Abstract
The effect of CL 184,005, a potent and specific platelet-activating factor antagonist, has been examined in a variety of animal models relevant to gram-negative bacterial sepsis. Pretreatment of mice with CL 184,005 protected them from the lethal effects of platelet-activating factor. When rats or primates rendered hypotensive with endotoxin were treated with CL 184,005, blood pressure was normalized. Pretreatment of rats with CL 184,005 protected them from the gastrointestinal lesions induced by endotoxin. Pretreatment of rats and mice with CL 184,005 protected them from the lethal effects of endotoxin. Plasma tumor necrosis factor levels in endotoxin-treated mice were lower when the mice were pretreated with CL 184,005. These observations suggest that CL 184,005 may be potentially useful in the treatment of gram-negative bacterial sepsis, and the agent is undergoing clinical evaluation.
Full text
PDF

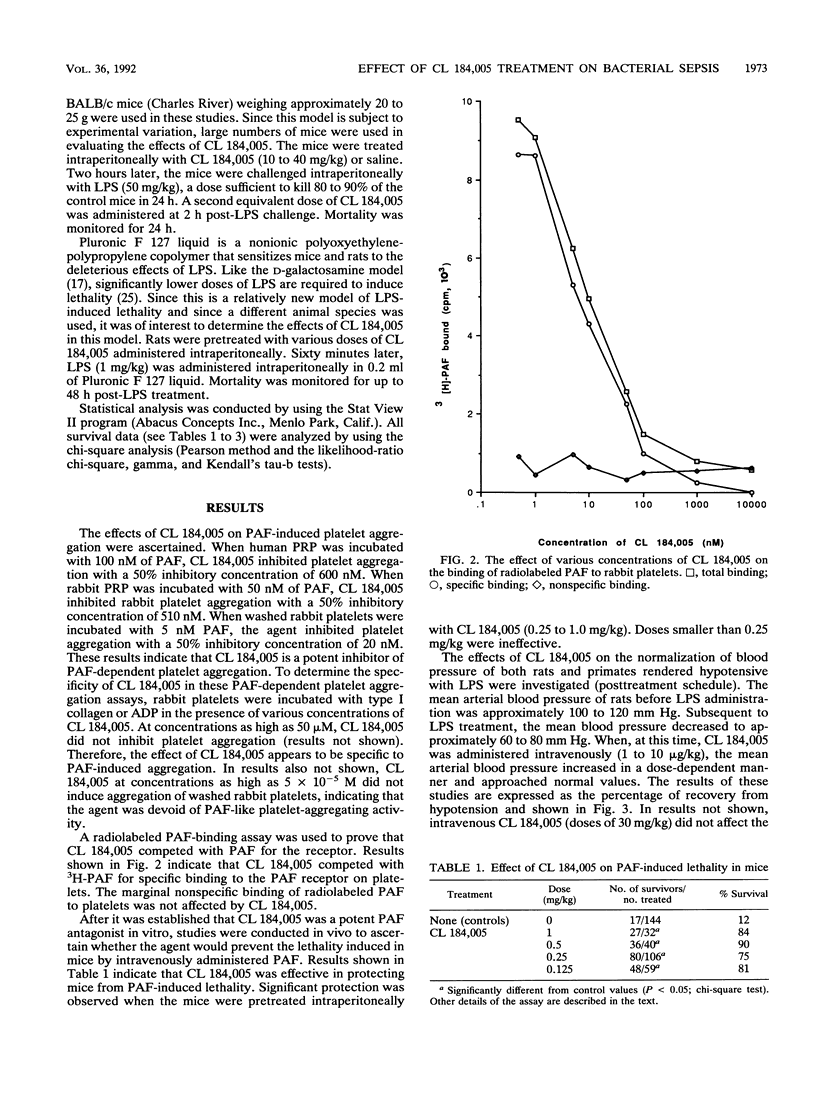
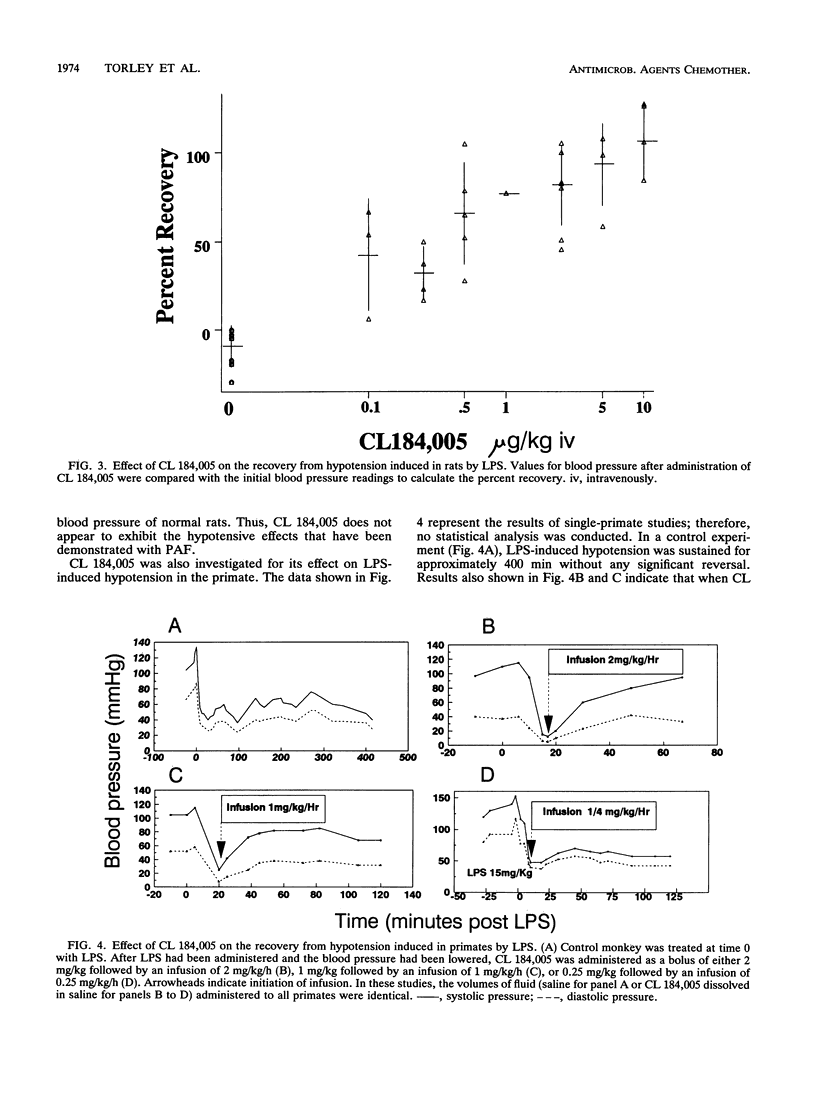
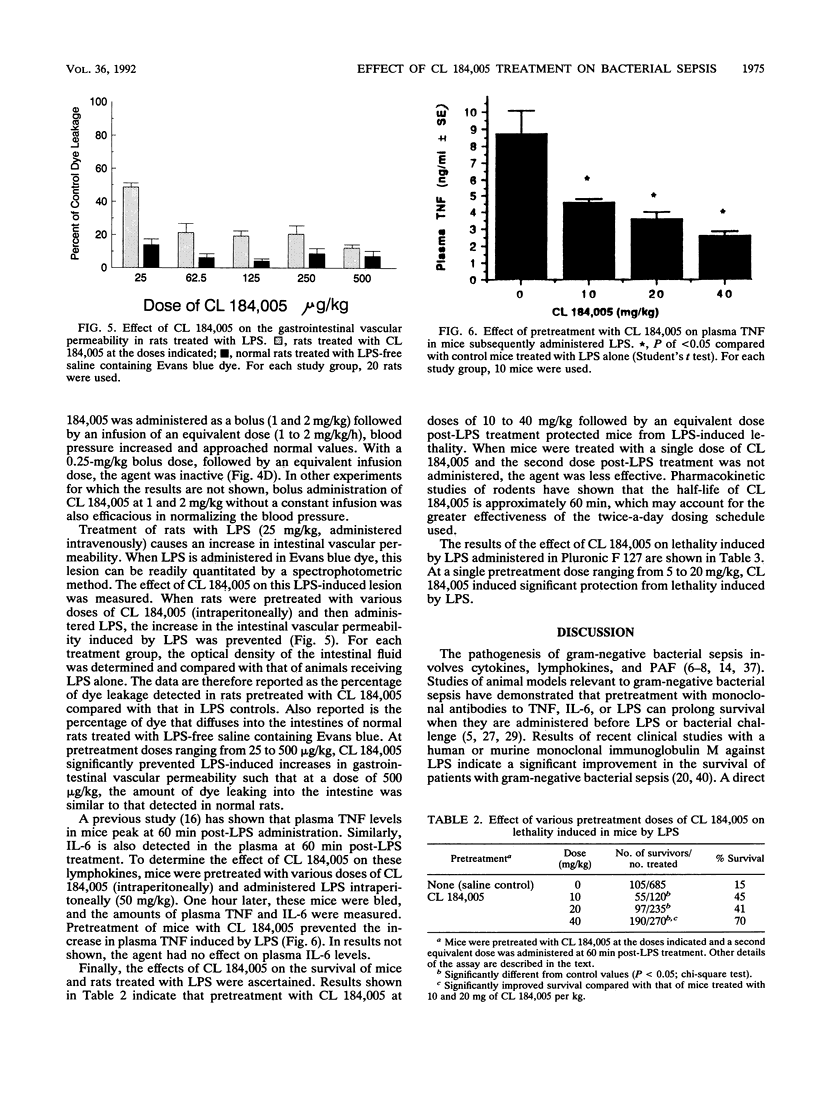


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B. O., Bensard D. D., Harken A. H. The role of platelet activating factor and its antagonists in shock, sepsis and multiple organ failure. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1991 May;172(5):415–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J., Chung K. F., Page C. P. Inflammatory mediators and asthma. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Mar;40(1):49–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste J., Henson P. M., Cochrane C. G. Leukocyte-dependent histamine release from rabbit platelets. The role of IgE, basophils, and a platelet-activating factor. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1356–1377. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C. A critical evaluation of new agents for the treatment of sepsis. JAMA. 1991 Sep 25;266(12):1686–1691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C. Gram-negative sepsis. Background, clinical features, and intervention. Chest. 1991 Sep;100(3):802–808. doi: 10.1378/chest.100.3.802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C. Let's agree on terminology: definitions of sepsis. Crit Care Med. 1991 Jul;19(7):973–976. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199107000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braquet P., Touqui L., Shen T. Y., Vargaftig B. B. Perspectives in platelet-activating factor research. