatment of experimental pneumocystosis: review of 7 years of experience and development of a new system for classifying antimicrobial drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Sep;36(9):1943–1950. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.9.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Kim C. K., Foy J. M., Linke M. J., Cushion M. T. Inhibitors of folic acid synthesis in the treatment of experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jan;32(1):96–103. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.1.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Kim C. K., Foy J., Linke M. J., Cushion M. T. Cationic antitrypanosomal and other antimicrobial agents in the therapy of experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jun;32(6):896–905. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.6.896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Kim C. K., Foy J., Zhang J. L. Furazolidone and nitrofurantoin in the treatment of experimental Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jan;35(1):158–163. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.1.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton J. M., Coleman D. L., Wofsy C. B., Luce J. M., Blumenfeld W., Hadley W. K., Ingram-Drake L., Volberding P. A., Hopewell P. C. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or pentamidine for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. A prospective randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Jul;105(1):37–44. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


