Abstract
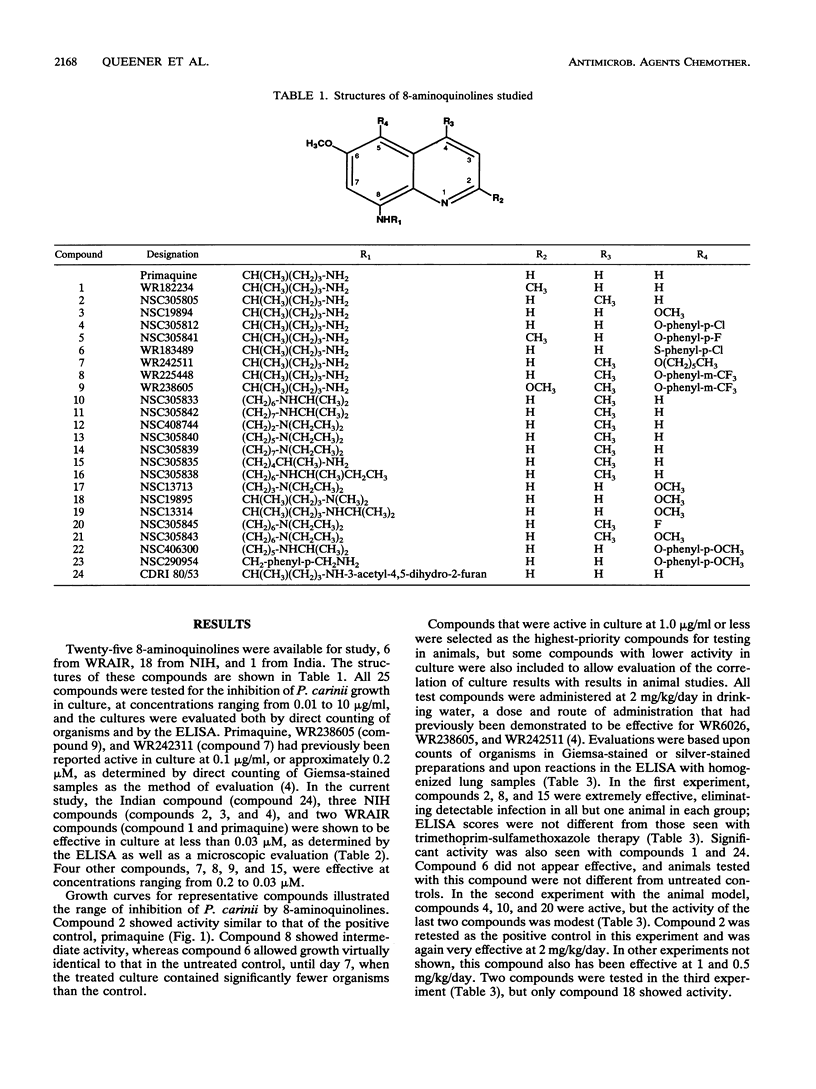
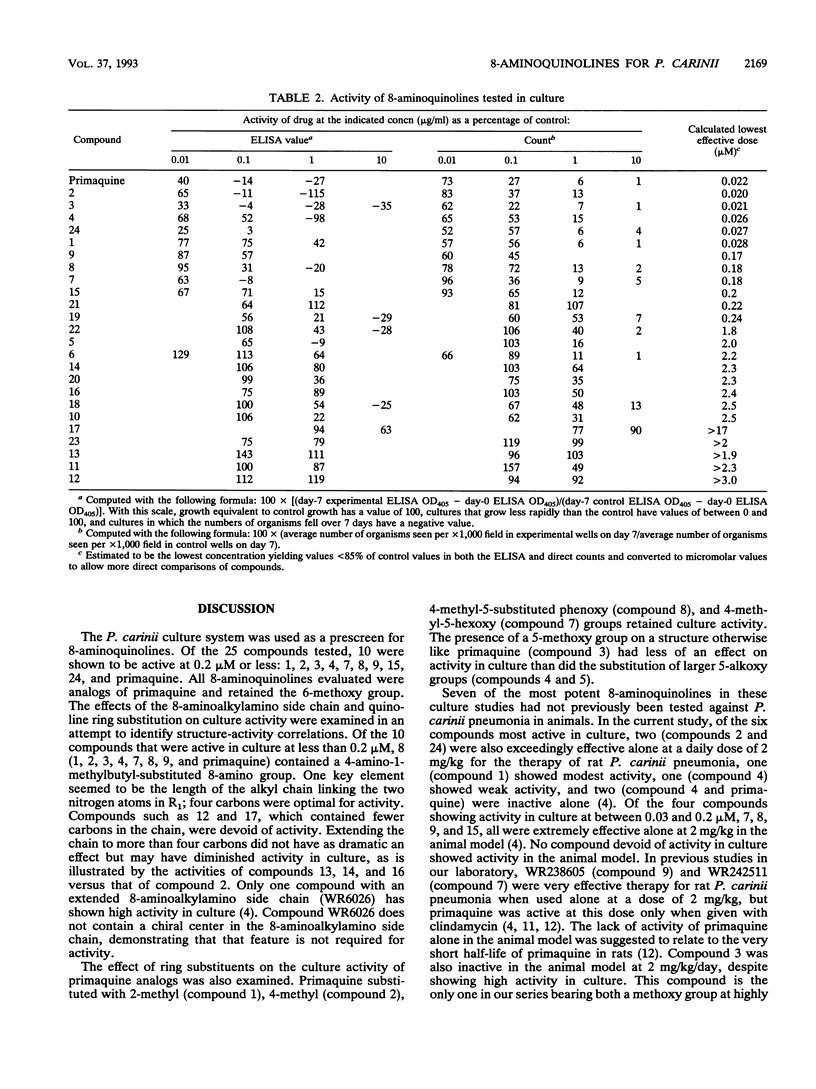
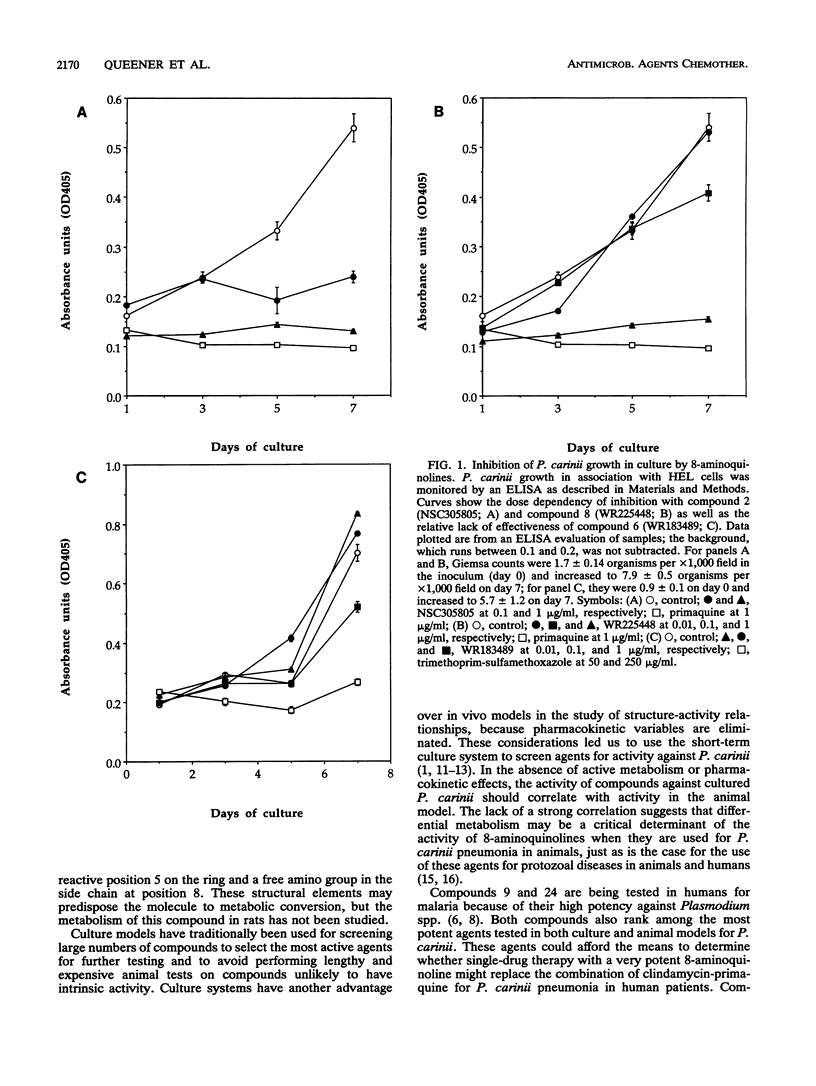
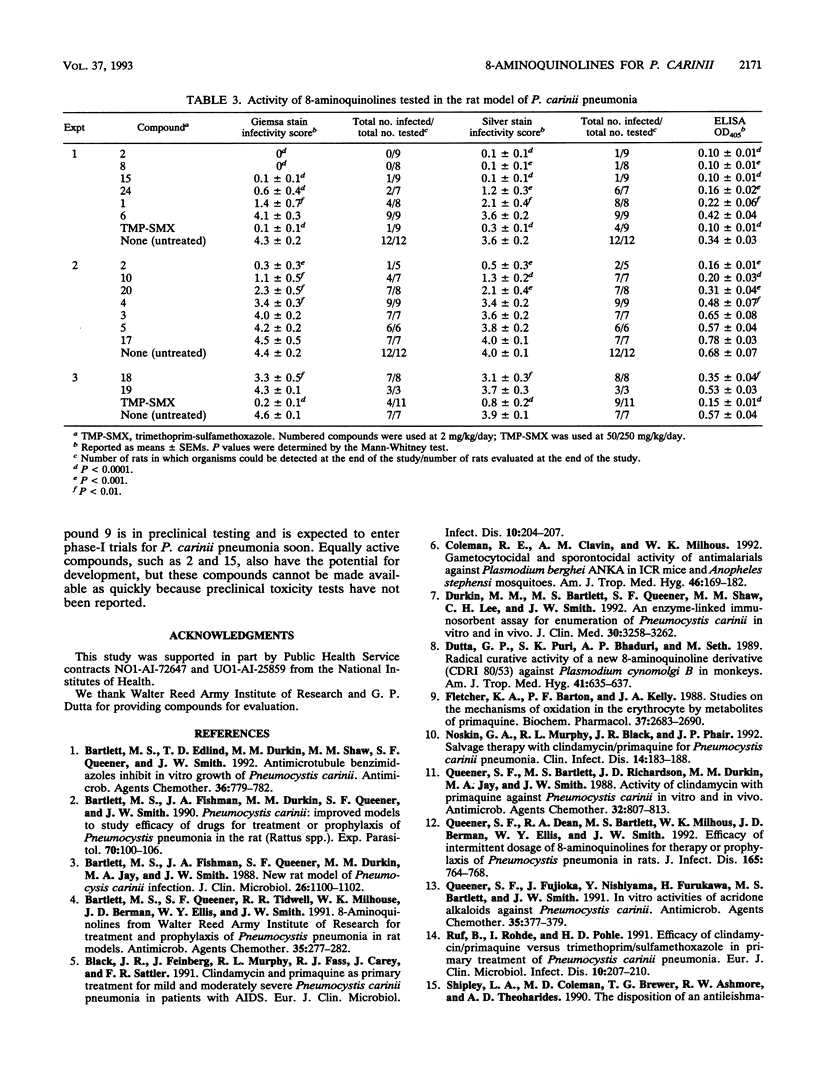
The activities of 25 8-aminoquinolines were compared in tests assessing the ability of the compounds to inhibit the growth of Pneumocystis carinii in culture. Six compounds were effective at or below 0.03 microM: CDRI 80/53, NSC19894, NSC305805, NSC305812, WR182234, and primaquine. Four others were effective at between 0.2 and 0.03 microM: NSC305835, WR225448, WR238605, and WR242511. Fourteen drugs were also tested in a standard model of P. carinii pneumonia in rats at daily doses of 2 mg/kg of body weight in drinking water. CDRI 80/53, NSC305805, NSC305835, and WR225448 were extremely effective in the animal model. The effectiveness of WR238605, WR242511, and primaquine in the rat model has been reported elsewhere (M. S. Bartlett, S. F. Queener, R. R. Tidwell, W. K. Milhouse, J. D. Berman, W. Y. Ellis, and J. W. Smith, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 35:277-282, 1991). The length of the alkyl chain separating the nitrogens in the substituent at position 8 of the quinoline ring was a strong determinant of anti-P. carinii activity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett M. S., Edlind T. D., Durkin M. M., Shaw M. M., Queener S. F., Smith J. W. Antimicrotubule benzimidazoles inhibit in vitro growth of Pneumocystis carinii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Apr;36(4):779–782. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.4.