Abstract
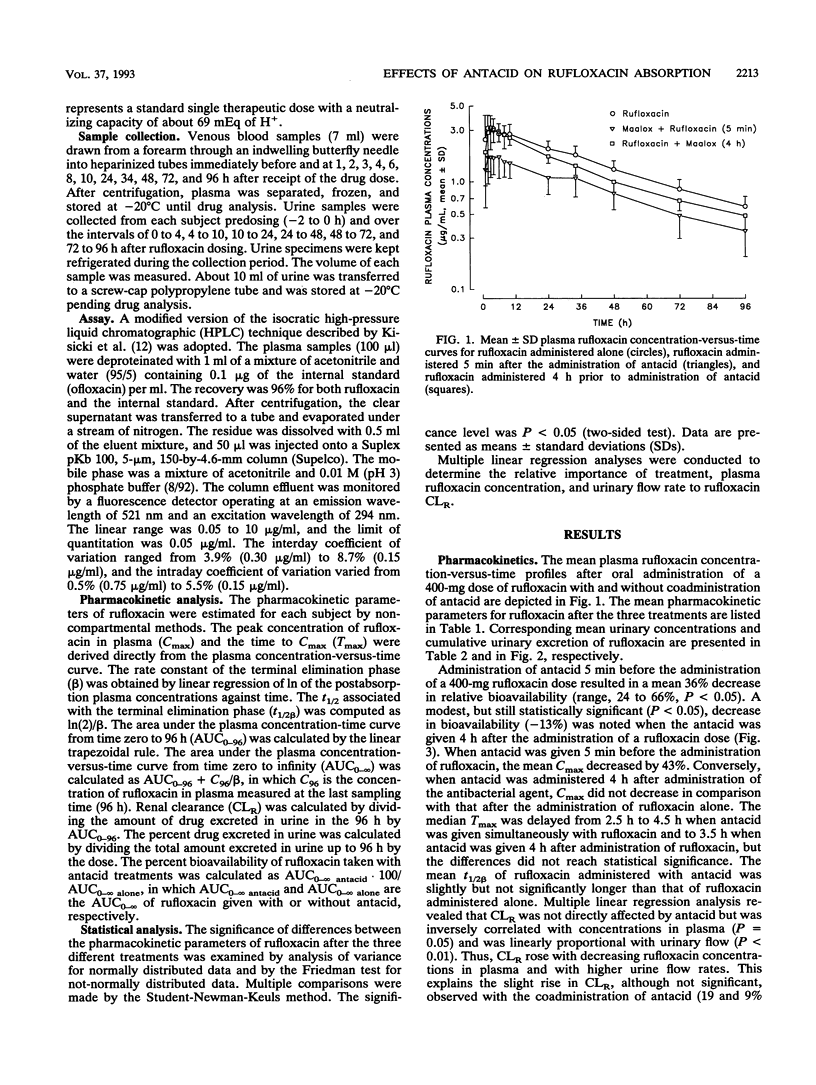
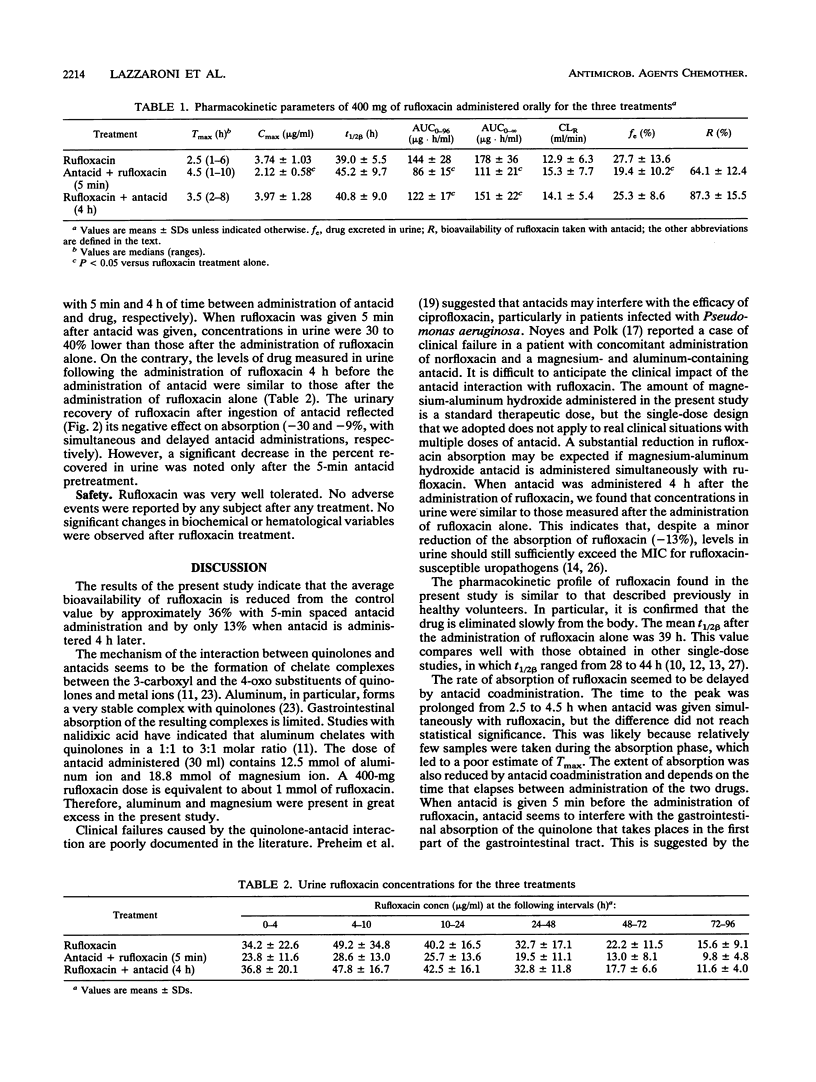
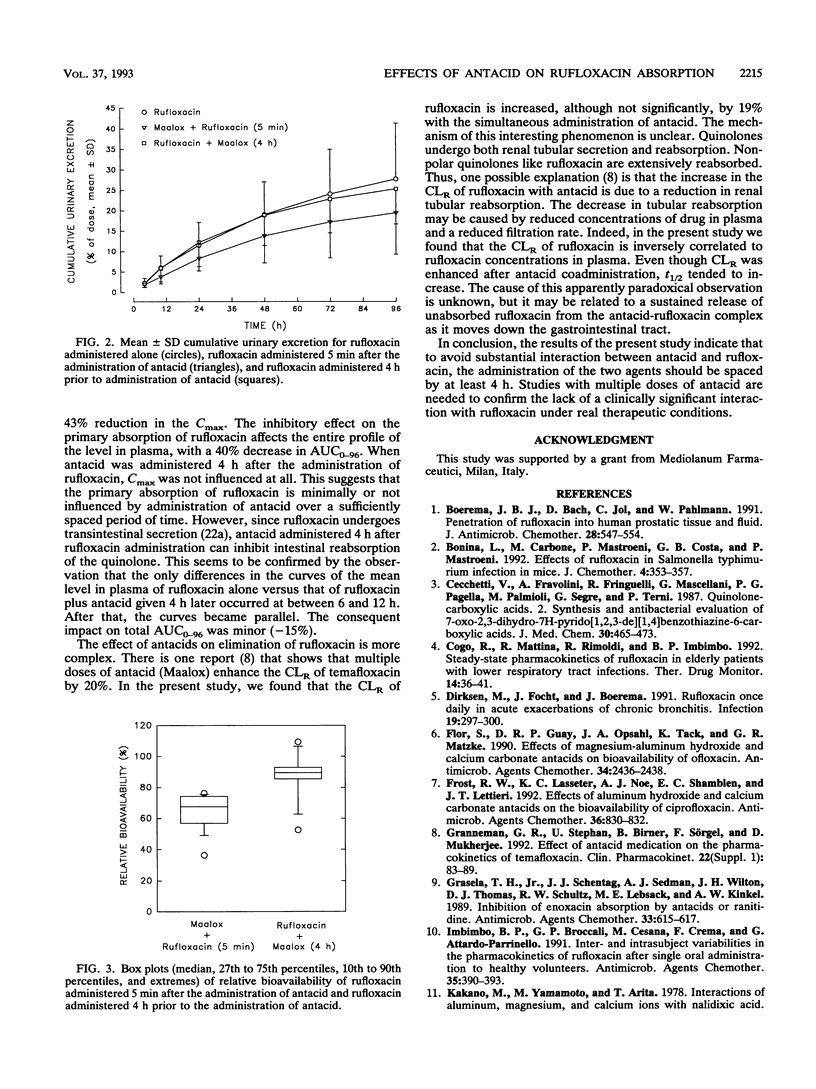
The present study was designed to determine the effects of an antacid suspension containing magnesium hydroxide and aluminum hydroxide (30 ml of Maalox) on the oral bioavailability of rufloxacin (400 mg). Rufloxacin was administered orally to 12 healthy volunteers according to a randomized, balanced, crossover design. Three treatments were administered to each subject, with a 10-day washout period between treatments; the treatments included rufloxacin alone, rufloxacin taken 5 min after antacid, and rufloxacin taken 4 h before antacid. Administration of antacid within 5 min before the administration of rufloxacin resulted in a substantial decrease in rufloxacin absorption, with a mean percent relative bioavailability compared with control values of 64% (range, 42 to 77%). Administration of antacid 4 h after the administration of rufloxacin slightly affected the absorption of the quinolone (mean relative bioavailability, 87%; range, 51 to 110%). Antacids that contain magnesium and aluminum salts reduce the absorption of rufloxacin. The extent of this interaction depends on the time that elapses between administration of the two drugs.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boerema J. B., Bach D., Jol C., Pahlmann W. Penetration of rufloxacin into human prostatic tissue and fluid. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Oct;28(4):547–554. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonina L., Carbone M., Mastroeni P., Costa G. B., Mastroeni P. Effects of rufloxacin in Salmonella typhimurium infection in mice. J Chemother. 1992 Dec;4(6):353–357. doi: 10.1080/1120009x.1992.11739191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cecchetti V., Fravolini A., Fringuelli R., Mascellani G., Pagella P., Palmioli M., Segre G., Terni P. Quinolonecarboxylic acids. 2. Synthesis and antibacterial evaluation of 7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7H-pyrido[1,2,3-de][1,4]benzothiazine-6-carboxylic acids. J Med Chem. 1987 Mar;30(3):465–473. doi: 10.1021/jm00386a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogo R., Rimoldi R., Mattina R., Imbimbo B. P. Steady-state pharmacokinetics of rufloxacin in elderly patients with lower respiratory tract infections. Ther Drug Monit. 1992 Feb;14(1):36–41. doi: 10.1097/00007691-199202000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirksen M., Focht J., Boerema J. Rufloxacin once daily in acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis. Infection. 