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Jun;39(2):97–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calandra T., Baumgartner J. D., Grau G. E., Wu M. M., Lambert P. H., Schellekens J., Verhoef J., Glauser M. P. Prognostic values of tumor necrosis factor/cachectin, interleukin-1, interferon-alpha, and interferon-gamma in the serum of patients with septic shock. Swiss-Dutch J5 Immunoglobulin Study Group. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):982–987. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Tompkins R. G., Gelfand J. A., Michie H. R., Stanford G. G., van der Meer J. W., Endres S., Lonnemann G., Corsetti J., Chernow B. Circulating interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor in septic shock and experimental endotoxin fever. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jan;161(1):79–84. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J., Glauser M. P. Septic shock: treatment. Lancet. 1991 Sep 21;338(8769):736–739. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91453-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danner R. L., Elin R. J., Hosseini J. M., Wesley R. A., Reilly J. M., Parillo J. E. Endotoxemia in human septic shock. Chest. 1991 Jan;99(1):169–175. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.1.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson-Chanowitz K. M., Katocs A. S., Jr, Pickett W. C., Kaplan J. B., Sass P. M., Oronsky A. L., Kerwar S. S. Platelet-activating factor or a platelet-activating factor antagonist decreases tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the plasma of mice treated with endotoxin. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1081–1086. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Freudenberg M. A., Reutter W. Galactosamine-induced sensitization to the lethal effects of endotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5939–5943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glauser M. P., Zanetti G., Baumgartner J. D., Cohen J. Septic shock: pathogenesis. Lancet. 1991 Sep 21;338(8769):732–736. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91452-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenman R. L., Schein R. M., Martin M. A., Wenzel R. P., MacIntyre N. R., Emmanuel G., Chmel H., Kohler R. B., McCarthy M., Plouffe J. A controlled clinical trial of E5 murine monoclonal IgM antibody to endotoxin in the treatment of gram-negative sepsis. The XOMA Sepsis Study Group. JAMA. 1991 Aug 28;266(8):1097–1102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. J. Platelet activating factor: a biologically active phosphoglyceride. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:483–509. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler C. A., Zoltan B. J. Automated platelet aggregation analysis using a digitizer. J Pharmacol Methods. 1984 Sep;12(2):113–123. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(84)90029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koltai M., Hosford D., Guinot P., Esanu A., Braquet P. PAF. A review of its effects, antagonists and possible future clinical implications (Part II). Drugs. 1991 Aug;42(2):174–204. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199142020-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice-based oral electrolyte solutions in infantile diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jul 25;325(4):283–284. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199107253250412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder F. Biochemistry of platelet-activating factor: a unique class of biologically active phospholipids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1989 Feb;190(2):125–135. doi: 10.3181/00379727-190-42839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starnes H. F., Jr, Pearce M. K., Tewari A., Yim J. H., Zou J. C., Abrams J. S. Anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibodies protect against lethal Escherichia coli infection and lethal tumor necrosis factor-alpha challenge in mice. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4185–4191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez Crespo M., Fernández-Gallardo S. Pharmacological modulation of PAF: a therapeutic approach to endotoxin shock. J Lipid Mediat. 1991 Sep-Oct;4(2):127–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng N. N., Kaplan H. S., Hebert J. M., Moore C., Douglas H., Wunderlich A., Braude A. I. Protection against gram-negative bacteremia and endotoxemia with human monoclonal IgM antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1790–1794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terashita Z., Imura Y., Nishikawa K., Sumida S. Is platelet activating factor (PAF) a mediator of endotoxin shock? Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 26;109(2):257–261. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The HA-1A monoclonal antibody for gram-negative sepsis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jul 25;325(4):279–283. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199107253250411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The HA-1A monoclonal antibody for gram-negative sepsis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jul 25;325(4):279–283. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199107253250411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) in the biology of septic shock syndrome. Circ Shock. 1991 Oct;35(2):123–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J., Cayphas S., Vink A., Uyttenhove C., Coulie P. G., Rubira M. R., Simpson R. J. Purification and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of a T-cell-derived lymphokine with growth factor activity for B-cell hybridomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9679–9683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandongen R. Platelet activating factor and the circulation. J Hypertens. 1991 Sep;9(9):771–778. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199109000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Brandtzaeg P., Halstensen A., Kierulf P., Espevik T. The complex pattern of cytokines in serum from patients with meningococcal septic shock. Association between interleukin 6, interleukin 1, and fatal outcome. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):333–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi G., Gelfand J. A., Burke J. F., Thompson R. C., Dinarello C. A. A specific receptor antagonist for interleukin 1 prevents Escherichia coli-induced shock in rabbits. FASEB J. 1991 Mar 1;5(3):338–343. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.3.1825816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wissner A., Carroll M. L., Green K. E., Kerwar S. S., Pickett W. C., Schaub R. E., Torley L. W., Wrenn S., Kohler C. A. Analogues of platelet activating factor. 6. Mono- and bis-aryl phosphate antagonists of platelet activating factor. J Med Chem. 1992 May 1;35(9):1650–1662. doi: 10.1021/jm00087a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff S. M. The treatment of gram-negative bacteremia and shock. N Engl J Med. 1982 Nov 11;307(20):1267–1268. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198211113072010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler E. J., Fisher C. J., Jr, Sprung C. L., Straube R. C., Sadoff J. C., Foulke G. E., Wortel C. H., Fink M. P., Dellinger R. P., Teng N. N. Treatment of gram-negative bacteremia and septic shock with HA-1A human monoclonal antibody against endotoxin. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The HA-1A Sepsis Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1991 Feb 14;324(7):429–436. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199102143240701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