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett M. S., Fishman J. A., Durkin M. M., Queener S. F., Smith J. W. Pneumocystis carinii: improved models to study efficacy of drugs for treatment or prophylaxis of Pneumocystis pneumonia in the rat (Rattus spp.). Exp Parasitol. 1990 Jan;70(1):100–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(90)90089-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett M. S., Fishman J. A., Queener S. F., Durkin M. M., Jay M. A., Smith J. W. New rat model of Pneumocystis carinii infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jun;26(6):1100–1102. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.6.1100-1102.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett M. S., Queener S. F., Tidwell R. R., Milhous W. K., Berman J. D., Ellis W. Y., Smith J. W. 8-Aminoquinolines from Walter Reed Army Institute for Research for treatment and prophylaxis of Pneumocystis pneumonia in rat models. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Feb;35(2):277–282. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. R., Feinberg J., Murphy R. L., Fass R. J., Carey J., Sattler F. R. Clindamycin and primaquine as primary treatment for mild and moderately severe Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in patients with AIDS. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;10(3):204–207. doi: 10.1007/BF01964465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman R. E., Clavin A. M., Milhous W. K. Gametocytocidal and sporontocidal activity of antimalarials against Plasmodium berghei ANKA in ICR Mice and Anopheles stephensi mosquitoes. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Feb;46(2):169–182. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1992.46.