1991 Jul-Aug;19(4):297–300. doi: 10.1007/BF01644971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flor S., Guay D. R., Opsahl J. A., Tack K., Matzke G. R. Effects of magnesium-aluminum hydroxide and calcium carbonate antacids on bioavailability of ofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Dec;34(12):2436–2438. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.12.2436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost R. W., Lasseter K. C., Noe A. J., Shamblen E. C., Lettieri J. T. Effects of aluminum hydroxide and calcium carbonate antacids on the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Apr;36(4):830–832. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.4.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman G. R., Stephan U., Birner B., Sörgel F., Mukherjee D. Effect of antacid medication on the pharmacokinetics of temafloxacin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1992;22 (Suppl 1):83–89. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199200221-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasela T. H., Jr, Schentag J. J., Sedman A. J., Wilton J. H., Thomas D. J., Schultz R. W., Lebsack M. E., Kinkel A. W. Inhibition of enoxacin absorption by antacids or ranitidine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 May;33(5):615–617. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.5.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbimbo B. P., Broccali G., Cesana M., Crema F., Attardo-Parrinello G. Inter- and intrasubject variabilities in the pharmacokinetics of rufloxacin after single oral administration to healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Feb;35(2):390–393. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisicki J. C., Griess R. S., Ott C. L., Cohen G. M., McCormack R. J., Troetel W. M., Imbimbo B. P. Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics and safety of rufloxacin in normal volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jun;36(6):1296–1301. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.6.1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattina R., Bonfiglio G., Cocuzza C. E., Gulisano G., Cesana M., Imbimbo B. P. Pharmacokinetics of rufloxacin in healthy volunteers after repeated oral doses. Chemotherapy. 1991;37(6):389–397. doi: 10.1159/000238885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattina R., Cocuzza C. E., Cesana M., Bonfiglio G. In vitro activity of a new quinolone, rufloxacin, against nosocomial isolates. Chemotherapy. 1991;37(4):260–269. doi: 10.1159/000238865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattina R., Cocuzza C. E., Cesana M. Rufloxacin once daily versus ofloxacin twice daily for treatment of complicated cystitis and upper urinary tract infections. Italian Multicentre UTI Rufloxacin Group. Infection. 1993 Mar-Apr;21(2):106–111. doi: 10.1007/BF01710743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nix D. E., Wilton J. H., Ronald B., Distlerath L., Williams V. C., Norman A. Inhibition of norfloxacin absorption by antacids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Mar;34(3):432–435. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.3.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyes M., Polk R. E. Norfloxacin and absorption of magnesium-aluminum. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Jul 15;109(2):168–169. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-2-168_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Mant T. G., Morrison P. J., Sacks S., Woodcook J., Wise R., Imbimbo B. P. Pharmacokinetics of rufloxacin in patients with impaired renal function. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Apr;37(4):637–641. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.4.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimoldi R., Fioretti M., Albrici A., Imbimbo B. P. Pharmacokinetics of rufloxacin once daily in patients with lower respiratory tract infections. Infection. 1992 Mar-Apr;20(2):89–93. doi: 10.1007/BF01711071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada J., Shiba K., Oguma T., Miwa H., Yoshimura Y., Nishikawa T., Okabayashi Y., Kitagawa T., Yamamoto S. Effect of antacid on absorption of the quinolone lomefloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jun;36(6):1219–1224. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.6.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmers K., Sternglanz R. Ionization and divalent cation dissociation constants of nalidixic and oxolinic acids. Bioinorg Chem. 1978 Aug;9(2):145–155. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3061(00)80286-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Johnson J., O'Sullivan N., Andrews J. M., Imbimbo B. P. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of rufloxacin, a long acting quinolone antimicrobial agent. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Dec;28(6):905–909. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.6.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