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durkin M. M., Bartlett M. S., Queener S. F., Shaw M. M., Lee C. H., Smith J. W. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for enumeration of Pneumocystis carinii in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Dec;30(12):3258–3262. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.12.3258-3262.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta G. P., Puri S. K., Bhaduri A. P., Seth M. Radical curative activity of a new 8-aminoquinoline derivative (CDRI 80/53) against Plasmodium cynomolgi B in monkeys. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Dec;41(6):635–637. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.41.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher K. A., Barton P. F., Kelly J. A. Studies on the mechanisms of oxidation in the erythrocyte by metabolites of primaquine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 1;37(13):2683–2690. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90263-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noskin G. A., Murphy R. L., Black J. R., Phair J. P. Salvage therapy with clindamycin/primaquine for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;14(1):183–188. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queener S. F., Bartlett M. S., Richardson J. D., Durkin M. M., Jay M. A., Smith J. W. Activity of clindamycin with primaquine against Pneumocystis carinii in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jun;32(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.6.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queener S. F., Dean R. A., Bartlett M. S., Milhous W. K., Berman J. D., Ellis W. Y., Smith J. W. Efficacy of intermittent dosage of 8-aminoquinolines for therapy or prophylaxis of Pneumocystis pneumonia in rats. J Infect Dis. 1992 Apr;165(4):764–768. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.4.764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queener S. F., Fujioka H., Nishiyama Y., Furukawa H., Bartlett M. S., Smith J. W. In vitro activities of acridone alkaloids against Pneumocystis carinii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Feb;35(2):377–379. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruf B., Rohde I., Pohle H. D. Efficacy of clindamycin/primaquine versus trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole in primary treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;10(3):207–210. doi: 10.1007/BF01964466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theoharides A. D., Chung H., Velazquez H. Metabolism of a potential 8-aminoquinoline antileishmanial drug in rat liver microsomes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Jan 15;34(2):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90122-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toma E. Clindamycin/primaquine for treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in AIDS. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;10(3):210–213. doi: 10.1007/BF01964467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toma E., Fournier S., Poisson M., Morisset R., Phaneuf D., Vega C. Clindamycin with primaquine for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Lancet. 1989 May 13;1(8646):1046–1048. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92446-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


